
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The reason for carbon dioxide to be nonpolar molecule even though its bonds are polar is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of molecules; polar and nonpolar. There are partial charges on atoms of a polar molecule. A polar molecule has a dipole as it has two poles; a positive end and a negative end.
Answer to Problem 3E
A polar molecule is a molecule that possesses partial charges on its atoms. In carbon dioxide molecules, the two dipole moments in CO2 balance each other, and there is no partial positive or negative charge on the molecule. So the overall molecule is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
In a carbon dioxide molecule, there is a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. These bonds are polar. So there are two polar bonds in a molecule of CO2. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon so both oxygen atoms pull the electrons away from the carbon atom in opposite directions. Both the dipoles in CO2 balance each other, and there is no partial positive or negative charge on the molecule. So the overall molecule is nonpolar.
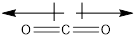
Carbon dioxide is a nonpolar molecule even though its bonds are polar as the two dipoles cancel out each other and there is no net charge on the molecule.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reactions.arrow_forward
- Provide the complete mechanism for the reactions below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. C6H5 CH3arrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene and I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene, indicate the compound that I should add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Ο HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Select to Draw I Submitarrow_forwardFeedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





