
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The reason for fewer hydrogen atoms in
Concept introduction:
Organic compounds that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms are said to be hydrocarbons. There are two types of hydrocarbons that is saturated and
Saturated hydrocarbon: Those hydrocarbons which contains only single covalent bond, include
Unsaturated hydrocarbon: Those hydrocarbons which contains multiple covalent bonds, include
Answer to Problem 3E
Due to the presence of double bond in
Explanation of Solution
Alkanes are hydrocarbons that is they contain only carbon and hydrogens attached by single bonds only. The general formula for alkane is CnH2n + 2, where n is number of carbon atoms.
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that is they contain carbon and hydrogens attached by single bonds and presence of one or more double covalent bond between two carbon atoms. The general formula for alkene is CnH2n, where n is number of carbon atoms.
The structure of
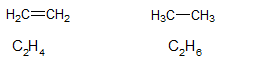
From the above structures, it is clear that. there is a presence of double bond in two carbon atoms in
Due to the presence of double bond in
Hence, due to the presence of double bond in
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
- First image: I have to show the mecanism (with arows and structures) of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary Second image: I have to show the mecanism (with arrows and structures) for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion its not an examarrow_forwardwhat is the skeletal structure of a tertiary alkyl fluoride with six carbon atoms and no rings.arrow_forwardOne step of glycolysis is a retro-aldol reaction (aldolase) to produce ATP.Below is the aldol reaction of the equilibrium. Show the mechanism for the base catalyzed reaction. *see imagearrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





