
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation : Number of lone pairs present in the given carbon dioxide molecule has to be identified.
Concept Introduction :
When atoms combine together to form molecule they share valence electrons to complete the noble gas configuration of eight electrons. Some electrons are part of the bonds formed while some are not. Pair of electrons that are not shared between atoms in a molecule are called lone pair of electrons.
In CO2 molecule there are two lone pairs of electrons on each oxygen atom and no lone pair on carbon atom. The two oxygen atoms are joined by double bonds to carbon atom.
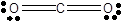
In carbon dioxide molecule, one carbon atom bonds with two oxygen atoms through double bonds. So, all four valence electrons of carbon bond with a pair of electrons of oxygen. Since oxygen has 6 valence electrons, only two electrons are used in bonding. Two pairs of lone electrons are left. Hence, there are two lone pairs of electrons on each oxygen atom and no lone pair on carbon atom.
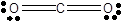
(b)
Interpretation : Number of lone pairs present in the given silicon SiF4molecule has to be identified.
Concept Introduction :
When atoms combine together to form molecule they share valence electrons to complete the noble gas configuration of eight electrons. Some electrons are part of the bonds formed while some are not. Pair of electrons that are not shared between atoms in a molecule are called lone pair of electrons.
In SiF4 molecule there are zero lone pairs on silicon atom and three lone pairs of electrons on each fluorine atom.
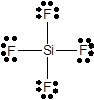
In SiF4molecule, one silicon atom bonds with four fluorine atoms through single bonds. So, all four valence electrons of silicon bond with a one valence electron of fluorine. Since fluorine has 7 valence electrons, only one electron is used in bonding. Three pairs of lone electrons are left on each fluorine atom. Hence, there are three lone pairs of electrons on each fluorine atom and no lone pair on silicon atom.
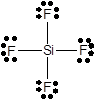
(c)Interpretation : Number of lone pairs present in the given methane molecule has to be identified.
Concept Introduction :
When atoms combine together to form molecule they share valence electrons to complete the noble gas configuration of eight electrons. Some electrons are part of the bonds formed while some are not. Pair of electrons that are not shared between atoms in a molecule are called lone pair of electrons.
In CH4 molecule there are zero lone pairs on carbon atom and hydrogen atom.
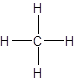
Carbon combines with four hydrogen atoms to form methane, CH4. Carbon has four valence electrons and hydrogen has one electron. So each hydrogen atom shares l electron with carbon to form four single bonds. All the electrons of carbon and hydrogen form bonded pair of electrons. Hence, there are no lone pairs of electrons on methane molecule.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- For the titration of a divalent metal ion (M2+) with EDTA, the stoichiometry of the reaction is typically: 1:1 (one mole of EDTA per mole of metal ion) 2:1 (two moles of EDTA per mole of metal ion) 1:2 (one mole of EDTA per two moles of metal ion) None of the abovearrow_forwardPlease help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





