
(a)
Interpretation:
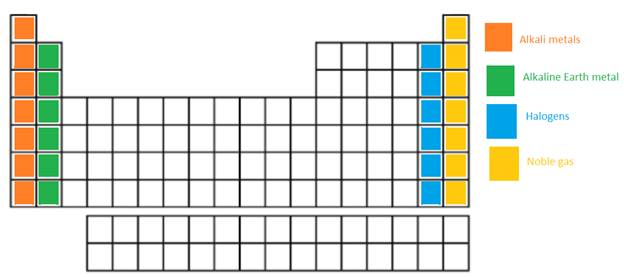
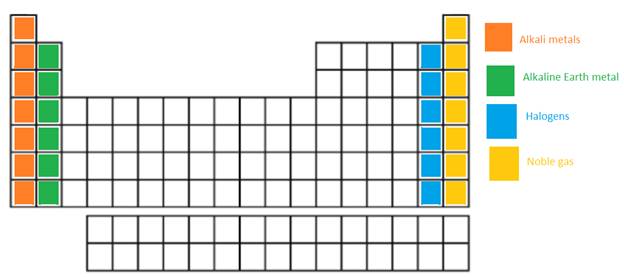
The alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogen and the Noble gases in the periodic table need to be labeled.
Concept introduction:
Element is the basic unit of any substance which can combine with same or different elements to form molecules and compounds. Elements are composed of the same type of atoms therefore they exhibit unique physical and chemical properties.
The
(a)
Answer to Problem 3E
Explanation of Solution
In the long form of periodic table; alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogen and the Noble gases are name of certain groups. In periodic table, the vertical columns are called as groups.
Alkali metal = The IA or 1st group is named as alkali metals as these metallic elements form alkaline oxides and hydroxides.
Alkaline earth metals = The IIA or 2nd group is named as Alkaline earth metals as these metallic elements form alkaline compounds and are also found in Earth crust.
Halogens = It is VIIA or 17th group of the periodic table. They are non-metallic elements.
Noble gases = These elements are placed in group 18th or also called as zero group. They are non-reactive and monoatomic gases.
The position of these elements in the periodic table is as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
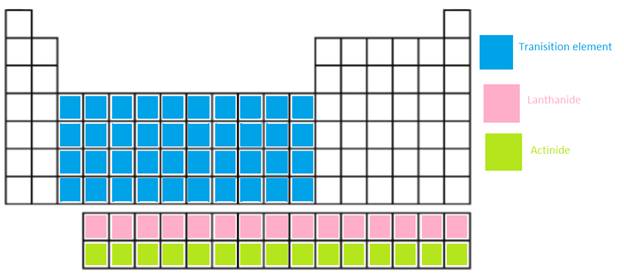
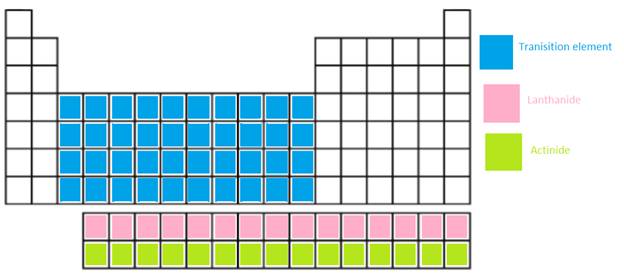
The main group elements, transition metal, Lanthanide and actinide needs to be shown in the periodic table.
Concept introduction:
Element is the basic unit of any substance which can combine with same or different elements to form molecules and compounds. Elements are composed of same type of atoms therefore they exhibit unique physical and chemical properties.
The chemical reaction of two or more elements leads to the formation of new molecules and compounds.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3E
Explanation of Solution
In periodic table, the vertical columns are called as groups and horizontal rows are period.
Transition metal =
Lanthanide = These are the f-block elements which are placed at the bottom of main body. It is a series of 14 elements where electrons are filled in 4f orbitals.
Actinide = These are the f-block elements which are placed at the bottom of main body. It is series of 14 elements where electrons are filled in 5f orbitals.
