
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The ray model, wave model and photon model of light needs to be explained. The sketch for each model also needs to be drawn showing transmission through a thin red film of plastic.
Concept introduction:
The optical phenomena can be explained with the help of three important models. These are based on three different ways of describing the
Explanation of Solution
A ray model of light represents light as a ray travelling in the straight path. The direction of this ray can be changed when obstacles is placed in its path otherwise it always travel in straight path.
The ray model of the light is represented as follows:
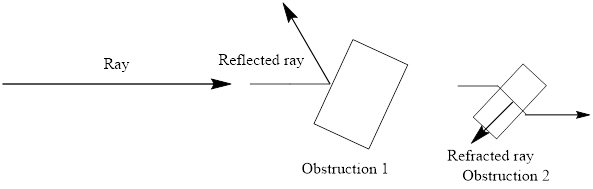
Ray model of light
The reflected ray is the light ray which gets reflect by the surface of medium during transmission. Here, refracted ray is the ray which transmitted to the second medium and the direction will be different from the incident ray.
The wave model of light explains that light travels as a wave. According to this model, when a wave is passed through an opening, it spreads out. The spreading of wave depends on its wavelength. The short wavelength waves spread out little but long wavelength waves spread out more.
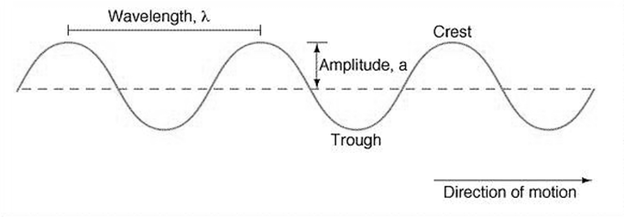
Wave model of light
In the above wave model, wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crest or trough, frequency in the number of times a wave passes through a point in 1 second, amplitude is the height of crest or trough in a wave or it is the maximum distance moved by a point in the vibrating body.
It does not explain the
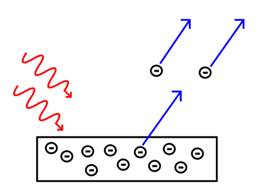
Photon model of light
According to Einstein, light travels in the form of discrete packets known as photons with energy.
Here,
Where, h is Planck’s constant and
Chapter U5 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- First image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in those conditions. Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in these conditions Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardHelp fix my arrows pleasearrow_forward
- Provide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





