
Interpretation:Whether the molecule HOCl is polar or non-polar needs to be explained using the Lewis dot structure.
Concept Introduction: Molecules are divided into two on the basis of their polarity- polar and non-polar.
Answer to Problem 6E
When two atoms do not share equal electrons in a covalent bond, the molecule becomes polar, whereas when there is equal sharing of electrons between atoms, it becomes non-polar.
Explanation of Solution
In the case of HOCl molecule, two covalent bonds are formed in between Cl-O and O-H, both are formed by an equal number of electrons. A polar molecule must contain polar bonds due to the difference between the bonded atoms. Another way to find out the polarity of any molecule is its electronegativity difference. If electronegativity difference is less than 0.5, then the molecule is considered as non-polar.
The Lewis dot structure of HOCl is represented as follows:
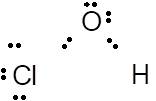
The electronegativity difference between O (3.4)and Cl (3.2) atom is 0.2 thus, it has polar covalent bond.
Also, the electronegativity difference between O (3.4) and H (2.2) is 1.2 thus, it also has polar covalent bond.
The molecule has bent shape and there are two lone pair of electrons on O atom. Therefore, overall molecule is non-polar in nature.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- If the energy absorbed per mole of gas is 480 kJ mol-1, indicate the number of Einsteins per mole.Data: Energy of each photon: 0.7835x10-18 J.arrow_forwardIf the energy absorbed per mole of gas is 480 kJ mol-1, indicate the number of Einsteins per mole.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculating the moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forward
- The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculate the number of Einsteins absorbed per mole knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardIf the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forward
- When propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forwardDraw mechanismarrow_forwardDoes Avogadro's number have units?arrow_forward
- Explain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forwardIndicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





