
Interpretation:
The change in reactivity for the Group IA elements needs to be explained on moving down the group.
Concept introduction:
Element is the basic unit of any substance which can combine with same or different elements to form molecules and compounds. Elements are composed of same type of atoms therefore they exhibit unique physical and chemical properties.
The
Answer to Problem 1E
As the atomic size increases, the reactivity of metallic element increases.
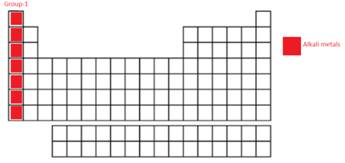
Explanation of Solution
In the long form of periodic table; alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogen and the Noble gases are name of certain groups. In periodic table, the vertical columns are called as groups. Alkali metal are the Group IA or 1st group elements. These elements forms alkaline oxides and hydroxides.
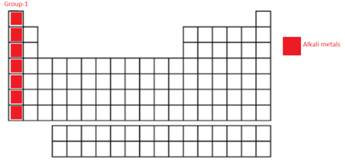
Moving down the group, the atomic size of elements increases thus, the outermost electron is more easily available for the reaction. Thus, the reactivity of metallic element increases by losing the outermost electron. This is because as the atomic size increases, the nuclear attraction decreases for valence electrons and it becomes easier to excite in different chemical reactions. Therefore, the chemical reactivity increases down in the group.
As the atomic size increases, the reactivity of metallic element increases.
Chapter U1 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
- 20. The Brusselator. This hypothetical system was first proposed by a group work- ing in Brussels [see Prigogine and Lefever (1968)] in connection with spatially nonuniform chemical patterns. Because certain steps involve trimolecular reac tions, it is not a model of any real chemical system but rather a prototype that has been studied extensively. The reaction steps are A-X. B+X-Y+D. 2X+ Y-3X, X-E. 305 It is assumed that concentrations of A, B, D, and E are kept artificially con stant so that only X and Y vary with time. (a) Show that if all rate constants are chosen appropriately, the equations de scribing a Brusselator are: dt A-(B+ 1)x + x²y, dy =Bx-x²y. diarrow_forwardProblem 3. Provide a mechanism for the following transformation: H₂SO A Me. Me Me Me Mearrow_forwardYou are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: xi 1. ☑ 2. H₂O хе i Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. There is no reagent that will make this synthesis work without complications. : ☐ S ☐arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: H OH 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G C टेarrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C-C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 CI MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No MgBr ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No G टेarrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. དྲ。 ✗MgBr ? O CI Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new C-C bond? Yes No • ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No × : ☐ Xarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: OH NaBH4 H ? CH3OH Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ : Sarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LIAIHA 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X : ☐arrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C - C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 tu ? ? OH Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No C $ ©arrow_forward
- As the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule with a new C-C bond as its major product: 1. MgCl ? 2. H₂O* If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If the major products of this reaction won't have a new CC bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. This reaction will not make a product with a new CC bond. G marrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M NH4 Ksp Hg2Br2 = 5.6×10-23.arrow_forwardgive example for the following(by equation) a. Converting a water insoluble compound to a soluble one. b. Diazotization reaction form diazonium salt c. coupling reaction of a diazonium salt d. indacator properties of MO e. Diazotization ( diazonium salt of bromobenzene)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





