
Interpretation:
The Lewis structures of SF4 and SF6 molecules needs to be determined by interpreting the polarity.
Concept introduction:
The Lewis structure of an organic compound represents the bonding of atoms with lone pairs (if any). It indicates the bonds with atoms and also arrangement of atoms in molecule. The polarity of molecule can be determined by the arrangements of bonded atoms in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 77SSC
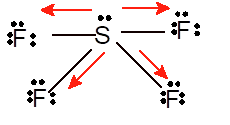
Polar molecule
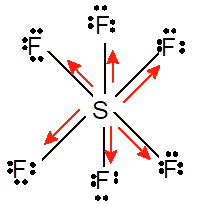
Non-polar molecule
Explanation of Solution
In the SF4 molecule, Satom contains 6 valence electrons and F has 7 valence electrons. The total number of valence electron can be determined in it as follows:
Number of valence electron = Number of atom S (valence electron in S) + Number of atom F (valence electron in F) =
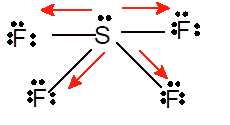
Hence the Lewis structure must be:
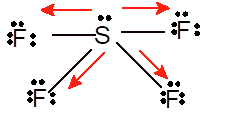
Since the standard geometry must be trigonal bipyramid yet the geometry changes to see-saw due to presence of one lone pair on S atom.
Since the polarity directions are towards F atom therefore overall it is a polar molecule.
In the SF6 molecule, S atom contains 6 valence electrons, and F has 7 valence electrons. The total number of valence electron can be determined in it as follows:
Number of valence electron = Number of atom S (valence electron in S) + Number of atom F (valence electron in F) =
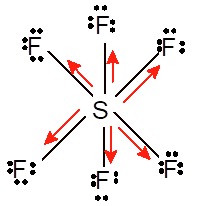
Hence the Lewis structure must be:
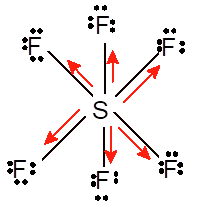
Due to symmetrical structure of molecule it is non-polar molecule.
Thus,
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- 3. Synthesize the following synthon from the indicated starting material. i HO.arrow_forwardIdentifying the stereochemistry of natural Write the complete common (not IUPAC) name of each molecule below. Note: if a molecule is one of a pair of enantiomers, be sure you start its name with D- or L- so we know which enantiomer it is. molecule H O-C-CH2 H3N. HN N H C=O common name (not the IUPAC name) NH3 ☐ H3N H ☐ CH2 Xarrow_forward> Draw the structure of alanine at pH 1.2. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Understanding the general acid-base properties of amino acids O Proteins Imagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule The solution is... 010 H3N-CH-C-OH CH HO CH3 O acidic O basic neutral O (unknown) H3N HO 0 O acidic O basic neutral ○ (unknown) H3N-CH-C-O CH2 CH3-CH-CH3 O acidic O basic Oneutral ○ (unknown) O= X H2N-CH-C-O CH3 CH CH3 acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) ? 000arrow_forwardImagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule 0=0 H3N-CH-C-o HO CH2 OH The solution is... O acidic O basic O neutral O (unknown) H₂N acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) + H3N O OH O acidic O basic O neutral O (unknown) H2N-CH-C-O CH3 O acidic O basic neutral ○ (unknown) X ? olo HEarrow_forwardRecognizing ampli Draw an a amino acid with a methyl (-CH3) side chain. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Carrow_forward
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure name × HO OH ☐ OH CI CI O CI OH OHarrow_forwardく Check the box under each a amino acid. If there are no a amino acids at all, check the "none of them" box under the table. Note for advanced students: don't assume every amino acid shown must be found in nature. COO H3N-C-H CH2 HO CH3 NH3 O CH3-CH CH2 OH Onone of them Explanation Check + H3N O 0. O OH + NH3 CH2 CH3-CH H2N C-COOH H O HIC + C=O H3N-C-O CH3- - CH CH2 OH Х 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure HO-C-CH2-CH3 O -OH CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-C-OH CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-C-OH Explanation Check S namearrow_forward
- theres 2 productsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this solvolysis reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + CH3CH2OH Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OCH2CH3 || OEt Charges OH 00-> | Undo Reset | Br Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. CH3CO2Na CH3CO2H Drawing + Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OAC Charges OH ОАс Na ဂ Br Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





