
Concept explainers
(a)
To write: thelinear model that expresses the book value V of the computer as a function of its age x .
(a)
Answer to Problem 45AYU
The function is given by the equation
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
Let
Now, the value of the computer is depreciated over 3 years. So, the value is depreciated by
Since each computer is depreciated by $1000 per year, the slope of the function is
Therefore, the function is given by the equation
Conclusion:
Therefore, the function is given by the equation
(c)
To graph: the linear function.
(c)
Answer to Problem 45AYU
Thegraph is drawn.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Compare the equation
To plot the graph, take the y -intercept
The graph can be plotted as follows.
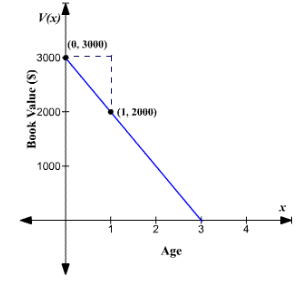
Conclusion:
Therefore, thegraph is drawn.
(d)
To find: the book value of the computer after 2 years.
(d)
Answer to Problem 45AYU
Therefore, the book value of the computer after 2 years is $1000.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Substitute 2 for x in
Conclusion:
Therefore, the book value of the computer after 2 years is $1000.
(e)
To find: when will the computer have a book value of $2000.
(e)
Answer to Problem 45AYU
The book value of the computer will be $2000 after 1year.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Substitute 2000 for
Subtract 3000 from both the sides.
Swap the sides of the equation.
Divide both the sides by − 1000.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the book value of the computer will be $2000 after 1year.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Using and Understanding Mathematics: A Quantitative Reasoning Approach (6th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- question 10 pleasearrow_forward00 (a) Starting with the geometric series Σ X^, find the sum of the series n = 0 00 Σηχη - 1, |x| < 1. n = 1 (b) Find the sum of each of the following series. 00 Σnx", n = 1 |x| < 1 (ii) n = 1 sin (c) Find the sum of each of the following series. (i) 00 Σn(n-1)x^, |x| <1 n = 2 (ii) 00 n = 2 n² - n 4n (iii) M8 n = 1 շոarrow_forward(a) Use differentiation to find a power series representation for 1 f(x) = (4 + x)²* f(x) = 00 Σ n = 0 What is the radius of convergence, R? R = (b) Use part (a) to find a power series for f(x) = 1 (4 + x)³° f(x) = 00 Σ n = 0 What is the radius of convergence, R? R = (c) Use part (b) to find a power series for f(x) = x² (4 + x)³* 00 f(x) = Σ n = 2 What is the radius of convergence, R? R = Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWERarrow_forward
- answer for question 4 pleasearrow_forward(3) (20 points) Let F(x, y, z) = (y, z, x²z). Define E = {(x, y, z) | x² + y² ≤ z ≤ 1, x ≤ 0}. (a) (2 points) Calculate the divergence V. F. (b) (4 points) Let D = {(x, y) | x² + y² ≤ 1, x ≤ 0} Without calculation, show that the triple integral √ (V · F) dV = √ 2²(1. = x²(1 − x² - y²) dA. Earrow_forward(2) (22 points) Let F(x, y, z) = (x sin y, cos y, ―xy). (a) (2 points) Calculate V. F. (b) (6 points) Given a vector field is everywhere defined with V G₁(x, y, z) = * G2(x, y, z) = − G3(x, y, z) = 0. 0 0 F(x, y, z) = (F₁(x, y, z), F₂(x, y, z), F(x, y, z)) that F = 0, let G = (G1, G2, G3) where F₂(x, y, y, t) dt - √ F³(x, t, 0) dt, * F1(x, y, t) dt, t) dt - √ F Calculate G for the vector field F(x, y, z) = (x sin y, cos y, -xy).arrow_forward
- Evaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √ √(x + y) A R R = {(x, y) | 25 < x² + y² ≤ 36, x < 0} Hint: The integral and Region is defined in rectangular coordinates.arrow_forwardFind the volume of the solid that lies under the paraboloid z = 81 - x² - y² and within the cylinder (x − 1)² + y² = 1. A plot of an example of a similar solid is shown below. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). Volume using Double Integral Paraboloid & Cylinder -3 Hint: The integral and region is defined in polar coordinates.arrow_forwardEvaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √4(1–2² 4(1 - x² - y²) dA R 3 R = {(r,0) | 0 ≤ r≤ 2,0π ≤0≤¼˜}. Hint: The integral is defined in rectangular coordinates. The Region is defined in polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- Evaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). R - 1 · {(r,0) | 1 ≤ r≤ 5,½π≤ 0<1π}. Hint: Be sure to convert to Polar coordinates. Use the correct differential for Polar Coordinates.arrow_forwardEvaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √ √2(x+y) dA R R = {(x, y) | 4 < x² + y² < 25,0 < x} Hint: The integral and Region is defined in rectangular coordinates.arrow_forwardHW: The frame shown in the figure is pinned at A and C. Use moment distribution method, with and without modifications, to draw NFD, SFD, and BMD. B I I 40 kN/m A 3 m 4 marrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





