
Concept explainers
(a)
To check: The ordered pair
(a)
Answer to Problem 22AYU
Not function
Explanation of Solution
Given: A marketing firm wishes to find a function that relates the sales S of a product and A , the amount spent on advertising the product. The data are obtained from past experience. Advertising and sales are measured in thousands of dollars.
The ordered pair
So, Independent variable is
From table, Two same input get two different output.
Therefore, above table doesn’t represent function.
(b)
To draw: The
(b)
Answer to Problem 22AYU
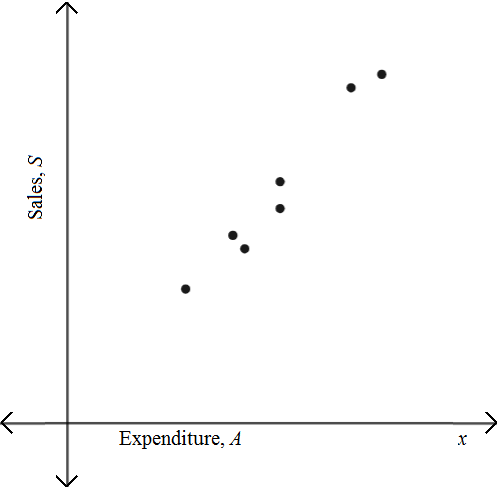
Explanation of Solution
Given: A marketing firm wishes to find a function that relates the sales S of a product and A , the amount spent on advertising the product. The data are obtained from past experience. Advertising and sales are measured in thousands of dollars.
Using graphing utility to draw scatter plot.
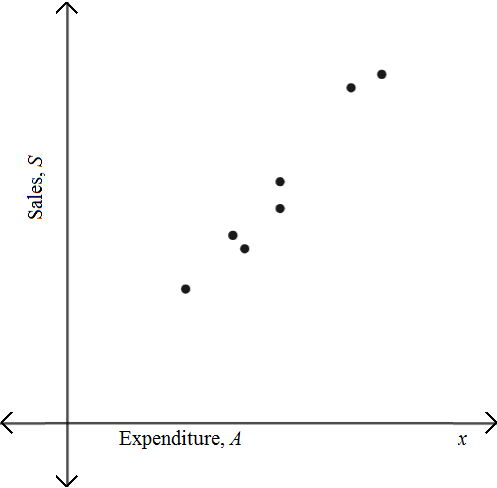
(c)
To find: The line of best fit that models the relation between expenditures and sales.
(c)
Answer to Problem 22AYU
Explanation of Solution
Given: A marketing firm wishes to find a function that relates the sales S of a product and A , the amount spent on advertising the product. The data are obtained from past experience. Advertising and sales are measured in thousands of dollars.
Using graphing utility, the equation of line of best fit.
(d)
To find: The slope of line of best fit.
(d)
Answer to Problem 22AYU
Explanation of Solution
Given: A marketing firm wishes to find a function that relates the sales S of a product and A , the amount spent on advertising the product. The data are obtained from past experience. Advertising and sales are measured in thousands of dollars.
Using graphing utility, the equation of line of best fit.
Slope is coefficient of x.
Therefore, the slope is 2.067
(e)
To express: The relationship from part (c) using function notation.
(e)
Answer to Problem 22AYU
Explanation of Solution
Given: A marketing firm wishes to find a function that relates the sales S of a product and A , the amount spent on advertising the product. The data are obtained from past experience. Advertising and sales are measured in thousands of dollars.
Using graphing utility, the equation of line of best fit.
Now, write as function form.
Therefore,
Where, A represents expenditure and S represent sales.
(f)
To find: The domain of function.
(f)
Answer to Problem 22AYU
Explanation of Solution
Given: A marketing firm wishes to find a function that relates the sales S of a product and A , the amount spent on advertising the product. The data are obtained from past experience. Advertising and sales are measured in thousands of dollars.
Using graphing utility, the equation of line of best fit.
Now, write as function form.
Therefore,
Where, A represents expenditure and S represent sales.
