
A water bath is used to maintain canisters containing experimental biological reactions at a uniform temperature of 37°C. The top of the bath has a width and length of 0.25m and 0.50 m, respectively, and is uncovered to allow easy access for removal or insertion of the canisters. The bath is located in a draft-free laboratory with air at atmospheric pressure, a temperature of 20°C, and a relative humidity of 60%. The walls of the laboratory are at a uniform temperature of 25°C. 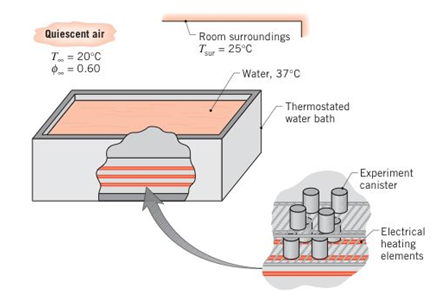
(a) Estimate the heat loss from the surface of the bath by radiation exchange with the surroundings.
(b) Calculate the Grashof number using Equation 9.65, which can be applied to natural convection flows driven by temperature and concentration gradients. Use a characteristic length L that is appropriate for the exposed surface of the water bath.
(c) Estimate the free convection heat transfer coefficient using the result for
(d) Invoke the heat and
(e) Calculate the total heat loss from the surface, and compare the relative contributions of the sensible, latent, and radiative effects. Review the assumptions made in your analysis, especially those relating to the heat and mass transfer analogy.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Experiencing MIS
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
- 1.7 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.23 using two beam elements. A. E. I constant M₂ T + FIGURE 1.23 A fixed-pinned beam subjected to a momentarrow_forward42 PART 1 Introduction A. E. I constant FIGURE 1.22 A fixed-pinned beam. 1.6 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.22 using two beam elements.arrow_forward1.4 Using a one-beam element idealization, find the stress distribution under a load of P for the uniform cantilever beam shown in Fig. 1.20. A, E, I constant L FIGURE 1.20 A uniform cantilever beamarrow_forward
- Mechanical engineering,FBD required.arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardPlease Please use MATLAB with codes and graph. Recreate the following four Figures of the textbook using MATLAB and the appropriate parameters. Comment on your observations for each Figure. List all of the parameters that you have used. The figure is attached below.arrow_forward
- Please only step 6 (last time I asked it was cut off at that point)arrow_forwardPlease Please use a MATLAB with codes and grap. Recreate the following four Figures of the textbook using MATLAB and the appropriate parameters. Comment on your observations for each Figure. List all of the parameters that you have used. The figure attached below.arrow_forwardI REPEAT!!!!! I NEED HANDDRAWING!!!!! NOT A USELESS EXPLANATION!!!! I REPEAT SUBMIT A HANDDRAWING IF YOU CANNOT UNDERSTAND THIS SKIP IT ! I need the real handdrawing complete it by adding these : Pneumatic Valves Each linear actuator must be controlled by a directional control valve (DCV) (e.g., 5/2 or 4/2 valve). The bi-directional motor requires a reversible valve to change rotation direction. Pressure Regulators & Air Supply Include two pressure regulators as per the assignment requirement. Show the main compressed air supply line connecting all components. Limit Switches & Safety Features Attach limit switches to each actuator to detect positions. Implement a two-handed push-button safety system to control actuator movement. Connections Between Components Draw air supply lines linking the compressor, valves, and actuators. Clearly label all inputs and outputs for better understanding.arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
