
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The type of the light source needed for the spectrometer needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The observed light is always complementary to the color of the light absorbed by it.
Explanation of Solution
To determine the concentration of solution using spectrometer, the source of light are generally Tungsten filament with wavelength range 300-2500 nm, xenon arc lamb with wavelength range 160-2000 nm, deuterium arc lamp with wavelength range 190-400 nm and light emitting diodes for visible wavelengths (360-950 nm).
Since, the given solution is red color with wavelength range 640-700 nm.
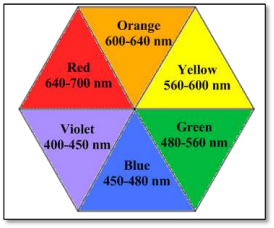
The observed light is always complementary to the color of the light absorbed by it. From the color wheel, the color of light complementary to red is green. Thus, red solution absorbs in the wavelength range of 480-560 nm. The wavelength of red light that is 640-700 nm is transmitted by the red solution.
Thus, the solution absorbs the wavelength range of 480-560 nm (green light) and the light source used can be tungsten filament with range 300-2500 nm. Light emitting diodes can also be used with wavelength range 360-950 nm.
(b)
Interpretation:
The placement of light source, the detector and the sample needs to be sketched. The path of the light should be shown in the drawing.
Concept introduction:
A spectrometer is used to determine the amount of light a sample can absorb.
Explanation of Solution
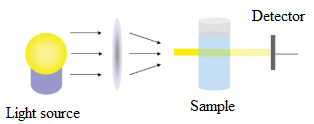
In the spectrometer, the main components are light source, detector and sample.
The light from the source first falls on the sample solution and detector is placed after the sample to obtain the results.
The sketch can be drawn as follows:
(c)
Interpretation:
The observation for the two different solutions needs to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
A spectrometer is used to determine the amount of light a sample can absorb.
Explanation of Solution
If the two solutions are different, the
The intensity of light absorbed by two different solutions will be different. Also, depending on the range of the wavelength of transmitted light different detectors are used.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether a UV-sensitive paper can be used for the detector or not needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
In the spectrometer, detector is used show the presence or absence of spectrum which is extracted for different type of elements present in the sample. The intensity of the spectrum is also measured by detector.
Explanation of Solution
The wavelength range for UV light is 100-400 nm since, the wavelength of red light which is transmitted by the solution is 640-700 nm which is not in UV range thus, UV sensitive paper cannot be used for the detector. Due to difference in wavelength range, UV sensitive paper cannot detect the light transmitted by red color solution.
Chapter U5 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- Iarrow_forwardDraw the anti-Markovnikov product of the hydration of this alkene. this problem. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for esc esc ☐ Explanation Check F1 1 2 F2 # 3 F3 + $ 14 × 1. BH THE BH3 2. H O NaOH '2 2' Click and drag to start drawing a structure. F4 Q W E R A S D % 905 LL F5 F6 F7 © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility < & 6 7 27 8 T Y U G H I F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 9 0 J K L P + // command option Z X C V B N M H H rol option commandarrow_forwardAG/F-2° V 3. Before proceeding with this problem you may want to glance at p. 466 of your textbook where various oxo-phosphorus derivatives and their oxidation states are summarized. Shown below are Latimer diagrams for phosphorus at pH values at 0 and 14: -0.93 +0.38 -0.50 -0.51 -0.06 H3PO4 →H4P206 →H3PO3 →→H3PO₂ → P → PH3 Acidic solution Basic solution -0.28 -0.50 3--1.12 -1.57 -2.05 -0.89 PO HPO H₂PO₂ →P → PH3 -1.73 a) Under acidic conditions, H3PO4 can be reduced into H3PO3 directly (-0.28V), or via the formation and reduction of H4P206 (-0.93/+0.38V). Calculate the values of AG's for both processes; comment. (3 points) 0.5 PH P 0.0 -0.5 -1.0- -1.5- -2.0 H.PO, -2.3+ -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 2 H,PO, b) Frost diagram for phosphorus under acidic conditions is shown. Identify possible disproportionation and comproportionation processes; write out chemical equations describing them. (2 points) H,PO 4 S Oxidation stale, Narrow_forward
- 4. For the following complexes, draw the structures and give a d-electron count of the metal: a) Tris(acetylacetonato)iron(III) b) Hexabromoplatinate(2-) c) Potassium diamminetetrabromocobaltate(III) (6 points)arrow_forward2. Calculate the overall formation constant for [Fe(CN)6]³, given that the overall formation constant for [Fe(CN)6] 4 is ~1032, and that: Fe3+ (aq) + e = Fe²+ (aq) E° = +0.77 V [Fe(CN)6]³ (aq) + e¯ = [Fe(CN)6] (aq) E° = +0.36 V (4 points)arrow_forward5. Consider the compounds shown below as ligands in coordination chemistry and identify their denticity; comment on their ability to form chelate complexes. (6 points) N N A B N N N IN N Carrow_forward
- 1. Use standard reduction potentials to rationalize quantitatively why: (6 points) (a) Al liberates H2 from dilute HCl, but Ag does not; (b) Cl2 liberates Br2 from aqueous KBr solution, but does not liberate C12 from aqueous KCl solution; c) a method of growing Ag crystals is to immerse a zinc foil in an aqueous solution of AgNO3.arrow_forwardWhat would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1 1. PPh3 2. n-BuLi 3 2 • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant R in this organic reaction? N N H3O+ +R + • Draw the structure of R in the drawing area below. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if it's necessary to draw one particular enantiomer. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. fmarrow_forward
- The product on the right-hand side of this reaction can be prepared from two organic reactants, under the conditions shown above and below the arrow. Draw 1 and 2 below, in any arrangement you like. 1+2 NaBH3CN H+ N Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 5arrow_forwardAssign this HSQC Spectrum ( please editing clearly on the image)arrow_forward(a 4 shows scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of extruded actions of packing bed for two capillary columns of different diameters, al 750 (bottom image) and b) 30-μm-i.d. Both columns are packed with the same stationary phase, spherical particles with 1-um diameter. A) When the columns were prepared, the figure shows that the column with the larger diameter has more packing irregularities. Explain this observation. B) Predict what affect this should have on band broadening and discuss your prediction using the van Deemter terms. C) Does this figure support your explanations in application question 33? Explain why or why not and make any changes in your answers in light of this figure. Figure 4 SEM images of sections of packed columns for a) 750 and b) 30-um-i.d. capillary columns.³arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





