
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis dot symbol of Te, I, K, Bi, In and Pb must be drawn. These must also be arranged according to the group number in the periodic table.
Concept Introduction :
Lewis dot symbol is the
(a)
Answer to Problem 3E
Lewis dot symbols for all the given elements are drawn below.
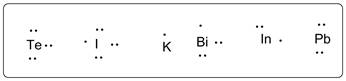
K (1), I (13), Pb (14), Bi (15) Te (16) I (17).
All the elements are arranged according to increasing group number.
Explanation of Solution
K, I, Pb, Bi, Te and I have 1, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 valence electrons respectively. The Lewis dot structures are shown as follows:
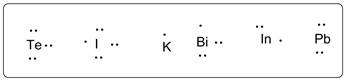
These belong to group 1, 13, 14, 15, 16 and 17 respectively. , all are arranged in increasing group number as follows:
K (1), I (13), Pb (14), Bi (15) Te (16) I (17).
Here, group number are in brackets.
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of covalent bonds each element would make must be determined.
Concept Introduction :
Number of covalent bonds depends on the valency of the element.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3E
K, In, Pb, Bi, Te and I will form 1, 3, 4, 3, 2, 1 covalent bonds respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Valency is equal to number of valence electrons (upto 4). When valence electrons are greater than 4 then valency is obtained by subtracting valence electrons from 8.
Thus valency for K, In and Pb are 1, 3 and 4 respectively as there are 1, 3, 4 valence electrons.
These will form 1, 3 and 4 covalent bonds respectively.
Bi, Te and I have 5, 6 and 7 valence electrons respectively. Thus valencies of these elements are 3, 2 and 1 respectively. So these will form 3, 2 and 1 covalent bond respectively.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
- What would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forward
- Please complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





