
Concept explainers
(a)
To draw: a
(a)
Answer to Problem 28AYU
Explanation of Solution
Given:
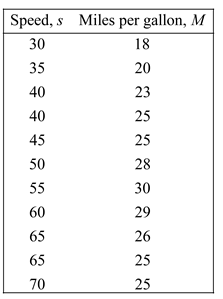
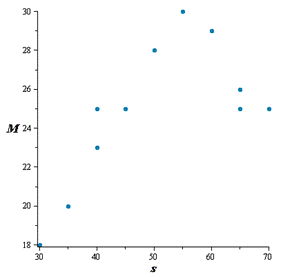
Calculation:
Draw a scatter diagram of the data treating speed as the independent variable and find the type of relation appears to exist between speed and miles per gallon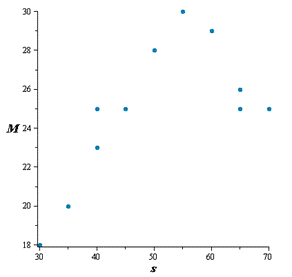
From the scatter plot of the data it is seen that there is quadratic relation exists between speed
and miles per gallon.
Conclusion:
Thus, the scatter diagram is drawn.
(b)
To find: the quadratic function of best fit
(b)
Answer to Problem 28AYU
The relation between speed and miles per gallon is given below;
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The linear model that describes the relation between speed and miles per gallon is given below;
Conclusion:
The relation between speed and miles per gallon is given below;
(c)
miles per gallon for the Camry that is travelling 63 miles per hours
(c)
Answer to Problem 28AYU
Hence, miles per gallon for the Camry that is travelling 63 miles per hours is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
To predict miles per gallon for the Camry that is travelling 63 miles per hours, substitute
Hence, miles per gallon for the Camry that is travelling 63 miles per hours is
Conclusion:
Hence, miles per gallon for the Camry that is travelling 63 miles per hours is
Chapter 3 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
- ٣:٥٣ النموذج الاول . . . O O O بشما ند الحمر الحمر الجمهورية الجنية وزارة التربية والتعليم اليوم التاريخ اللجنة العليا للاختبارات الزمن اختبار مادة الجبر والهندسة لجنة المطابع السرية المركزية للشهادة الثانوية العامة (القسم العلمي) الفترة %97 (1) ظلل في ورقة الإجابة الدائرة التي تحتوي على الحرف ( ص ) للإجابة الصحيحة والحرف ( خ ) للإجابة الخطأ بحسب رقم الفقرة لكل مما يأتي ( درجة لكل فقرة ) )1 ) 2 ) 3 ) 4 ) بؤرة القطع س" = ١٢ ص هي ( ۲ ) طول المحور الأصغر للقطع ٩ س + ص = ٩ يساوي 6 وحدات طول . ) إذا كان & عدد مركب ، 181 + 11 = ٦ ، فإن ١١ = ٣ . ) إذا كان م + ۳ ت = ۲ + ت ب م ، ب دع ، فإن م + ب = 5 ( ) إذا كان & = ۱ + ٣ ت ، فإن ٠ = ١٠ . 6 ( - ) إذا كان ٥٠ - ٣ - ١٢٠ ٤ - ٣ ، فإن قيمة ٧ = ٥ . 1 ) = N ) إذا كان ح هو الحد الخالي من س في المفكوك ( س + v. N 8 ( ( قيمة المقدار , = + ۱ ، * . . + ، فإن قيمة ٧ = ١٦ . ۱ + 9 ( ) المستقيمان المقاربان للقطع الذي معادلته س" = ١ هما ص = : ۹ 10 ( ) إذا كان ٥ + س = ٢٤ ، فإن قيمة س = - 1 س 11 ( ) إذا كانت النسبة بين الحدين الأوسطين تساوي 9 في المفكوك ( س + - ) ،…arrow_forwardالاسم يمنع استخدام الآلة الحاسبة ظلل في ورقة الإجابة الدائرة التي تحتوي على الحرف (ص) للإجابة الصحيحة والحرف (خ) للإجابة الخطأ بحسب رقم الفقرة لكل مما يأتي: درجة لكل فقرة. ( ) نها جا 元 جتا = صفر س ۱ س س -۱ ( ) يمكن إعادة تعريف الدالة د(س) = س قاس لكي تكون متصلة عند س = 7 ( ) إذا كانت د(س) = (٢) س - س ) ؛ فإن د(١) = ٦ ٢ س ص ( ) إذا كانت س + 0= ؛ فإن عند ) - ١ ، - ٦ ) تساوي (٦) ( ) إذا كانت د(س) = س ه ، و (س) = ٣ س ٢ + ٢ س ؛ فإن ( د ) (۱) = ۸ ) ( معادلة ناظم الدالة ص = د(س) عند النقطة ) ( ، د (۲)) هي ص - (د (م) - - د (۲) ( س - م ) ( ) إذا كانت ص = ظتا٢ س ؛ فإن ص = ٢ ص قتا ٢س ) ( إذا كانت د(س) = س ؛ فإن د (T) = جتاس 1- T ( ) إذا كانت د(س) = 1 - جناس جاس ؛ فإن د () = - 1 ( ) إذا كانت الدالة د (س) تحقق شروط مبرهنة القيمة المتوسطة على [ ، ب ] ، فإنه يوجد جـ ] ، ب [ بحيث (جـ) = (P) + (~)- - ب + P 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ( ) للدالة د(س) = لو ( س ) + (٣) نقطة حرجة عند س = . ( ) إذا كان س = - ٢ مقارباً رأسياً للدالة د(س) 12 10 13 14 15 16 17 س = لو|س | + ث - = ۲ س + ٣ ب س + ٤ ، فإن معادلة…arrow_forward2. Symmetry Evaluate the following integrals using symmetry argu- ments. Let R = {(x, y): -a ≤ x ≤ a, −b ≤ y ≤ b}, where a and b are positive real numbers. a. SS Sf xye xye¯(x² + y²) dA R b. C sin (x − y) - dA x² + y² + 1 Rarrow_forward
- 3. P 2. 1 -3-2-10 1 2 3 -2- X The graph of point P is given in the xy-plane. Which of the following are possible polar coordinates of point P? A Ⓐ(2, 2) (2, 1/1/1) B (2, 3) C Ⓒ =) (2√2, 41 ) D (2√2, 3) 4arrow_forwardThe graph of f' is below. Use it to determine where the local minima and maxima for f are. If there are multiple answers, separate with commas. 2 f'(x) N -5 -4 3-2-1 -1 -2 -3 -4 12 3 4 5 -x Local minima at x Local maxima at xarrow_forwardThe graph of f' is below. Use it to determine the intervals where f is increasing. -5-4-32 4- 3 2 1 -2 -3 +x 2 3 4 5arrow_forward
- The graph of f' is below. Use it to determine where the inflection points are and the intervals where f is concave up and concave down. If there are multiple inflection points, separate with a comma. 6 5 4 3 2 1 f'(x) +x -6-5-4-3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6+ Inflection point(s) at x = Concave up: Concave down:arrow_forwardThe graph of f' is below. Use it to determine where the local minima and maxima for f are. If there are multiple answers, separate with commas. f'(x) 4- -5-4-3-8-1 3 2 1 x 1 2 3 4 5 -1 -2 -3 -4 Local minima at a Local maxima at =arrow_forwardThe graph of f' is below. Use it to determine the intervals where f is increasing. f'(xx) 4- -5 -3 -2 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 Cit +x 7 2arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