The domain depends on the input value of A .
(g)
To predict: The sales for expenditures are $25,000.
(g)
Answer to Problem 22AYU
Explanation of Solution
Given: A marketing firm wishes to find a function that relates the sales S of a product and A , the amount spent on advertising the product. The data are obtained from past experience. Advertising and sales are measured in thousands of dollars.
Using graphing utility, the equation of line of best fit.
Now, write as function form.
Therefore,
Where, A represents expenditure and S represent sales.
Put
Hence, the sales of $34457.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Precalculus
- question 10 pleasearrow_forward00 (a) Starting with the geometric series Σ X^, find the sum of the series n = 0 00 Σηχη - 1, |x| < 1. n = 1 (b) Find the sum of each of the following series. 00 Σnx", n = 1 |x| < 1 (ii) n = 1 sin (c) Find the sum of each of the following series. (i) 00 Σn(n-1)x^, |x| <1 n = 2 (ii) 00 n = 2 n² - n 4n (iii) M8 n = 1 շոarrow_forward(a) Use differentiation to find a power series representation for 1 f(x) = (4 + x)²* f(x) = 00 Σ n = 0 What is the radius of convergence, R? R = (b) Use part (a) to find a power series for f(x) = 1 (4 + x)³° f(x) = 00 Σ n = 0 What is the radius of convergence, R? R = (c) Use part (b) to find a power series for f(x) = x² (4 + x)³* 00 f(x) = Σ n = 2 What is the radius of convergence, R? R = Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWERarrow_forward
- answer for question 4 pleasearrow_forward(3) (20 points) Let F(x, y, z) = (y, z, x²z). Define E = {(x, y, z) | x² + y² ≤ z ≤ 1, x ≤ 0}. (a) (2 points) Calculate the divergence V. F. (b) (4 points) Let D = {(x, y) | x² + y² ≤ 1, x ≤ 0} Without calculation, show that the triple integral √ (V · F) dV = √ 2²(1. = x²(1 − x² - y²) dA. Earrow_forward(2) (22 points) Let F(x, y, z) = (x sin y, cos y, ―xy). (a) (2 points) Calculate V. F. (b) (6 points) Given a vector field is everywhere defined with V G₁(x, y, z) = * G2(x, y, z) = − G3(x, y, z) = 0. 0 0 F(x, y, z) = (F₁(x, y, z), F₂(x, y, z), F(x, y, z)) that F = 0, let G = (G1, G2, G3) where F₂(x, y, y, t) dt - √ F³(x, t, 0) dt, * F1(x, y, t) dt, t) dt - √ F Calculate G for the vector field F(x, y, z) = (x sin y, cos y, -xy).arrow_forward
- Evaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √ √(x + y) A R R = {(x, y) | 25 < x² + y² ≤ 36, x < 0} Hint: The integral and Region is defined in rectangular coordinates.arrow_forwardFind the volume of the solid that lies under the paraboloid z = 81 - x² - y² and within the cylinder (x − 1)² + y² = 1. A plot of an example of a similar solid is shown below. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). Volume using Double Integral Paraboloid & Cylinder -3 Hint: The integral and region is defined in polar coordinates.arrow_forwardEvaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √4(1–2² 4(1 - x² - y²) dA R 3 R = {(r,0) | 0 ≤ r≤ 2,0π ≤0≤¼˜}. Hint: The integral is defined in rectangular coordinates. The Region is defined in polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- Evaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). R - 1 · {(r,0) | 1 ≤ r≤ 5,½π≤ 0<1π}. Hint: Be sure to convert to Polar coordinates. Use the correct differential for Polar Coordinates.arrow_forwardEvaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √ √2(x+y) dA R R = {(x, y) | 4 < x² + y² < 25,0 < x} Hint: The integral and Region is defined in rectangular coordinates.arrow_forwardHW: The frame shown in the figure is pinned at A and C. Use moment distribution method, with and without modifications, to draw NFD, SFD, and BMD. B I I 40 kN/m A 3 m 4 marrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





