
(a)
Interpretation: The dipole in the
Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(a)
Answer to Problem 4E
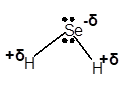
Explanation of Solution
In
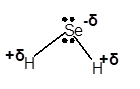
(b)
Interpretation: The dipole in the
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(b)
Answer to Problem 4E
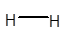
No dipole exists on
Explanation of Solution
In
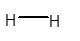
(c)
Interpretation: The dipole in the
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(c)
Answer to Problem 4E
No dipole exists on
Explanation of Solution
Because of no bond formation, the overall dipole on the
(d)
Interpretation: The dipole in the
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(d)
Answer to Problem 4E
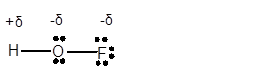
Explanation of Solution
In
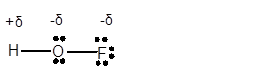
(e)
Interpretation: The dipole in the
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(e)
Answer to Problem 4E
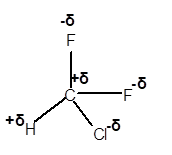
Explanation of Solution
In
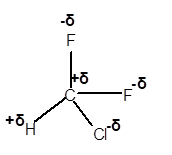
(f)
Interpretation: The dipole in the
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(f)
Answer to Problem 4E
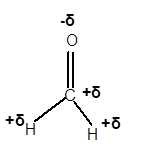
Explanation of Solution
In
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- Chloroform, long used as an anesthetic and now considered carcinogenic, has a heat of vaporization of 31.4 kJ/mol. During vaporization, its entropy increases by 94.2 J/mol.K. Therefore, select the alternative that indicates the temperature, in degrees Celsius, at which chloroform begins to boil under a pressure of 1 atm. A) 28 B) 40 C) 52 D) 60 E) 72arrow_forwardIf we assume a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of n as a function of current density: 1. at low fields is linear 2. at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law Obtain the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value when calculated for 1 and 2 cases (maximum relative difference of 5% compared to the behavior for higher fields). To which overpotential range does this correspond? Data: i = 1.5 mA cm², T = 300°C, B = 0.64, R = 8.314 J K1 mol-1 and F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forwardAnswer by equation pleasearrow_forward
- Some of the theories used to describe interface structure can be distinguished by:1. the measured potential difference.2. the distribution of ions in solution.3. the calculation of charge density.4. the external Helmoltz plane.arrow_forwardWhen talking about the acidity of carboxylic acids, is it the same thing to say higher or stronger acidity?arrow_forwardUsing the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$arrow_forward
- Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Galactose with hydroxylamine.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





