
Interpretation:
The evidence for the blue-green color obtained during the flame test of copper salt needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
When salt is heated in burner, electron from valence shell gets excited and moves from ground state to excited state. This electron jumps back to the ground state and imparts flame color.
Answer to Problem 6E
Copper salt absorbs light in red zone. So, the expected emission zone is blue-green.
Explanation of Solution
Emission wavelength of a substance is complementary to absorption wavelength. It means if a substance absorbs longer wavelength then it will emit light of shorter wavelength. The complimentary colors can be obtained from Newton’s color wheel which is represented as follows:
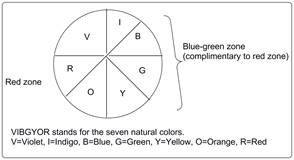
As blue-green color is emitted by copper salt it means copper absorbs red light.
This is expected from the electronic configuration of Cu.
Here, [Ar] stands for the electronic configuration of argon gas which is an inert gas.
Once the electron is removed from the 4s sub-shell then remaining electrons have fully filled 3d sub-shell.
So, copper requires very low energy in the first ionization.
Copper absorbs red light and emits blue-green light. Ionization energy of copper is less which is supplied by red light (a light with greater wavelength and lower energy).
Chapter U1 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