The position of these elements in the periodic table is given below:
Chapter U1 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- eks.com/aleksogi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS17Hd6m-HIl6n52njJN-TXdQA2X9yID-1SWQJTgnjARg30 111 States of Matter Understanding conceptual components of the enthalpy of solution 0/5 Ge A small amount of acetonitrile (CH, CN) is dissolved in a large amount of water. Imagine separating this process into the four stages sketched below. (These sketches show only a portion of the substances, so you can see the density and distribution of atoms and molecules in them.) CH,CN H₂O B 88 C Use these sketches to answer the questions in the table below. The enthalpy of solution AH is negative soln when CH3CN dissolves in water. Use this information to list the stages in order of increasing enthalpy. Would heat be absorbed or released if the system moved from Stage C to D? What force would oppose or favor the system moving from Stage C to D? Check all that apply. 1 absorbed O released neither absorbed nor released. none O ionic bonding force covalent bonding force…arrow_forwardIn a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of ŋ as a function of the current density: 1. at low fields is linear 2. at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law Find the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value as when calculated for cases 1 and 2 (maximum relative difference of 5% with respect to the behavior for higher fields). To which overpotential range does this correspond? Data: 10 = 1.5 mA cm², T = 300°C, ẞ = 0.64, R = 8.314 J K 1 mol¹ and F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forwardIndicate 10.6 with only one significant figure.arrow_forward
- If I have 10 data points for variables x and y, when I represent y versus x I obtain a line with the equation y = mx + b. Is the slope m equal to dy/dx?arrow_forwardThe data for the potential difference of a battery and its temperature are given in the table. Calculate the entropy change in J mol-1 K-1 (indicate the formulas used).Data: F = 96485 C mol-1arrow_forwardIn a cell, the change in entropy (AS) can be calculated from the slope of the E° vs 1/T graph. The slope is equal to -AS/R, where R is the gas constant. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- Using the Arrhenius equation, it is possible to establish the relationship between the rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction and the temperature (T), in Kelvin (K), the universal gas constant (R), the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). This equation is widely applied in studies of chemical kinetics, and is also widely used to determine the activation energy of reactions. In this context, the following graph shows the variation of the rate constant with the inverse of the absolute temperature, for a given chemical reaction that obeys the Arrhenius equation. Based on the analysis of this graph and the concepts acquired about the kinetics of chemical reactions, analyze the following statements: I. The activation energy (Ea) varies with the temperature of the system. II. The activation energy (Ea) varies with the concentration of the reactants. III. The rate constant (K) varies proportionally with temperature. IV. The value of the…arrow_forwardIn an electrolytic cell, indicate the formula that relates E0 to the temperature T.arrow_forward-- 14:33 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 11. Compound A can transform into compound B through an organic reaction. From the structures below, mark the correct one: HO A تھے۔ די HO B ○ A) Compounds A and B are isomers. B) Both have the same number of chiral carbons. C) Compound A underwent an addition reaction of Cl2 and H2O to form compound B. D) Compound A underwent a substitution reaction forming the intermediate chlorohydrin to obtain compound B. E) Compound A underwent an addition reaction of Cl2 forming the chloronium ion and then added methanol to obtain compound B. 60arrow_forward
- -- 14:40 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 13. The compound 1-bromo-hex-2-ene reacts with methanol to form two products. About this reaction, mark the correct statement: OCH3 CH3OH Br OCH3 + + HBr A B A) The two products formed will have the same percentage of formation. B) Product B will be formed by SN1 substitution reaction with the formation of an allylic carbocation. C) Product A will be formed by SN1 substitution reaction with the formation of a more stable carbocation than product B. D) Product A will be formed by an SN2 substitution reaction occurring in two stages, the first with slow kinetics and the second with fast kinetics. E) The two compounds were obtained by addition reaction, with compound B having the highest percentage of formation. 57arrow_forward-- ☑ 14:30 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 10. Amoxicillin (figure X) is one of the most widely used antibiotics in the penicillin family. The discovery and synthesis of these antibiotics in the 20th century made the treatment of infections that were previously fatal routine. About amoxicillin, mark the correct one: HO NH2 H S -N. HO Figura X. Amoxicilina A) It has the organic functions amide, ester, phenol and amine. B) It has four chiral carbons and 8 stereoisomers. C) The substitution of the aromatic ring is of the ortho-meta type. D) If amoxicillin reacts with an alcohol it can form an ester. E) The structure has two tertiary amides. 62arrow_forwardThe environmental police of a Brazilian state received a report of contamination of a river by inorganic arsenic, due to the excessive use of pesticides on a plantation on the riverbanks. Arsenic (As) is extremely toxic in its many forms and oxidation states. In nature, especially in groundwater, it is found in the form of arsenate (AsO ₄ ³ ⁻ ), which can be electrochemically reduced to As ⁰ and collected at the cathode of a coulometric cell. In this case, Potentiostatic Coulometry (at 25°C) was performed in an alkaline medium (pH = 7.5 throughout the analysis) to quantify the species. What potential (E) should have been selected/applied to perform the analysis, considering that this is an exhaustive electrolysis technique (until 99.99% of all AsO ₄ ³ ⁻ has been reduced to As ⁰ at the electrode, or n( final) = 0.01% n( initial )) and that the concentration of AsO ₄ ³ ⁻ found in the initial sample was 0.15 mmol/L ? Data: AsO ₄ 3 ⁻ (aq) + 2 H ₂ O ( l ) + 2 e ⁻ → A s O ₂ ⁻ ( a…arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





