
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Selenium is a 16th group element which has 6 valence electrons and fluorine is a 17th group element which has 7 valence electrons.
Total valence electrons = 6 + 2×7
= 6 + 14
= 20
Therefore; the total valence electron is 20.
The Lewis dot structure of SeF2 is shown below:
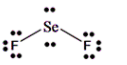
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Chlorine is a 17th group element which has 7 valence electrons and oxygen is a 16th group element which has 6 valence electrons.
Total valence electrons = 7 + 2×6 + 1
= 20
Therefore; the total valence electrons is 20.
The Lewis dot structure is shown below:
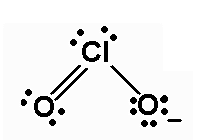
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Phosphorus is a 15th group element which has 5 valence electrons and oxygen is a 16th group element which has 6 valence electrons.
The total number of valence electrons = 5 + 3(6) + 3 = 26
Therefore; the total valence electron is 20
The Lewis dot structure is shown below:
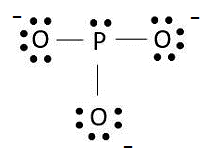
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Phosphorus is a 15th group element which has 5 valence electrons and oxygen is a 16th group element which has 6 valence electron and chlorine is a 17th group element which has 7 valence electrons.
Total number of valence electrons = 5 + 6 + 3(7)
= 5+ 6+ 21
= 32
Therefore; the total valence electron is 32
The Lewis dot structure is shown below:
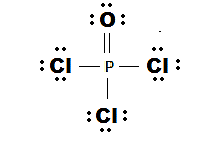
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
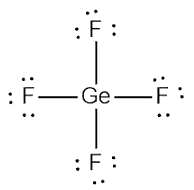
Germanium is a 14th group element which has 4 valence electrons and fluorine is a 17th group element which has 7 valence electrons.
The total valence electron = 4+ 4(7)
= 4 + 28
= 32
Therefore; the total valence electron is 32
The Lewis dot structure is shown below:
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- Is this aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardOn what basis are Na and Nb ranked against each other?arrow_forwardStep 1: add a curved arrow. Select Draw Templates More / " C H Br 0 Br : :o: Erase H H H H Q2Q Step 2: Draw the intermediates and a curved arrow. Select Draw Templates More MacBook Air / " C H Br 0 9 Q Erase 2Qarrow_forward
- O Macmillan Learning Question 23 of 26 > Stacked Step 7: Check your work. Does your synthesis strategy give a substitution reaction with the expected regiochemistry and stereochemistry? Draw the expected product of the forward reaction. - - CN DMF MacBook Air Clearly show stereochemistry. Questionarrow_forwardNH2 1. CH3–MgCl 2. H3O+ ? As the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule with a new C - C bond as its major product: If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If the major products of this reaction won't have a new C - C bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. This reaction will not make a product with a new C - C bond. Х ☐: Carrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction. If there will be no major products, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. : + Х è OH K Cr O 2 27 2 4' 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Laminar compounds are characterized by havinga) a high value of the internal surface of the solid.b) a high adsorption potential.arrow_forwardIntercalation compounds have their sheetsa) negatively charged.b) positively charged.arrow_forwardIndicate whether the following two statements are correct or not:- Polythiazine, formed by N and S, does not conduct electricity- Carbon can have a specific surface area of 3000 m2/garrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





