
Concept explainers
(a)
To find: the slope and y-intercept of the given linear function.
(a)
Answer to Problem 3RE
Slope
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
The slope intercept form of a line is
Where the slope of the line is
And
Compare the function
Slope
Conclusion:
Therefore, the slope
(b)
To find: the average rate of change of the given function
(b)
Answer to Problem 3RE
The rate of change
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The linear function
For calculating average rate of change to given function, it is needed two points
Let
So second point in
Now as rate of change
Here
So rate of change
Conclusion:
Therefore, the rate of change
(c)
To graph: the given function.
(c)
Answer to Problem 3RE
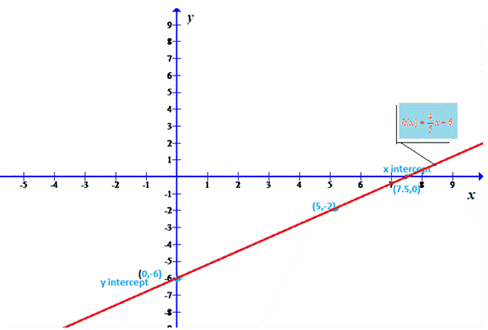
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The line joining two points (0,-6) and (5,-2) is shown as below where (7.5,0) is x intercept.
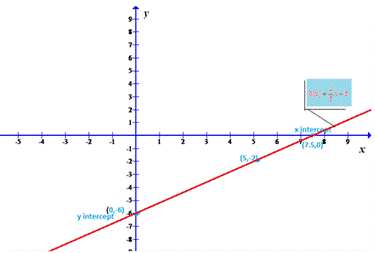
Conclusion:
Thus, the given function is drawn.
(d)
whether the function is increasing decreasing or constant.
(d)
Answer to Problem 3RE
Thus function is increasing in the interval
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
As the slope of the function
That means it is increasing function.
Thus function is increasing in the interval
Conclusion:
Thus function is increasing in the interval
Chapter 3 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- Evaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √ √(x + y) A R R = {(x, y) | 25 < x² + y² ≤ 36, x < 0} Hint: The integral and Region is defined in rectangular coordinates.arrow_forwardFind the volume of the solid that lies under the paraboloid z = 81 - x² - y² and within the cylinder (x − 1)² + y² = 1. A plot of an example of a similar solid is shown below. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). Volume using Double Integral Paraboloid & Cylinder -3 Hint: The integral and region is defined in polar coordinates.arrow_forwardEvaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √4(1–2² 4(1 - x² - y²) dA R 3 R = {(r,0) | 0 ≤ r≤ 2,0π ≤0≤¼˜}. Hint: The integral is defined in rectangular coordinates. The Region is defined in polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- Evaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). R - 1 · {(r,0) | 1 ≤ r≤ 5,½π≤ 0<1π}. Hint: Be sure to convert to Polar coordinates. Use the correct differential for Polar Coordinates.arrow_forwardEvaluate the following integral over the Region R. (Answer accurate to 2 decimal places). √ √2(x+y) dA R R = {(x, y) | 4 < x² + y² < 25,0 < x} Hint: The integral and Region is defined in rectangular coordinates.arrow_forwardHW: The frame shown in the figure is pinned at A and C. Use moment distribution method, with and without modifications, to draw NFD, SFD, and BMD. B I I 40 kN/m A 3 m 4 marrow_forward
- Let the region R be the area enclosed by the function f(x)= = 3x² and g(x) = 4x. If the region R is the base of a solid such that each cross section perpendicular to the x-axis is an isosceles right triangle with a leg in the region R, find the volume of the solid. You may use a calculator and round to the nearest thousandth. y 11 10 9 00 8 7 9 5 4 3 2 1 -1 -1 x 1 2arrow_forwardLet the region R be the area enclosed by the function f(x) = ex — 1, the horizontal line y = -4 and the vertical lines x = 0 and x = 3. Find the volume of the solid generated when the region R is revolved about the line y = -4. You may use a calculator and round to the nearest thousandth. 20 15 10 5 y I I I | I + -1.5 -1 -0.5 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 -5 I -10 -15 I + I I T I I + -20 I + -25 I I I -30 I 3.5 4 xarrow_forwardplease show all the workarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





