
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure and structural formula of SiF4 needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Valence electrons are involved in covalent bonding where sharing of electrons takes place.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis dot structure can be drawn with the help of valence electrons. Silicon has 4 valence electrons, Fluorine has 7 valence electrons. To complete the octet, Si will share 4 electrons, one electron each with fluorine.
Thus, the Lewis dot structure and structural formula of SiF4is represented as follows:
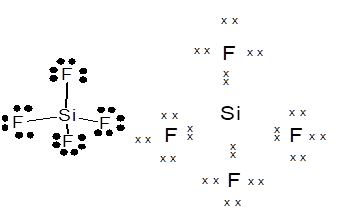
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure and structural formula of CO2 needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Valence electrons are involved in covalent bonding where sharing of electrons takes place.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis dot structure can be drawn with the help of valence electrons. Carbon has 4 valence electrons, oxygen has 6 valence electrons. To complete the octet, carbon will share 4 electrons, two electrons each with oxygen and form double covalent bond.
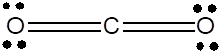
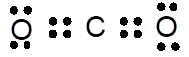
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure and structural formula of CH4 needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Valence electrons are involved in covalent bonding where sharing of electrons takes place.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis dot structure can be drawn with the help of valence electrons. Carbon has 4 valence electrons, hydrogen has one valence electrons. To complete the octet, carbon will share 4 electrons, one electron each with hydrogen and form single covalent bond.
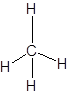
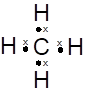
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure and structural formula of SF2 needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Valence electrons are involved in covalent bonding where sharing of electrons takes place.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis dot structure can be drawn with the help of valence electrons. Sulphur has 6 valence electrons, Fluorine has 7 valence electrons. To complete the octet, sulphur will share 2 electrons, one electron each with fluorine and form single covalent bond.
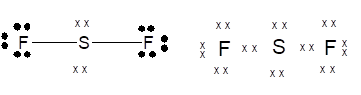
(e)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure and structural formula of C2H4needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Valence electrons are involved in covalent bonding where sharing of electrons takes place.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Carbon has 4 valence electrons, hydrogen has one valence electrons. To complete the octet, carbon will share 4 electrons, one electron each with hydrogen and form single covalent bond.
When carbon shares two electrons with other carbon atom, it forms double bond.
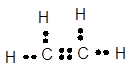
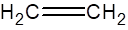
(f)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure and structural formula of C2H2 needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Valence electrons are involved in covalent bonding where sharing of electrons takes place.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Carbon has 4 valence electrons, hydrogen has one valence electrons. To complete the octet, carbon will share 4 electrons, one electron each with hydrogen and form single covalent bond.
When carbon share three electrons with other carbon atom, it forms triple bond.
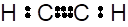

(g)
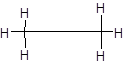
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure and structural formula of C2H6needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Valence electrons are involved in covalent bonding where sharing of electrons takes place.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Carbon has 4 valence electrons, hydrogen has one valence electrons. To complete the octet, carbon will share 4 electrons, one electron each with hydrogen and form single covalent bond.
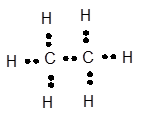
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





