
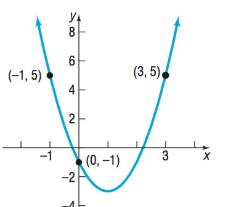
In Problems 49-54, determine the quadratic function whose graph is given.
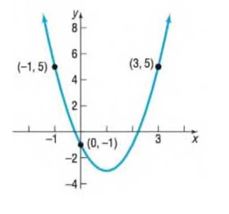
To calculate: The quadratic function using the given graphs.
Answer to Problem 51AYU
The equation of the given graph is .
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given graph is
Formula Used:
The general form of a quadratic equation is .
This general equation can also be written as , where
If , the graph opens upwards.
If , the graph opens downwards.
The vertex of the above function is .
The axis of symmetry will be .
We can find the by equating the equation at .
We can find the by equation the equation at .
1. If then the vertex is the .
2. If then the graph has no .
3. If then the vertex is the .
Calculation:
Let us consider the quadratic equation of the given graph to be
-----(1)
From the given graph, we can see that the of the given function is .
We know that the is the value of the function at , thus, we have
-----(2)
At , (1) becomes
-----(3)
Thus, using (2) and (3), we get the value of .
Thus, equation (1) becomes
-----(4)
Now, we need to find and .
We know that a point in a graph is written as .
The given graph has 2 points and .
Consider the point .
Here, we have and .
Therefore, substituting it in (4), we get
-----(5)
Now, consider the point .
Here, we have and .
Therefore, substituting it in (4), we get
-----(6)
In order to find the values of and , we have to solve the equations (5) and (6).
Therefore, we have
-----(5) And
-----(6).
Now, on adding (5) and (6), we get
On substituting the above value in (5), we get
Therefore, the equation of the given graph is
Chapter 3 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Evaluate the double integral ' √ √ (−2xy² + 3ry) dA R where R = {(x,y)| 1 ≤ x ≤ 3, 2 ≤ y ≤ 4} Double Integral Plot of integrand and Region R N 120 100 80- 60- 40 20 -20 -40 2 T 3 4 5123456 This plot is an example of the function over region R. The region and function identified in your problem will be slightly different. Answer = Round your answer to four decimal places.arrow_forwardFind Te²+ dydz 0 Write your answer in exact form.arrow_forwardxy² Find -dA, R = [0,3] × [−4,4] x²+1 Round your answer to four decimal places.arrow_forward
- Find the values of p for which the series is convergent. P-?- ✓ 00 Σ nº (1 + n10)p n = 1 Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER [-/4 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 8.3.513.XP. Consider the following series. 00 Σ n = 1 1 6 n° (a) Use the sum of the first 10 terms to estimate the sum of the given series. (Round the answer to six decimal places.) $10 = (b) Improve this estimate using the following inequalities with n = 10. (Round your answers to six decimal places.) Sn + + Los f(x) dx ≤s ≤ S₁ + Jn + 1 + Lo f(x) dx ≤s ≤ (c) Using the Remainder Estimate for the Integral Test, find a value of n that will ensure that the error in the approximation s≈s is less than 0.0000001. On > 11 n> -18 On > 18 On > 0 On > 6 Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forward√5 Find Lª³ L² y-are y- arctan (+) dy dydx. Hint: Use integration by parts. SolidUnderSurface z=y*arctan(1/x) Z1 2 y 1 1 Round your answer to 4 decimal places.arrow_forwardFor the solid lying under the surface z = √√4-² and bounded by the rectangular region R = [0,2]x[0,2] as illustrated in this graph: Double Integral Plot of integrand over Region R 1.5 Z 1- 0.5- 0 0.5 1 1.5 205115 Answer should be in exact math format. For example, some multiple of .arrow_forward
- Find 2 S² 0 0 (4x+2y)5dxdyarrow_forward(14 points) Let S = {(x, y, z) | z = e−(x²+y²), x² + y² ≤ 1}. The surface is the graph of ze(+2) sitting over the unit disk.arrow_forward6. Solve the system of differential equations using Laplace Transforms: x(t) = 3x₁ (t) + 4x2(t) x(t) = -4x₁(t) + 3x2(t) x₁(0) = 1,x2(0) = 0arrow_forward
- 3. Determine the Laplace Transform for the following functions. Show all of your work: 1-t, 0 ≤t<3 a. e(t) = t2, 3≤t<5 4, t≥ 5 b. f(t) = f(tt)e-3(-) cos 4τ drarrow_forward4. Find the inverse Laplace Transform Show all of your work: a. F(s) = = 2s-3 (s²-10s+61)(5-3) se-2s b. G(s) = (s+2)²arrow_forward1. Consider the differential equation, show all of your work: dy =(y2)(y+1) dx a. Determine the equilibrium solutions for the differential equation. b. Where is the differential equation increasing or decreasing? c. Where are the changes in concavity? d. Suppose that y(0)=0, what is the value of y as t goes to infinity?arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





