
Interpretation:
The shape of Cl2, CO2 and H2O molecule must be described with the help of Lewis dot structures, periodic table and HONC 1234 rule.
Concept introduction:
The shape of a molecule depends on the number of valence electrons (including lone pair and bond pair electrons) present in the central atom. The number of valence electron is obtained from the location of the element in the periodic table.
HONC 1234 rule stases that H, O, N and C can form 1, 2, 3 and 4 bonds respectively.
Answer to Problem 3E
Shape of Cl2 is linear.
Shape of CO2is linear.
Shape of H2O molecule is angular.
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis dot structure for Cl2, CO2, and H2O is represented as follows:
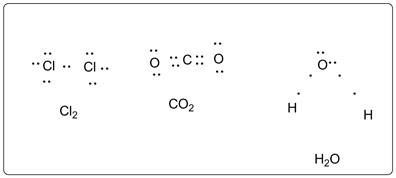
In Cl2 , two Cl atoms are bonded with each other in single bond. Total 7 valence electrons are present on each Cl atom. So there are 3 lone pairs of electrons on each Cl atom.
In CO2, two O atoms are bonded with central carbon atom in double bond. Total 4 valence electrons are there on the C atom. These electrons are all bonded. So there are 2 lone pairs of electrons on each O atom.
In H2O, two H atoms are bonded with central O atom in single bond. Total 6 valence electrons are present on O atom. So there are 2 lone pairs of electrons on O atom.
As per HONC 1234 rule each C and O has formed 4 bonds and 2 bonds respectively.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
- An einstein is the amount of energy needed to dissociate 1 mole of a substance. If we have 0.58 moles, do we need 0.58 einsteins to dissociate that substance?arrow_forwardIf the energy absorbed per mole of gas is 480 kJ mol-1, indicate the number of Einsteins per mole.Data: Energy of each photon: 0.7835x10-18 J.arrow_forwardIf the energy absorbed per mole of gas is 480 kJ mol-1, indicate the number of Einsteins per mole.arrow_forward
- The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculating the moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculate the number of Einsteins absorbed per mole knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forward
- If the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forwardWhen propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forwardDraw mechanismarrow_forward
- Does Avogadro's number have units?arrow_forwardExplain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





