
Interpretation:
The tetrahedron shape of CH4 molecule and the similarities with NH3 and H2O needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure of an organic compound represents the bonding of atoms with lone pairs (if any). It indicates the bonds with atoms and also the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Hybridization of an atom indicates the molecular geometry of a molecule. The formula to check the hybridization can be written as:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
The molecular geometry of molecules with lone pair on central atom is given by the VSEPR theory.
Answer to Problem 9E
All these three molecules have the same type of hybridization and should have tetrahedral geometry but due to the presence of lone pairs on the central atom, the molecular geometry changes to a pyramidal and bent shape.

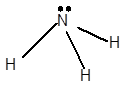
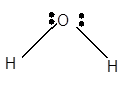
Explanation of Solution
For Lewis structure of CH4 molecule, calculate total number of valence electrons:
CH4 molecule = 4 electrons in C + 4 × 1 valence electrons in H = 8 electrons

Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Hybridization of C atom = 4 + 0 = 4 = sp3
Thus, with sp3 hybridization, the molecular shape must be tetrahedral and must be fit in a tetrahedron.
For Lewis structure of NH3 molecule, calculate total number of valence electrons:
NH3 molecule = 5 electrons in N + 3 × 1 valence electrons in H = 8 electrons
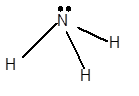
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Hybridization of N atom = 3 + 1 = 4 = sp3
Thus, with sp3 hybridization, the molecular shape must be tetrahedral but due to the presence of lone pair on the central N atom, the geometry alters to trigonal pyramidal shape.
For Lewis structure of H2O molecule, calculate total number of valence electrons:
H2O molecule = 6 electrons in O + 1 × 2 valence electrons in H = 8 electrons
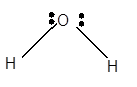
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Hybridization of O atom = 2 + 2 = 4 = sp3
Thus, with sp3 hybridization, the molecular shape must be tetrahedral but due to the presence of two lone pairs on the central O atom, the geometry alters to a bent shape.
Although all these three molecules have same type of hybridization and should have tetrahedral geometry but due to presence of lone pairs on central atom, the molecular geometry changes to pyramidal and bent shape.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
- 2-Propanone and ethyllithium are mixed and subsequently acid hydrolyzed. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward(Methanesulfinyl)methane is reacted with NaH, and then with acetophenone. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward3-Oxo-butanenitrile and (E)-2-butenal are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward
- What is the reason of the following(use equations if possible) a.) In MO preperation through diazotization: Addition of sodium nitrite in acidfied solution in order to form diazonium salt b.) in MO experiment: addition of sodium hydroxide solution in the last step to isolate the product MO. What is the color of MO at low pH c.) In MO experiment: addition of sodium hydroxide solution in the last step to isolate the product MO. What is the color of MO at pH 4.5 d.) Avoiding not cooling down the reaction mixture when preparing the diazonium salt e.) Cbvcarrow_forwardA 0.552-g sample of an unknown acid was dissolved in water to a total volume of 20.0 mL. This sample was titrated with 0.1103 M KOH. The equivalence point occurred at 29.42 mL base added. The pH of the solution at 10.0 mL base added was 3.72. Determine the molar mass of the acid. Determine the Ka of the acid.arrow_forwardAs the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will its major product: 2,0° with a new C-C bond as If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing aree below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and desh bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If the major products of this reaction won't have a new C-C bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank.arrow_forward
- write the mechanism of the nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, please give an examplearrow_forwardThe compound in the figure is reacted with 10 n-butyllihium, 2° propanone, and 3º H2O. Draw and name the products obtained. SiMe3arrow_forwardCaffeine (C8H10N4O2, pictured below) is a weak base. The pKb of caffeine is 10.4. What is the pH of a 0.0155 M solution of caffeine?arrow_forward
- 2-Cyclopentyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane is reacted with H₂SO₄. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of 1-cyclohexyl-2,2-dimethylpropan-1-one with CH3CO3H (). Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardWrite chemical equations for: the reaction of benzoic acid chloride with grignard reagent [CH3MgX] the reaction of butanoic acid with methyl amine [CH3NH2]arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





