
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure, molecular shape, bond angle and hybrid orbitals in
Concept introduction:
VSEPR theory stands for Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory. It helps to predict the molecular shape or geometry of the molecule with the help of the number of bond pairs or lone pairs present in it.
According to the VSEPR theory, the presence of lone pair on the central atom of a molecule causes deviation from standard molecular geometry. Thus, valence electrons provide a Lewis structure, which gives an idea about electron pair geometry and hybridization.
Answer to Problem 67SSC
| Lewis structure | molecular shape, | bond angle | hybrid orbitals | |
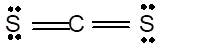 |
Linear | 180° | sp hybrid orbitals | |
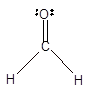 |
Trigonal planer | 120° | sp2 hybrid orbitals | |
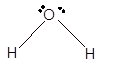 |
Bent | 104° | sp3 hybrid orbitals | |
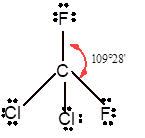 |
Tetrahedral | 109° | sp3 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Pyramid | 107° | sp3 hybrid orbitals |
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
In the
Number of valence electron = Number of atom C (valence electron in C) + Number of atom S (valence electron in S) =
Hence the Lewis structure must be:
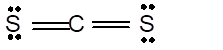
Geometry = Linear, bond angle = 180°
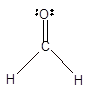
In the
Number of valence electron = Number of atom C (valence electron in C) + Number of atom O (valence electron in O)+ Number of atom H (valence electron in H) =
Hence the Lewis structure must be:
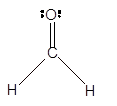
Geometry = Trigonal planer, bond angle = 120°
In the
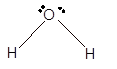
Number of valence electron = Number of atom O (valence electron in O) + Number of atom H (valence electron in H) =
Hence the Lewis structure must be:
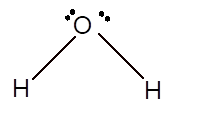
Geometry = bent, bond angle = 104°
In
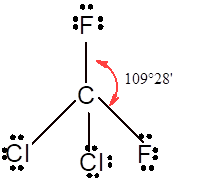
In the
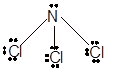
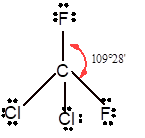
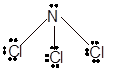
Number of valence electron = Number of atom P (valence electron in P) + Number of atom Cl (valence electron in Cl) =
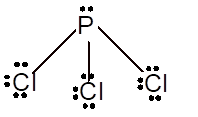
With sp3 hybridization, the geometry must be tetrahedral but the presence of one lone pair on central P atom alters the standard geometry of molecule to pyramid shape due to repulsion between lone pair and bond pair of the molecule.
Thus,
| Lewis structure | molecular shape, | bond angle | hybrid orbitals | |
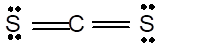 |
Linear | 180° | sp hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Trigonal planer | 120° | sp2 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Bent | 104° | sp3 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Tetrahedral | 109° | sp3 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Pyramid | 107° | sp3 hybrid orbitals |
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardFirst image: Why can't the molecule C be formed in those conditions Second image: Synthesis for lactone C its not an examarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion Second image: I have to show the mecanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primaryarrow_forward
- First image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in those conditions. Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in these conditions Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardHelp fix my arrows pleasearrow_forward
- Provide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





