
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis dot structure of butane must be drawn.
Concept Introduction :
Butane has molecular formula C4H10.
Lewis dot structure is the representation of a molecule where all the valence electrons of participating atoms are shown as dots.
(a)
Answer to Problem 7E
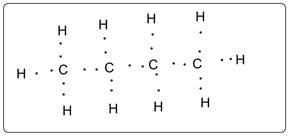
Lewis dot structure Butane is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Lewis dot structure of butane is shown in which all the C is tetravalent. There is no lone pair of electron. All the C is octet fulfilled whereas all the hydrogens are duplet.
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of electron domains there in butane must be explained.
Concept Introduction :
Electron domain is the regions of molecules where there are bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons. Each bond between two participating atoms has electron domains.
(b)
Answer to Problem 7E
Butane has 13 electron domains.
Explanation of Solution
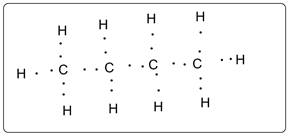
Structure of butane is shown. Each C has 4 bonds and each H has 1 bond. Thus there are total 13 bonds which are electron domains.
(c)
Interpretation:
Shape of butane must be predicted.
Concept Introduction :
Shape of a molecule depends on the total number of electrons pairs including bond pairs and lone pairs on an atom.
(c)
Answer to Problem 7E
Butane has zigzag shape in which all the carbon atoms have tetrahedral geometry.
Explanation of Solution
Each carbon atom has total 4 bonds. Each carbon atom is bonded to either 2 or 3 hydrogen atoms and 1 or 2 other carbon atoms. Thus the shape of the molecule is zigzag with tetrahedral arrangements of bonds around each C atom.
(d)
Interpretation:
The reason for the carbon atom chain to be not straight must be explained.
Concept Introduction :
A molecule attains a shape in which repulsive interaction among bonds is minimum.
(d)
Answer to Problem 7E
Carbon atom chain in butane is not straight to stabilize the molecule.
Explanation of Solution
Each carbon atom has four bonds which are tetrahedrally arranged to give maximum stability to the molecule.
Thus butane doesn’t have straight chain structure.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- help draw the moleculearrow_forwardHow to draw this claisen condensation reaction mechanisms/arrow_forwardWrite all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forward
- How can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





