
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The shape of CF4 molecule needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure of an organic compound represents the bonding of atoms with lone pairs (if any). It indicates the bonds with atoms and also the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Hybridization of any atom indicates the molecular geometry of molecule. The formula to check the hybridization can be written as:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Answer to Problem 6E
With sp3 hybridization, the molecular shape must be tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
For Lewis structure of CF4 molecule, calculate total number of valence electrons:
CF4 molecule = 4 electrons in C + 4 × 7 valence electrons in F = 32 electrons
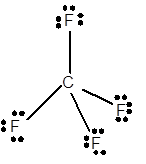
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Hybridization of C atom = 4 + 0 = 4 = sp3
Thus with sp3 hybridization, the molecular shape must be tetrahedral.
(b)
Interpretation:
The shape of NF3 molecule needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure of an organic compound represents the bonding of atoms with lone pairs (if any). It indicates the bonds with atoms and also the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Hybridization of any atom indicates the molecular geometry of molecule. The formula to check the hybridization can be written as:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Answer to Problem 6E
With sp3 hybridization, the molecular shape must be trigonal pyramidal.
Explanation of Solution
For Lewis structure of NF3 molecule, calculate total number of valence electrons:
NF3 molecule = 5 electrons in N + 3 × 7 valence electrons in F = 26 electrons
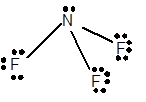
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Hybridization of N atom = 3 + 1 = 4 = sp3
Thus with sp3 hybridization, the molecular shape must be tetrahedral but due to presence of lone pair on central N atom, the geometry alters to trigonal pyramidal shape.
(c)
Interpretation:
The shape of H2Se molecule needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure of an organic compound represents the bonding of atoms with lone pairs (if any). It indicates the bonds with atoms and also the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Hybridization of any atom indicates the molecular geometry of molecule. The formula to check the hybridization can be written as:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Answer to Problem 6E
With sp3 hybridization, the molecular shape is bent or V-shape for molecule.
Explanation of Solution
For Lewis structure of H2Semolecule, calculate total number of valence electrons:
H2Se molecule = 6 electrons in Se + 1 × 2 valence electrons in H = 8 electrons
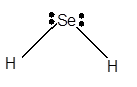
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Hybridization of Se atom = 2 + 2 = 4 = sp3
Thus with sp3 hybridization, the molecular shape must be tetrahedral but due to the presence of two lone pairs on the central Se atom, the geometry alters to a bent shape.
(d)
Interpretation:
The shape of H2CS molecule needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure of an organic compound represents the bonding of atoms with lone pairs (if any). It indicates the bonds with atoms and also the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Hybridization of any atom indicates the molecular geometry of molecule. The formula to check the hybridization can be written as:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Answer to Problem 6E
With sp2 hybridization, the molecular shape is trigonal planer for molecule.
Explanation of Solution
For Lewis structure of H2CS molecule, calculate total number of valence electrons:
H2CS molecule = 4 electrons in C + 1 × 2 valence electrons in H+6 electrons in S = 12 electrons
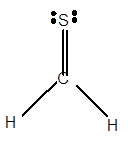
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pair
Hybridization of C atom = 3 + 0 = 3 = sp2
Thus with sp2 hybridization, the molecular shape must be trigonal planer.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
- 12. CH3 OH OH H&C CH3 H₂C N OH H₂C CH3 H&C CH3 H₂C' CH3 H.C CH3OH H.C CH2CH3OH CH3CEN Which one of these 17 compounds is represented by this IR and this 'H NMR spectrum? IR Spectrum 3000 4000 3000 NMR Spectrum 2000 £500 RAVENUMBER 2000 1500 9 8 6 5 10 HP-00-290 ppm m 1000 500 1000 4 °arrow_forwardDraw the structure of (E,6R) 6-methoxy-4-hepten-2-one. Give the IUPAC name of this compound, including stereochemistry. Draw the most stable chair conformation of (cis) 1,3-isobutylcyclohexane. H HC=CCH₂ CH2CH3 EN(CH3)2 -CN(CH3)2arrow_forward10. Write out the mechanism (intermediate/transition state) for this reaction; indicate stereochemistry in product. H3C CH₂OH CH3 SN1 Harrow_forward
- Write "most" under the member of each trio which is most stable. Write "least under the member of each trio which is least stable. b) Draw a Fischer projection of a pair of enantiomers with three chiral carbons. Which of these two would you expect to be more soluble in water? Why? 1-butanol 1-heptanol Which of these two would you expect to have the higher boiling point? Why? hexyl methyl ether 1-heptanolarrow_forwardWrite "most" under the most acidic compound. Write "least" under the least acidic compound. OH NO₂ OCH3 Br 9. Compound X, C50H84F2, reacts with excess H2/Pd to give a C50H88F2 compound. How many rings are in X? How many double bonds are in X? Show your work.arrow_forward4. State whether these two are: a) the same molecule b) c) d) different compounds that are not isomers constitutional isomers diastereomers e) enantiomers CH3 CH₁₂ H OH HO H H OH HO H CH, CH₂ 5. a) How many stereocenters does this compound have? b) How many stereoisomers are possible for this compound? CH₂ OH CHCHarrow_forward
- Calculating the pH at equivalence of a titration A chemist titrates 210.0 mL of a 0.1003 M hydrobromic acid (HBr) solution with 0.7550M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = ] ☑ o0o 18 Ararrow_forwardDo you do chemistry assignmentsarrow_forwardUsing the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A This reaction is always spontaneous, but proceeds slower at temperatures above 120. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 117. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) This reaction is slower below 20. °C than C above. AS is |(pick one) ? 18 Ar 1arrow_forward
- Calculating the pH at equivalence of a titration Try Again Your answer is incorrect. 0/5 a A chemist titrates 70.0 mL of a 0.7089 M hydrocyanic acid (HCN) solution with 0.4574M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK of hydrocyanic acid is 9.21. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = 11.43] G 00. 18 Ar B•arrow_forwardBiological Macromolecules Naming and drawing the products of aldose oxidation and reduction aw a Fischer projection of the molecule that would produce L-ribonic acid if it were subjected to mildly oxidizing reaction conditions. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X AP ‡ 1/5 Naor Explanation Check McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibilarrow_forward● Biological Macromolecules Identifying the parts of a disaccharide Take a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH O H H H OH OH OH H H CH2OH H O OH H OH H H H H OH Is this a reducing sugar? Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. Explanation Check O yes X O no ○ yes O no Uarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





