
Concept explainers
(a)
To find: the slope and y-intercept of the given linear function.
(a)
Answer to Problem 5RE
Slope
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
The slope intercept form of a line is
Where the slope of the line is
And
Compare the function
Slope
Conclusion:
Therefore, the slope
(b)
To find: the average rate of change of the given function
(b)
Answer to Problem 5RE
The rate of change is 0
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For calculating average rate of change of function
Let
So second point in
Now as rate of change
Here
So rate of change
Conclusion:
Therefore, the rate of change is 0
(c)
To graph: the given function.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5RE
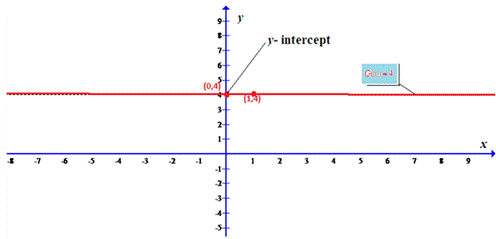
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The line joining two points (0.4) and (1,4) is shown below where there is no
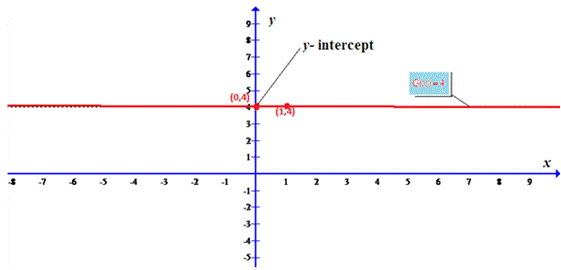
Conclusion:
Thus, the given function is drawn.
(d)
whether the function is increasing decreasing or constant.
(d)
Answer to Problem 5RE
The function is Constant in the interval
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
As the slope of the function
Thus function is Constant in the interval
Conclusion:
Thus function is Constant in the interval
Chapter 3 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- Let the region R be the area enclosed by the function f(x)= = 3x² and g(x) = 4x. If the region R is the base of a solid such that each cross section perpendicular to the x-axis is an isosceles right triangle with a leg in the region R, find the volume of the solid. You may use a calculator and round to the nearest thousandth. y 11 10 9 00 8 7 9 5 4 3 2 1 -1 -1 x 1 2arrow_forwardLet the region R be the area enclosed by the function f(x) = ex — 1, the horizontal line y = -4 and the vertical lines x = 0 and x = 3. Find the volume of the solid generated when the region R is revolved about the line y = -4. You may use a calculator and round to the nearest thousandth. 20 15 10 5 y I I I | I + -1.5 -1 -0.5 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 -5 I -10 -15 I + I I T I I + -20 I + -25 I I I -30 I 3.5 4 xarrow_forwardplease show all the workarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





