
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The heat of the reaction on each diagram is to be labeled.
Concept introduction:When a reaction occurs, some bond formed and some bonds are broken. Every reaction goes through the intermediate stage. The intermediate is very unstable and therefore have highest energy.The diagram which represents the relative energy of reactant, product, and transition state is termed as energy diagram.
(a)
Answer to Problem 5E
The heat of the reaction
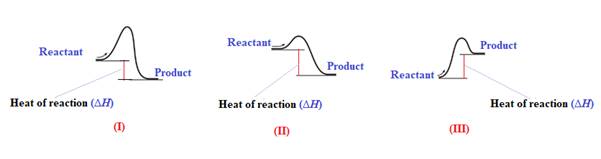
Explanation of Solution
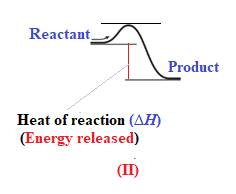
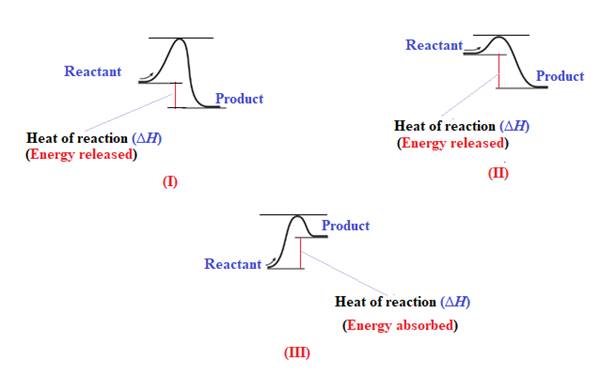
The given energy diagram is shown below:
The heat of a reaction
(b)
Interpretation: The activation energy on each diagram is to be labeled.
Concept introduction: When a reaction occurs, some bond formed and some bonds are broken. Every reaction goes through the intermediate stage. The intermediate is very unstable and therefore have highest energy. The diagram which represents the relative energy of reactant, product, and transition state is termed as energy diagram.
(b)
Answer to Problem 5E
The activation energy
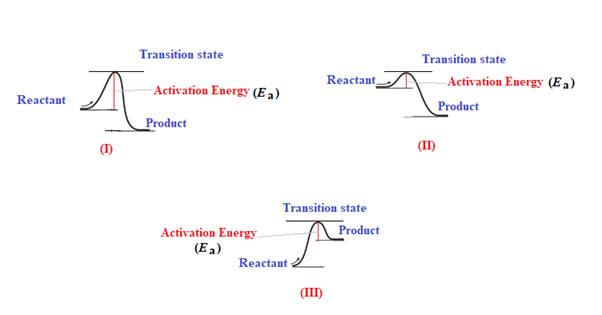
Explanation of Solution
The given energy diagram is shown below:
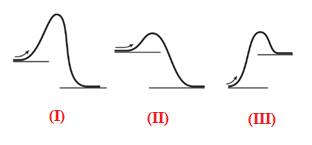
The energy required to reach a reactant to its transition state is termed as activation energy
(c)
Interpretation: The diagram which represents the most exothermic reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: When a reaction occurs, some bond formed and some bonds are broken. Every reaction goes through the intermediate stage. The intermediate is very unstable and therefore have highest energy. The diagram which represents the relative energy of reactant, product, and transition state is termed as energy diagram.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5E
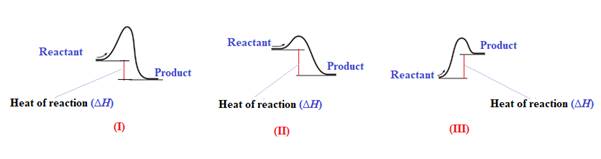
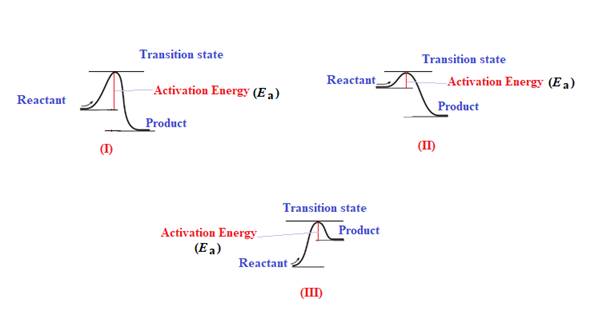
The diagram which represents the most exothermic reaction is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The given energy diagram is shown below:
The reaction in which the energy of the product is less than the energy of reactant is termed as exothermic reaction. In an exothermic reaction, energy releases.In diagram (I) and (II), the energy of energy of the product is less than the energy of reactant. Therefore, diagram (I) and (II)represents exothermic reaction as shown below:
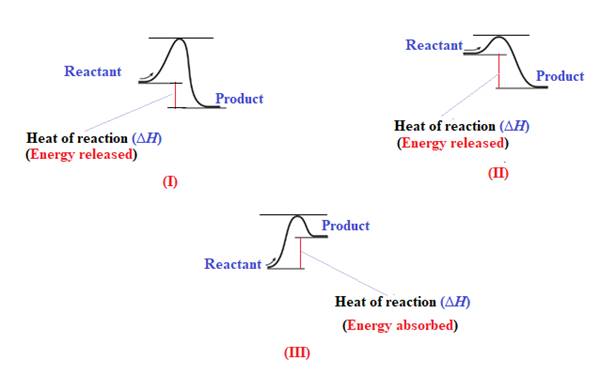
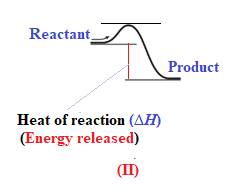
In diagram (II), the difference in the energy is more. Therefore, diagram (II) represents most exothermic reaction as shown below:
(d)
Interpretation: The reaction which requires energy to get started is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: When a reaction occurs, some bond formed and some bonds are broken. Every reaction goes through the intermediate stage. The intermediate is very unstable and therefore have highest energy. The diagram which represents the relative energy of reactant, product, and transition state is termed as energy diagram.
(d)
Answer to Problem 5E
Endothermic reaction requires energy to get started. Diagram (III) represents the endothermic reaction as shown below:
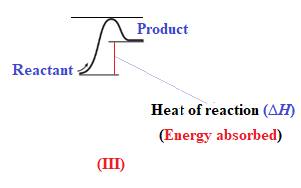
Explanation of Solution
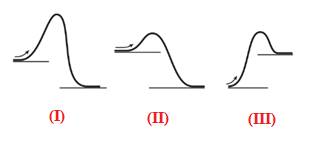
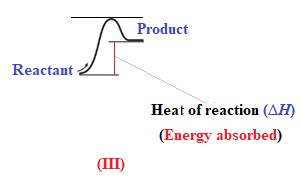
The given energy diagram is shown below:
The reaction in which the energy of the product is more than the energy of reactant is termed as endothermic reaction. In an endothermic reaction, energy absorbs. In diagram (III), the energy of energy of the product is more than the energy of reactant. Therefore, diagram (III) represents an endothermic reaction as shown below:
It is known that endothermic reaction requires energy to get started. Therefore, diagram (III) is represents the endothermic reaction as shown below:
Chapter U5 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- Which of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forwardDraw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
- Draw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forwardWhat is the unsaturation number for compounds with the formula C₂H₁₂Cl₂? O õ õ o o 4 3arrow_forwardIndicate the product obtained (formula). F3C. CF3 Br NH2 NH OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





