
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation :
Whether methyl salicylate follows HONC 1234 rule or not must be explained.
Concept Introduction :
HONC 1234 rule is the basic rule for drawing organic molecule. The rule states that H, O, N and C generally form 1, 2, 3 and 4 bonds respectively.
(a)
Answer to Problem 5RE
Methyl salicylate follows HONC 1234 rule.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of methyl salicylate is as follows:
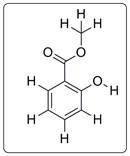
Each carbon has 4 bonds, each O has two bonds and each H has one bond. Thus methyl salicylate follows HONC 1234 rule.
b)
Interpretation :
Molecular formula of methyl salicylate must be written.
Concept Introduction :
Molecular formula is the representation of the molecule which shows the number of total number of different atoms.
b)
Answer to Problem 5RE
Molecular formula of methyl salicylate, C8H8O3 are given below.
Explanation of Solution
In methyl salicylate has total 8 carbons, 8 hydrogens and 3 oxygens. Thus, the molecular formula is C8H8O3.
c)
Interpretation :
Overall shape of the molecule must be explained.
Concept Introduction :
Overall shape of a molecule depends on the total number of electrons including lone pair and bond pair electrons.
c)
Answer to Problem 5RE
Methyl salicylate is planar structure with a tetrahedral methyl group. Here, all the carbon atoms are attached to 4 groups resulting in tetrahedral shape of the molecule.
Explanation of Solution
Methyl salicylate has six membered planar ring in which there are two side chains. One has hydroxyl group and another side chain has methyl ester group. Methoxy group is tetrahedral.
d)
Interpretation :
The oxygen atom must be found which is bonded to two carbon atoms. The reason forthe bond to be bent needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction :
Benting of bond takes place due to repulsion of electron pairs.
d)
Answer to Problem 5RE
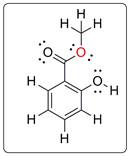
The oxygen shown in red is the one which is bonded with two carbon atoms. The bond is bent as there are two lone pairs on electrons. The lone pair-bond pair repulsion results in the bending of the bond.
Explanation of Solution
The oxygen shown in red has two bond pairs and two lone pairs. To minimise the repulsion among these electrons, the bond is bent.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
- Question 5: Name the following compound in two ways using side chain and using prefix amine (Common name and IUPAC name both) CH3NH2 CH3CH2NHCH3 CH₂CH₂N(CH3)2 Draw the structure of diethyl methyl amine Question 6. Write the balanced combustion reaction for: a. Hexane b. Propyne c. 2-pentene Question 7: Write the following electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: Hint: Use notes if you get confused a. Halogenation reaction: b. Nitration reaction : c. Sulphonation reaction: d. Alkylation reaction: e. Aceylation reaction:arrow_forwardQuestion 4. Name the following structures ○ CH3-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-CH3 Harrow_forwardA. Add Water to below compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) H₂C CH₂ CH, + H₂O-> ? Major product? Minor product? B. Add Bromine to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) CH₂ CH₂ + Br₂→ ? Major product and Minor product both are same in this? C. Add Hydrogen Bromide to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) H,C CH₂ CH₂ + HBr Major product? Minor product? D. Add Hydrogen to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) CH₂ CH₂ + H₂ Major product and Minor product both are same in this?arrow_forward
- 36) Complete the following multi-step reactions showing applications of enolate ions arising from ketones, esters, malonic ester, and keto ester, etc. (30 pts) (1) A NaOH, H₂O+ heat A NaOEt EtO OEt (11) EOH, H+ H. B LDA, H₂O+ -78°C B (i) NaOMe, Et-Br (ii) H₂O+, heat EtOOC (III) COOEt B A (i) NaOEt LiAlH 4-bromo-2-butene H₂O+ (ii) H3O+, heat Write the mechanism for Aldol Condensation (I A or B), and Claisen Condensation (II A).arrow_forward31) Complete two sets of reactions involving (R)-4-methyl-pent-2-ol producing racemic mixture of tertiary alcohols (D) and ketone derivative (C). Illustrate the mechanism of B and C or D. (25 pts) O OH 0 K2Cr2O7 Ph-CH2-Br, Mg, H2SO4 THF, H3O* (A) (D) Racemic mixture TsCl, Py (B) KCN, DMSO Ph-CH2-Br, Mg, THF, H3O+ (C) Mechanism for reactions B and C:arrow_forwardManoharan Mariappan, Ph.D., Dept. of Natur. Sci., NFC, Tallahassee, FL 33) Synthesize the aromatic compound containing para-substituted carbonyl compound starting from benzene. Illustrate the mechanism for reaction A. 1) NU (25 pts) A FeCl B (i) HNO3, H2SO4 (II) Sn, HCl(aq) NH₂ NO₂-D NH₂ (i) MeCO2Me, heat C (ii) K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 D (ii) SOCl2 (iii) 2 Et-NH2 Mechanism for reaction for the nitration of alkyl benzene (B-i): Characterize the product compound arising from the reaction D by IR and IH NMR spectral data: IR data (cm): 'H NMR data: Draw the structure and assign the chemical shift with the spin-splitting.arrow_forward
- Write structural formulas for the major products by doing addition reactions 1. You must add H2 as Pt is catalyst it does not take part in reactions only speed up the process H₂ CH2=CH-CH3 Pt 2. Add HCI break it into H and Cl CH3 HCI 3. Add Br2 only CC14 is catalyst CH3-CH=CH2 B12 CCl4 4. Add water to this and draw major product, H2SO4 is catalyst you have add water H20 in both the reaction below H₂SO4 CH3-CH=CH2 CH3 H2SO4/H₂O CH3-C=CH2 reflux ?arrow_forwardPlan the synthesis of the following compound using the starting material provided and any other reagents needed as long as carbon based reagents have 3 carbons or less. Either the retrosynthesis or the forward synthesis (mechanisms are not required but will be graded if provided) will be accepted if all necessary reagents and intermediates are shown (solvents and temperature requirements are not needed unless specifically involved in the reaction, i.e. DMSO in the Swern oxidation or heat in the KMnO4 oxidation). H Harrow_forwardHint These are benzene substitution reactions. ALCI3 and UV light are catalyst no part in reactions and triangle A means heating. A. Add ethyl for Et in benzene ring alkylation reaction EtCl = CH3CH2CL 1) EtC1 / AlCl3 / A ? B: Add Br to benzene ring ( substitution) 2) Br₂ / uv light ? C Add (CH3)2 CHCH2 in benzene ring ( substitution) (CH3)2CHCH,C1 / AICI, ?arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism to make the alcohol 2-hexanol. Draw the Mechanism to make the alcohol 1-hexanol.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with 1-pentanal in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forwardIdentify each chiral carbon as either R or S. Identify the overall carbohydrates as L or Darrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





