
Precalculus
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780321716835
Author: Michael Sullivan
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.5, Problem 4AYU
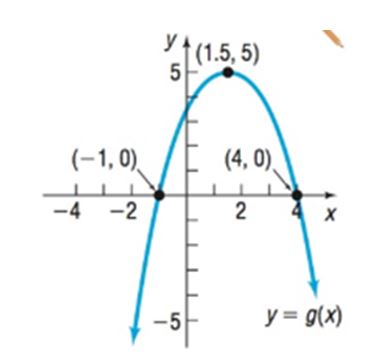
(a)
(b)
Expert Solution & Answer
To determine
To find: The solutions of the inequalities:
a.
b.
Answer to Problem 4AYU
Solution:
a.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The graph is:
Calculation:
a.
From the above graph it is clear that, the solution of the inequality will be: and .
b.
From the graph it is clear that the solution of the inequality will be: .
Chapter 3 Solutions
Precalculus
Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 1AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 2AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 3AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 4AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 5AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 6AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 7AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 8AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 9AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 10AYU
Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 11AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 12AYUCh. 3.1 - In Problems 13-20, a linear function is given. a....Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 13-20, a linear function is given. a....Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 13-20, a linear function is given. a....Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 13-20, a linear function is given. a....Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 13-20, a linear function is given. a....Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 13-20, a linear function is given. a....Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 13-20, a linear function is given. a....Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 13-20, a linear function is given. a....Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 21-28, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 21-28, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 21-28, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 21-28, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 21-28, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 21-28, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 21-28, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Problems 21-28, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - Suppose that f( x )=4x1 and g(x)=2x+5 . a. Solve...Ch. 3.1 - Suppose that f( x )=3x+5 and g(x)=2x+15 . a. Solve...Ch. 3.1 - In parts (a) - (f), use the following figure. a....Ch. 3.1 - In parts (a) - (f), use the following figure. a....Ch. 3.1 - In parts (a) and (b), use the following figure. a....Ch. 3.1 - In parts (a) and (b), use the following figure. a....Ch. 3.1 - In parts (a) and (b), use the following figure. a....Ch. 3.1 - In parts (a) and (b), use the following figure. a....Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 37AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 38AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 39AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 40AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 41AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 42AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 43AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 44AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 45AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 46AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 47AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 48AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 49AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 50AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 51AYUCh. 3.1 - Prob. 52AYUCh. 3.1 - Which of the following functions might have the...Ch. 3.1 - Which of the following functions might have the...Ch. 3.1 - Under what circumstances is a linear function f( x...Ch. 3.1 - Explain how the graph of f( x )=mx+b can be used...Ch. 3.2 - Plot the points ( 1,5 ),( 2,6 ),( 3,9 ),( 1,12 )...Ch. 3.2 - Find an equation of the line containing the points...Ch. 3.2 - A _____________ is used to help us to see what...Ch. 3.2 - True or False The correlation coefficient is a...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 5-10, examine the scatter diagram and...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 5-10, examine the scatter diagram and...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 5-10, examine the scatter diagram and...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 5-10, examine the scatter diagram and...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 5-10, examine the scatter diagram and...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 5-10, examine the scatter diagram and...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 11-16, (a) Draw a scatter diagram. (b)...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 11-16, (a) Draw a scatter diagram. (b)...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 11-16, (a) Draw a scatter diagram. (b)...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 11-16, (a) Draw a scatter diagram. (b)...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 11-16, (a) Draw a scatter diagram. (b)...Ch. 3.2 - In Problems 11-16, (a) Draw a scatter diagram. (b)...Ch. 3.2 - Candy The following data represent the weight (in...Ch. 3.2 - Tornadoes The following data represent the width...Ch. 3.2 - Video Games and Grade-Point Average Professor...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 20AYUCh. 3.2 - Prob. 21AYUCh. 3.2 - Prob. 22AYUCh. 3.2 - Prob. 23AYUCh. 3.2 - Prob. 24AYUCh. 3.2 - Prob. 25AYUCh. 3.2 - Prob. 26AYUCh. 3.2 - Prob. 27AYUCh. 3.3 - List the intercepts of the equation y= x 2 9 ....Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 2AYUCh. 3.3 - To complete the square of x 2 5x , you add the...Ch. 3.3 - To graph y= (x4) 2 you shift the graph of y= x 2...Ch. 3.3 - The graph of a quadratic function is called a(n)...Ch. 3.3 - The vertical line passing through the vertex of a...Ch. 3.3 - The x-coordinate of the vertex of f( x )=a x 2...Ch. 3.3 - True or False The graph of f( x )=2 x 2 +3x4 opens...Ch. 3.3 - True or False The y-coordinate of the vertex of f(...Ch. 3.3 - True or False If the discriminant b 2 4ac=0 , the...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 13-20, match each graph to one the...