
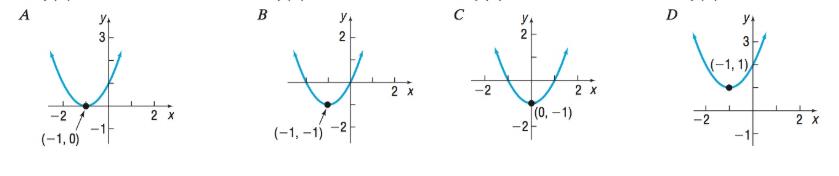
In Problems 13-20, match each graph to one the following functions.
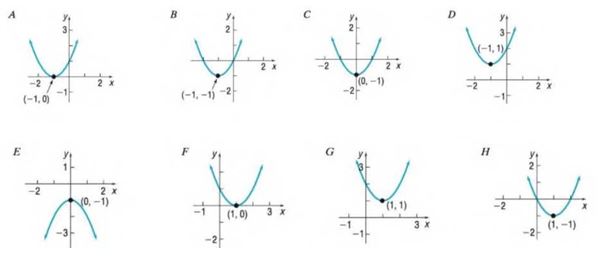
To calculate: The given graphs and matches the given equation .
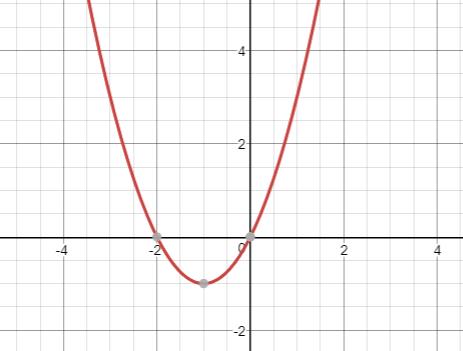
Answer to Problem 18AYU
The graph is the graph of the given equation.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given equation is .
Formula Used:
The general form of a quadratic equation is
The graph of the above quadratic function is the graph of with units shifted horizontally and units shifted vertically.
The graph opens up if and it opens downward if
If the given quadratic equation is then we can convert this into the standard form using technique.
Thus, we have to divide the whole equation by and then add and subtract the square of half of the .
Therefore, we get
Calculation:
Here, we have to convert the given formula into the standard format.
Therefore, we have to use the transformation method to convert the given equation into the standard format.
Therefore, we get
Here, in the given equation, we can see that and
Here, since is positive, the graph opens upward.
The graph of the given function will be the graph of with 1 unit shifted horizontally left and 1 unit shifted upward.
Therefore, the graph of the given function is
Chapter 3 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
- Consider the region below f(x) = (11-x), above the x-axis, and between x = 0 and x = 11. Let x; be the midpoint of the ith subinterval. Complete parts a. and b. below. a. Approximate the area of the region using eleven rectangles. Use the midpoints of each subinterval for the heights of the rectangles. The area is approximately square units. (Type an integer or decimal.)arrow_forwardRama/Shutterstock.com Romaset/Shutterstock.com The power station has three different hydroelectric turbines, each with a known (and unique) power function that gives the amount of electric power generated as a function of the water flow arriving at the turbine. The incoming water can be apportioned in different volumes to each turbine, so the goal of this project is to determine how to distribute water among the turbines to give the maximum total energy production for any rate of flow. Using experimental evidence and Bernoulli's equation, the following quadratic models were determined for the power output of each turbine, along with the allowable flows of operation: 6 KW₁ = (-18.89 +0.1277Q1-4.08.10 Q) (170 - 1.6 · 10¯*Q) KW2 = (-24.51 +0.1358Q2-4.69-10 Q¹²) (170 — 1.6 · 10¯*Q) KW3 = (-27.02 +0.1380Q3 -3.84-10-5Q) (170 - 1.6-10-ºQ) where 250 Q1 <1110, 250 Q2 <1110, 250 <3 < 1225 Qi = flow through turbine i in cubic feet per second KW = power generated by turbine i in kilowattsarrow_forwardHello! Please solve this practice problem step by step thanks!arrow_forward
- Hello, I would like step by step solution on this practive problem please and thanks!arrow_forwardHello! Please Solve this Practice Problem Step by Step thanks!arrow_forwarduestion 10 of 12 A Your answer is incorrect. L 0/1 E This problem concerns hybrid cars such as the Toyota Prius that are powered by a gas-engine, electric-motor combination, but can also function in Electric-Vehicle (EV) only mode. The figure below shows the velocity, v, of a 2010 Prius Plug-in Hybrid Prototype operating in normal hybrid mode and EV-only mode, respectively, while accelerating from a stoplight. 1 80 (mph) Normal hybrid- 40 EV-only t (sec) 5 15 25 Assume two identical cars, one running in normal hybrid mode and one running in EV-only mode, accelerate together in a straight path from a stoplight. Approximately how far apart are the cars after 15 seconds? Round your answer to the nearest integer. The cars are 1 feet apart after 15 seconds. Q Search M 34 mlp CHarrow_forward
- Find the volume of the region under the surface z = xy² and above the area bounded by x = y² and x-2y= 8. Round your answer to four decimal places.arrow_forwardУ Suppose that f(x, y) = · at which {(x, y) | 0≤ x ≤ 2,-x≤ y ≤√x}. 1+x D Q Then the double integral of f(x, y) over D is || | f(x, y)dxdy = | Round your answer to four decimal places.arrow_forwardD The region D above can be describe in two ways. 1. If we visualize the region having "top" and "bottom" boundaries, express each as functions of and provide the interval of x-values that covers the entire region. "top" boundary 92(x) = | "bottom" boundary 91(x) = interval of values that covers the region = 2. If we visualize the region having "right" and "left" boundaries, express each as functions of y and provide the interval of y-values that covers the entire region. "right" boundary f2(y) = | "left" boundary fi(y) =| interval of y values that covers the region =arrow_forward
- Find the volume of the region under the surface z = corners (0,0,0), (2,0,0) and (0,5, 0). Round your answer to one decimal place. 5x5 and above the triangle in the xy-plane witharrow_forwardGiven y = 4x and y = x² +3, describe the region for Type I and Type II. Type I 8. y + 2 -24 -1 1 2 2.5 X Type II N 1.5- x 1- 0.5 -0.5 -1 1 m y -2> 3 10arrow_forwardGiven D = {(x, y) | O≤x≤2, ½ ≤y≤1 } and f(x, y) = xy then evaluate f(x, y)d using the Type II technique. 1.2 1.0 0.8 y 0.6 0.4 0.2 0- -0.2 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 X X This plot is an example of the function over region D. The region identified in your problem will be slightly different. y upper integration limit Integral Valuearrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





