
(a)
Interpretation: The molecular formulas for citronellol and geraniol needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Chemical compounds with same molecular formula having different structure are known as isomers. Isomers having same number of atoms of each type but bonded together in a different sequence (spatial arrangement) are known as stereoisomers.
There are two kinds of stereo isomers- Geometrical and optical.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given structures are as follows:
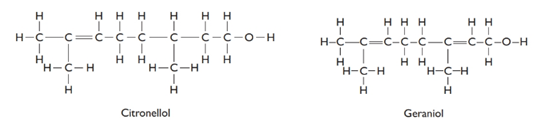
From the above structures, molecular formula of the compounds can be determined as follows:
C10H21O −Citronellol
C10H18O- Gerniol
(b)
Interpretation: The two distinct smells of the molecule citronellol needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: Chemical compounds with same molecular formula having different structure are known as isomers. Isomers having same number of atoms of each type but bonded together in a different sequence (spatial arrangement) are known as stereoisomers.
There are two kinds of stereo isomers- Geometrical and optical.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The formula of citronellol is C10H21O. The structure is represented as follows:
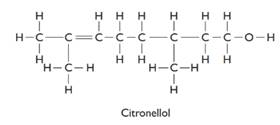
There are two optical isomers which are non-superimposable mirror image of each other.
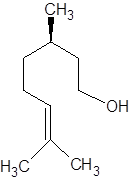
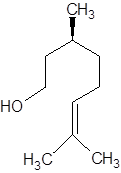
Isomer of Citronellol
Thus, the two different smells are due to two different optical isomers of citronellol.
(c)
Interpretation: The reason for only one smell of geraniol smell needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: Chemical compounds with same molecular formula having different structure are known as isomers. Isomers having same number of atoms of each type but bonded together in a different sequence (spatial arrangement) are known as stereoisomers.
There are two kinds of stereo isomers- Geometrical and optical.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of geraniol is C10H18O. The structure is represented as follows:
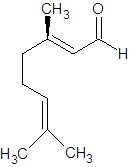
Geraniol
It can show geometrical isomerism. The E-isomer and Z-isomer are as follows:
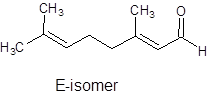
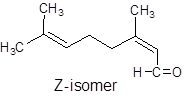
Trans-Form Cis-Form
Due to absence of optical isomerism, there is only one smell of the molecule.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- For a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forwardDescribe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forward
- State two similarities between fluorescence and phosphorescence.arrow_forwardState three photophysical processes that can be related to the effects of incident radiation on a molecule in its ground state. Consider that radiation can give rise to fluorescent emission, but not phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardIn a photochemical reaction, how is the rate of the process related to its quantum yield?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