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 13-20, match each graph to one the...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 13-20, match each graph to one the...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 13-20, match each graph to one the...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 13-20, match each graph to one the...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 13-20, match each graph to one the...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 13-20, match each graph to one the...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 13-20, match each graph to one the...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 21-32, graph the function f by...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 33-48, (a) graph each quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 49-54, determine the quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 49-54, determine the quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 49-54, determine the quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 49-54, determine the quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 49-54, determine the quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 49-54, determine the quadratic...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 6572, determine, without graphing,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 55-62, determine, without graphing,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 55-62, determine, without graphing,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 55-62, determine, without graphing,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems, determine, without graphing, whether...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 55-62, determine, without graphing,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems, determine, without graphing, whether...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 55-62, determine, without graphing,...Ch. 3.3 - The graph of the function f( x )=a x 2 +bx+c has...Ch. 3.3 - The graph of the function f(x)=a x 2 +bx+c has...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 77-82, for the given functions fandg ,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 77-82, for the given functions fandg ,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 77-82, for the given functions fandg ,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 77-82, for the given functions fandg ,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 77-82, for the given functions fandg ,...Ch. 3.3 - In Problems 77-82, for the given functions fandg ,...Ch. 3.3 - Answer Problems 83 and 84 using the following: A...Ch. 3.3 - Answer Problems 83 and 84 using the following: A...Ch. 3.3 - Suppose that f(x)= x 2 +4x21 . (a) What is the...Ch. 3.3 - Suppose that f( x )= x 2 +2x8 . (a) What is the...Ch. 3.3 - Analyzing the Motion of a Projectile A projectile...Ch. 3.3 - Analyzing the Motion of a Projectile A projectile...Ch. 3.3 - Maximizing Revenue Suppose that the manufacturer...Ch. 3.3 - Maximizing Revenue A lawn mower manufacturer has...Ch. 3.3 - Minimizing Marginal Cost The marginal cost of a...Ch. 3.3 - Minimizing Marginal Cost (See Problem 91.) The...Ch. 3.3 - Business The monthly revenue R achieved by selling...Ch. 3.3 - Business The daily revenue R achieved by selling x...Ch. 3.3 - Stopping Distance An accepted relationship between...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 82AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 83AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 84AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 85AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 86AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 87AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 88AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 89AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 90AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 91AYUCh. 3.3 - Prob. 92AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 1AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 2AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 3AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 4AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 5AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 6AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 7AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 8AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 9AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 10AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 11AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 12AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 13AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 14AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 15AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 16AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 17AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 18AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 19AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 20AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 21AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 22AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 23AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 24AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 25AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 26AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 27AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 28AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 29AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 30AYUCh. 3.4 - Prob. 31AYUCh. 3.5 - Solve the inequality 3x27 .Ch. 3.5 - Write (2,7] using inequality notation.Ch. 3.5 - (a) f( x )0 (b) f( x )0Ch. 3.5 - (a) g( x )0 (b) g( x )0Ch. 3.5 - (a) g( x )f( x ) (b) f( x )g( x )Ch. 3.5 - (a) f( x )g( x ) (b) f( x )g( x )Ch. 3.5 - x 2 3x100Ch. 3.5 - x 2 +3x100Ch. 3.5 - x 2 4x0Ch. 3.5 - x 2 +8x0Ch. 3.5 - x 2 90Ch. 3.5 - x 2 10Ch. 3.5 - x 2 +x12Ch. 3.5 - x 2 +7x12Ch. 3.5 - 2 x 2 5x+3Ch. 3.5 - 6 x 2 6+5xCh. 3.5 - x 2 x+10Ch. 3.5 - x 2 +2x+40Ch. 3.5 - 4 x 2 +96xCh. 3.5 - 25 x 2 +1640xCh. 3.5 - 6( x 2 1 )5xCh. 3.5 - 2( 2 x 2 3x )9Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 23AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 24AYUCh. 