
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Heating curve of water must be drawn to show the different stages when water is heated from 10°C to 120°C.
Concept Introduction:
Heating curve is the graphical representation of phase change when a substance is heated.
Freezing point and boiling point of water is 0°C and 100°C respectively.
(a)
Answer to Problem C18.8RE
Heating curve is shown below.
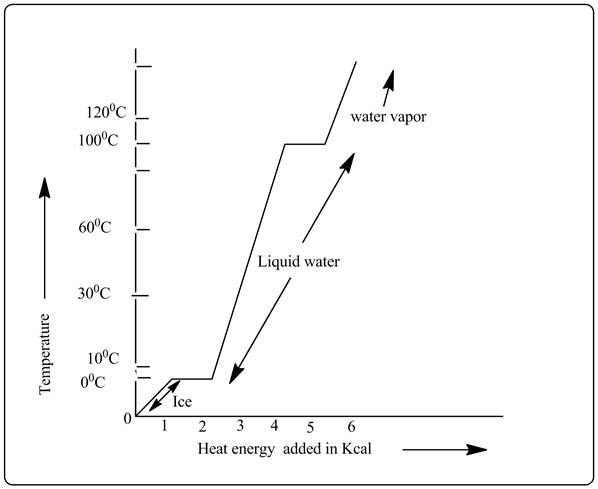
Explanation of Solution
In the heating curve it is shown that when water is heated from 10°C then at 100°C the phase changes from liquid water to water vapor and this is the boiling point. Then temperature is again increasing from 100°C to 120°C when further heat is given.
b)
Interpretation:
Amount of heat energy must be calculated which is transferred to water when the temperature is increased from 10°C to 120°C.
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy can be determined as follows:
Here m, s and t are mass, specific heat and temperature change respectively.
b)
Answer to Problem C18.8RE
Heat energy is 5500 cal.
Explanation of Solution
Initial temperature of water is 10°C and final temperature is 120°C. So temperature increase t=110°C. Specific heat(s) of water is 1cal/g.
Mass of the given water is 50 g.
Thus heat required to increase the temperature from 10°C to 120°C can be calculated as follows:
c)
Interpretation:
Which part of the heating process involves most heat transfer must be found from the calculation and heating curve.
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required for the increase of temperature (t) of mass in grams of any substance with specific heat s can be written as follow:
c)
Answer to Problem C18.8RE
Heating of water from 10°C to 100°C involves most heat transfer.
Explanation of Solution
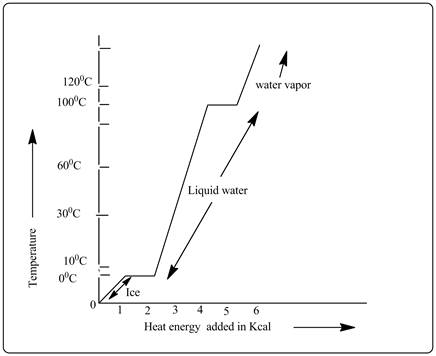
From the heating curve, it is clear that liquid water portion needs more heat as the graph is steeply rising.
The heat energy required for the increase of temperature of 50 g water from 10°C to 100°C
The heat energy required for the increase of temperature of 50 g water vapor from 100°C to 120°C
Chapter U5 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- In this question, the product of the aldol condensation is shown. What would be the reactants for this product? Please provide a detailed explanation, as well as a drawing showing how the reactants will react to produce the product.arrow_forward7. Propene undergoes a hydration reaction with water in the presence of an acid. a. There are two possible products for this reaction, both with the formula C,H,O. Show their structural formulas and names. (A1, B2) SCH4UR Name: (answer for part a. here!) VER 3 2021-2022 b. Which of the two products do you predict will form. Explain your choice using details from your learning. (B3)arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following organic reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forward
- What are the major products of the following reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following organic reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardPredict the organic product that forms in the reaction below: H + гон OH H+ H+ ☑ O Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the product. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic product X. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forward
- In the analysis of Mg content in a 25 mL sample, a titration volume of 5 mL was obtained using 0.01 M EDTA. Calculate the Mg content in the sample if the Ca content is 20 ppmarrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below: H. H+ + OH H+ Y Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the products. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G X C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Access +arrow_forward111 Carbonyl Chem Choosing reagants for a Wittig reaction What would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 3 1 2 2. n-BuLi • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





