
Concept explainers
A refrigerator door has a height and width of
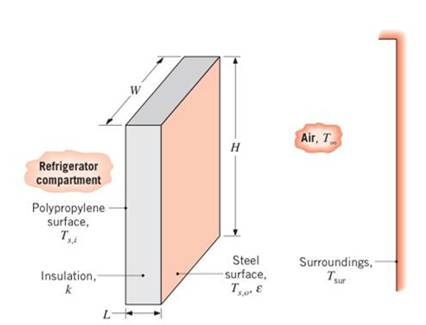
(a) Estimate the heat gain through the door for the worst case condition corresponding to no insulation
(b) Compute and plot the heat gain and the outer surface temperature
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Modern Database Management
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
- I need solve without AI and chatgptarrow_forwardAn ordinary egg can be approximated as a 5.5-cm-diameter sphere. The egg is initially at a uniform temperature of 8°C and is dropped into boiling water at 97°C. Taking the properties of the egg to be ρ = 1020 kg/m3 and cp = 3.32 kJ/kg·°C, determine how much heat is transferred to the egg by the time the average temperature of the egg rises to 82°C. The heat transferred to the egg in this case is kJ.arrow_forwardShip construction question. Sketch and describe the forward arrangements of a ship. Include componets of the structure and a explanation of each part/ term.arrow_forward
- 1.7 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.23 using two beam elements. A. E. I constant M₂ T + FIGURE 1.23 A fixed-pinned beam subjected to a momentarrow_forward42 PART 1 Introduction A. E. I constant FIGURE 1.22 A fixed-pinned beam. 1.6 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.22 using two beam elements.arrow_forward1.4 Using a one-beam element idealization, find the stress distribution under a load of P for the uniform cantilever beam shown in Fig. 1.20. A, E, I constant L FIGURE 1.20 A uniform cantilever beamarrow_forward
- Mechanical engineering,FBD required.arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardPlease Please use MATLAB with codes and graph. Recreate the following four Figures of the textbook using MATLAB and the appropriate parameters. Comment on your observations for each Figure. List all of the parameters that you have used. The figure is attached below.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