3.5 - In Problems 25-32, use the given functions f and g...Ch. 3.5 - In Problems 25-32, use the given functions f and g...Ch. 3.5 - In Problems 25-32, use the given functions f and g...Ch. 3.5 - In Problems 25-32, use the given functions f and g...Ch. 3.5 - In Problems 25-32, use the given functions f and g...Ch. 3.5 - In Problems 25-32, use the given functions f and g...Ch. 3.5 - In Problems 25-32, use the given functions f and g...Ch. 3.5 - In Problems 25-32, use the given functions f and g...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 33AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 34AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 35AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 36AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 37AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 38AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 39AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 40AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 41AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 42AYUCh. 3.5 - Prob. 43AYUCh. 3 - Prob. 1RECh. 3 - Prob. 2RECh. 3 - Prob. 3RECh. 3 - Prob. 4RECh. 3 - Prob. 5RECh. 3 - Prob. 6RECh. 3 - Prob. 7RECh. 3 - Prob. 8RECh. 3 - Prob. 9RECh. 3 - Prob. 10RECh. 3 - Prob. 11RECh. 3 - Prob. 12RECh. 3 - Prob. 13RECh. 3 - Prob. 14RECh. 3 - Prob. 15RECh. 3 - Prob. 16RECh. 3 - Prob. 17RECh. 3 - Prob. 18RECh. 3 - Prob. 19RECh. 3 - Prob. 20RECh. 3 - Prob. 21RECh. 3 - Prob. 22RECh. 3 - Prob. 23RECh. 3 - Prob. 24RECh. 3 - Prob. 25RECh. 3 - Prob. 26RECh. 3 - Prob. 27RECh. 3 - Prob. 28RECh. 3 - Prob. 29RECh. 3 - Prob. 30RECh. 3 - Prob. 31RECh. 3 - Prob. 32RECh. 3 - Prob. 33RECh. 3 - Prob. 34RECh. 3 - Prob. 35RECh. 3 - Prob. 36RECh. 3 - Prob. 37RECh. 3 - Prob. 38RECh. 3 - Prob. 39RECh. 3 - Prob. 40RECh. 3 - Prob. 41RECh. 3 - Prob. 42RECh. 3 - Prob. 43RECh. 3 - Prob. 44RECh. 3 - Prob. 45RECh. 3 - Prob. 46RECh. 3 - Prob. 47RECh. 3 - Prob. 1CTCh. 3 - Prob. 2CTCh. 3 - Prob. 3CTCh. 3 - Prob. 5CTCh. 3 - Prob. 4CTCh. 3 - Prob. 6CTCh. 3 - Prob. 7CTCh. 3 - Prob. 8CTCh. 3 - Prob. 9CTCh. 3 - Find the distance between the points P=( 1,3 ) and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 2CRCh. 3 - Solve the inequality 5x+30 and graph the solution...Ch. 3 - Find the equation of the line containing the...Ch. 3 - Find the equation of the line perpendicular to the...Ch. 3 - Graph the equation x 2 + y 2 4x+8y5=0 .Ch. 3 - Does the following relation represent a function?...Ch. 3 - For the function f defined by f( x )= x 2 4x+1 ,...Ch. 3 - Find the domain of h(z)= 3z1 6z7 .Ch. 3 - Is the following graph the graph of a function?Ch. 3 - Consider the function f(x)= x x+4 . a. Is the...Ch. 3 - Is the function f(x)= x 2 2x+1 even, odd, or...Ch. 3 - Approximate the local maximum values and local...Ch. 3 - If f(x)=3x+5 and g(x)=2x+1 , a. Solve f(x)=g( x )...Ch. 3 - For the graph of the function f , a. Find the...
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The following set of data is from sample of n=5: a. Compute the mean, median, and mode. b. Compute the range, v...
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
CHECK POINT 1 In a survey on musical tastes, respondents were asked: Do you listed to classical music? Do you l...
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A tree diagram for the given condition.
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Classifying Types of Probability In Exercises 53–58, classify the statement as an example of classical probabil...
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Violins Professional musicians listened to five violins being played, without seeing the instruments. One violi...
Introductory Statistics
76. Dew Point and Altitude The dew point decreases as altitude increases. If the dew point on the ground is 80°...
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the function f(x) = x²-1. (a) Find the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x=1 using the definition of the derivative. Show all your steps clearly. (b) Sketch the graph of f(x) around x = 1. Draw the secant line passing through the points on the graph where x 1 and x-> 1+h (for a small positive value of h, illustrate conceptually). Then, draw the tangent line to the graph at x=1. Explain how the slope of the tangent line relates to the value you found in part (a). (c) In a few sentences, explain what the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x = 1 represents in the context of the graph of f(x). How does the rate of change of this function vary at different points?arrow_forward1. The graph of ƒ is given. Use the graph to evaluate each of the following values. If a value does not exist, state that fact. и (a) f'(-5) (b) f'(-3) (c) f'(0) (d) f'(5) 2. Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = g(x) at x = 5 if g(5) = −3 and g'(5) = 4. - 3. If an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = f(x) at the point where x 2 is y = 4x — 5, find ƒ(2) and f'(2).arrow_forwardDoes the series converge or divergearrow_forward
- Suppose that a particle moves along a straight line with velocity v (t) = 62t, where 0 < t <3 (v(t) in meters per second, t in seconds). Find the displacement d (t) at time t and the displacement up to t = 3. d(t) ds = ["v (s) da = { The displacement up to t = 3 is d(3)- meters.arrow_forwardLet f (x) = x², a 3, and b = = 4. Answer exactly. a. Find the average value fave of f between a and b. fave b. Find a point c where f (c) = fave. Enter only one of the possible values for c. c=arrow_forwardplease do Q3arrow_forward
- Use the properties of logarithms, given that In(2) = 0.6931 and In(3) = 1.0986, to approximate the logarithm. Use a calculator to confirm your approximations. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (a) In(0.75) (b) In(24) (c) In(18) 1 (d) In ≈ 2 72arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. (Remember the constant of integration.) √tan(8x) tan(8x) sec²(8x) dxarrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral by making a change of variables. (Remember the constant of integration.) √(x+4) 4)√6-x dxarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning
01 - What Is A Differential Equation in Calculus? Learn to Solve Ordinary Differential Equations.; Author: Math and Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K80YEHQpx9g;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Higher Order Differential Equation with constant coefficient (GATE) (Part 1) l GATE 2018; Author: GATE Lectures by Dishank;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ODxP7BbqAjA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Solution of Differential Equations and Initial Value Problems; Author: Jefril Amboy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q68sk7XS-dc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY