
Interpretation:
The pairs of elements that would form an ionic bond are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The ability of an atom to attract electrons in a
Answer to Problem 4STP
The pair of elements having
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct option: Let’s assume a bond is formed between two elements A and B. For a bond to be ionic, the electro negativity difference (Δε) between A and B should be greater than 1.7.
The given graph is shown below.
From graph, the electronegativy value of element having atomic number 8 is 3.5 and the electronegativy value of element having atomic number 12 is 1.25. The corresponding graph is shown below.
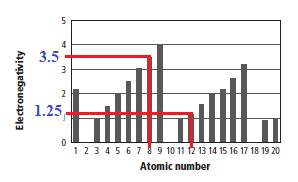
The electro negativity difference (Δε) is calculated as shown below.
The electro negativity difference (Δε) is 2.25 which is greater than 1.7. Therefore, the pair of elements having atomic number 8 and atomic number 12 would form an ionic bond. Therefore, option (D) is the correct option.
Reason for incorrect option: The electro negativity difference (Δε) between elements having atomic number 3 and 5 is 0.50. So, A is incorrect option.
The electro negativity difference (Δε) between elements having atomic number 7 and 8 is 0.50. So, B is incorrect option.
The electro negativity difference (Δε) between elements having atomic number 4 and 18 is 1.50. So, C is incorrect option.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
- These are in the wrong boxes. Why does the one on the left have a lower molar mass than the one on the right?arrow_forwardSYNTHESIS REACTIONS. For the following reactions, synthesize the given products from the given reactants. Multiple reactions/steps will be needed. For the one of the steps (ie reactions) in each synthesis, write out the mechanism for that reaction and draw an energy diagram showing the correct number of hills and valleys for that step's mechanism. CI b. a. Use acetylene (ethyne) and any alkyl halide as your starting materials Br C. d. "OH OH III. OHarrow_forwardCalculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.200 M HClarrow_forward
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forward
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





