
(a)
Interpretation: A Lewis dot structure for H2Se needs to be drawn and the shape needs to be indicated. This is to be determined if H2Se has smell or not.
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure of H2Se is similar to H2O, it is because Oxygen and selenium both have same number of valence electrons as both are of same group.
(a)
Answer to Problem 3E
Lewis dot structure of different molecules with different shapes can be formed with the help of valence electrons.
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis dot structure of H2Se is as follows:
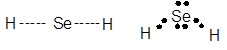
The molecule is polar, bond angle is 1050 and it hassp3 hybridization. The overall molecule has bent shape. It has horseradish like smell.
(b)
Interpretation: A Lewis dot structure for H2 needs to be drawn and the shape needs to be indicated. This is to be determined if H2 has smell or not.
Concept Introduction: In Lewis dot structure of H2, Hydrogen has one valence electron.Both hydrogen atoms will share one electron to form one covalent bond.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3E
Lewis dot structure of different molecules with different shapes can be formed with the help of valence electrons.
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis dot structure of H2molecule is as follows:
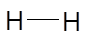
Hydrogen-hydrogen bond is formed after sharing of 1 electron by each H atom. Since, there is no lone pair of electrons on H atom thus, it has linear shape. The hydrogen gas is non-toxic, it does not have any smell or color.
(c)
Interpretation: A Lewis dot structure for Ar needs to be drawn and the shape needs to be indicated. This is to be determined if Ar has smell or not.
Concept Introduction: In Lewis dot structure of Ar, Argon has eight valence electrons. Due to presence of 8 electrons, it will not share even single electron with any other atom.
(c)
Answer to Problem 3E
Lewis dot structure of different molecules with different shapes can be formed with the help of valence electrons.
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis dot structure is represented as follows:
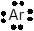
Argon is an inert gas with valence electrons 8, there will be no sharing of electrons. The element does not have any shape as it does not form bond with any other atom of element. Argon gas being inert has no smell and color. It is non-toxic in nature.
(d)
Interpretation: A Lewis dot structure for HOF needs to be drawn and the shape needs to be indicated. This is to be determined if HOF has smell or not.
Concept Introduction: In Lewis dot structure of HOF, hydrogen has one,oxygen has six and fluorine has seven valence electrons. Hydrogen and fluorine both will share one electron to form single covalent bond. Oxygen will share one electron each with hydrogen as well as with fluorine.
(d)
Answer to Problem 3E
Lewis dot structure of different molecules with different shapes can be formed with the help of valence electrons.
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis dot structure of HOF molecule is represented as follows:
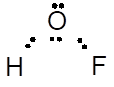
It has bent shape and molecule has sp3hybridization.
(e)
Interpretation: A Lewis dot structure for CHClF2needs to be drawn and the shape needs to be indicated. This is to be determined if CHClF2 has smell or not.
Concept Introduction: In Lewis dot structure of CHClF2, hydrogen has one, carbon has four and chlorine and fluorinehave seven valence electrons. Hydrogen, chlorine and fluorine both will share one electron with carbon atom to form single covalent bond.
(e)
Answer to Problem 3E
Lewis dot structure of different molecules with different shapes can be formed with the help of valence electrons.
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis dot structure is represented as follows:
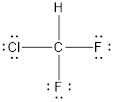
The shape of the molecule is tetrahedral and molecule has sp3 hybridization. It is a colorless gas with ethereal smell.
(f)
Interpretation: A Lewis dot structure for HCHO needs to be drawn and the shape needs to be indicated. This is to be determined if HCHO has smell or not.
Concept Introduction: In Lewis dot structure of HCHO, hydrogen has one, oxygen has six valence electrons. Hydrogen will share one electron with carbon atom to form single covalent bond and oxygen will share two electrons with carbon to complete its octet.
(f)
Answer to Problem 3E
Lewis dot structure of different molecules with different shapes can be formed with the help of valence electrons.
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis dot structure is as follows:
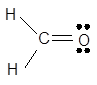
The shape is trigonal planar and molecule is sp2 hybridized. It has a strong pickle like smell.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- When talking about the acidity of carboxylic acids, is it the same thing to say higher or stronger acidity?arrow_forwardUsing the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$arrow_forwardIndicate characteristics of oxodec acid.arrow_forward
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





