
Interpretation:
Two ways of finding the identity of an atom from its electronic configuration needs to be described.
Concept introduction:
The arrangement of electrons in various orbitals of atoms through a shorthand notation is called electron configuration. This helps to keep track of the electrons in an atom. Each subshell is written using the shell number and the subshell letter. The number of electrons in each subshell is indicated with a superscript number.
Answer to Problem 12E
Counting the number of electrons in the electron configuration will help to know the
The valence electronic configuration gives the exact location of the atom on the periodic table. The subscript tells the period number, the subshell letter tells the block and the superscript number tells the row number of that block.
Explanation of Solution
A periodic table can be divided into four zones, s block, p block, d block and f block.
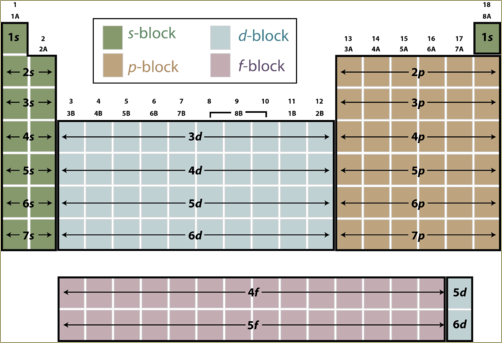
Elements belong to one of these four zones.
Any element located in the s block will have its outermost electron(s) in s subshell. On moving across the periodic table from one element to the next, one additional proton and one additional electron are added, along with one or more neutrons. Each additional electron goes into a specific subshell. If an atom is located in the p block of the table, the last electron is placed into a p subshell. If an atom is located in the d block of the table, the last electron is placed into a d subshell and so on.
Suppose the electron configuration of an element is 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p6 3d104s24p5.
- Counting all the superscript numbers one can get the total number of electrons present in an atom of that element. So atomic number = 2 + 2 + 6 + 2 + 6 + 10 + 2 + 5 = 35 By locating this atomic number on the periodic table, one can find the element is bromine.
- By looking at the distribution of electrons in the subshells the last filled subshell can be determined. In this case it is 4p. So the element belongs to p block. The valence electron configuration can help in figuring out the identity of the element. It gives the exact location of the atom on the periodic table. Here 4p5 is the valence electronic configuration. The subscript tells the period number, the subshell letter tells the block and the superscript number tells the row number of that block. Hence the element belongs to period 4 in the p block in row number 5. So the group number is 7A (halogens). The element is bromine.
The valence electronic configuration of each atom can help in figuring out the identity of the element. It gives the exact location of the atom on the periodic table.
Chapter U1 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- Provide photos of models of the following molecules. (Include a key for identification of the atoms) 1,2-dichloropropane 2,3,3-trimethylhexane 2-bromo-3-methybutanearrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forward
- Firefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardGiven a complex reaction with rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, what is the overall reaction order?arrow_forward
- Please draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the steady-state approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the limiting or determining step approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forward
- CHEMICAL KINETICS. Indicate the approximation methods for solving the rate equation.arrow_forwardTRANSMITTANCE เบบ Please identify the one structure below that is consistent with the 'H NMR and IR spectra shown and draw its complete structure in the box below with the protons alphabetically labeled as shown in the NMR spectrum and label the IR bands, including sp³C-H and sp2C-H stretch, indicated by the arrows. D 4000 OH LOH H₂C CH3 OH H₂C OCH3 CH3 OH 3000 2000 1500 HAVENUMBERI-11 1000 LOCH3 Draw your structure below and label its equivalent protons according to the peak labeling that is used in the NMR spectrum in order to assign the peaks. Integrals indicate number of equivalent protons. Splitting patterns are: s=singlet, d=doublet, m-multiplet 8 3Hb s m 1Hd s 3Hf m 2Hcd 2Had 1He 鄙视 m 7 7 6 5 4 3 22 500 T 1 0arrow_forwardRelative Transmittance 0.995 0.99 0.985 0.98 Please draw the structure that is consistent with all the spectral data below in the box and alphabetically label the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc ....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. Label the absorption bands in the IR spectrum indicated by the arrows. INFRARED SPECTRUM 1 0.975 3000 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) 1000 Structure with assigned H peaks 1 3 180 160 140 120 100 f1 (ppm) 80 60 40 20 0 C-13 NMR note that there are 4 peaks between 120-140ppm Integral values equal the number of equivalent protons 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 fl (ppm)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





