
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of 3, 5-dimethylnonane needs to be drawn and the number of possible stereoisomers should be determined.
Concept introduction:
The molecules having same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in spatial arrangements of atoms in the molecule are said to be stereoisomers of each other.
(a)
Answer to Problem 94A
The structure of the compound is:
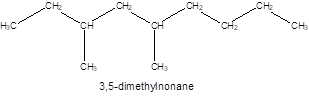
The compound 3, 5-dimethylnonane has
Explanation of Solution
A molecule is said to be chiral molecule when all the attached groups to central carbon atom are different and lacks in plane of symmetry in the molecule. The molecules having chiral centres show optical isomerism (one form of stereoisomer) as there are two mirror image representations possible for a molecule having chiral center in its structure and if the mirror images are non-superimposable to each other then, they are said to be optical isomers.
The given name of the compound is 3, 5-dimethylnonane which represents a parent chain of 9 carbon atoms having two methyl substituents at position 3 and 5 so, the structure of the compound will be:
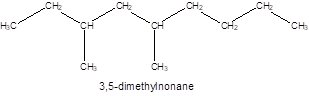
The number of chiral carbons in the compound is shown “*” as they are attached by 4 different atoms/groups:
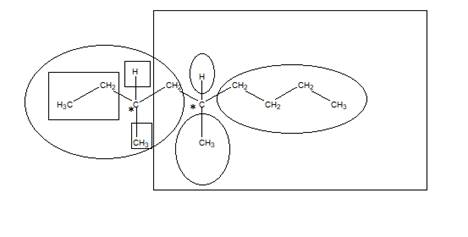
The square represents 4 different atoms and groups for first chiral carbon and oval represents 4 different atoms and groups for second chiral carbon. Hence, the total number of chiral carbons is 2.
Now, for each chiral carbon in a compound, the total number possible isomer for the compound is
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of 3, 7-dimethyl-5-ethyldecane needs to be drawn and the number of possible stereoisomers should be determined.
Concept introduction:
The molecules having same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in spatial arrangements of atoms in the molecule are said to be stereoisomers of each other.
(b)
Answer to Problem 94A
The structure of the compound is:
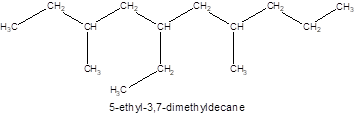
The compound 3, 7-dimethyl-5-ethyldecane has
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 3, 7-dimethyl-5-ethyldecane which represents a parent chain of 10 carbon atoms having two methyl and one ethyl substituents at position 3, 7 and 5 respectively so, the structure of the compound will be:
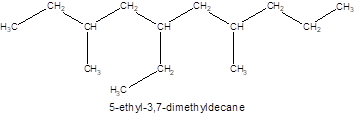
The number of chiral carbons in the compound is shown “*” as they are attached by 4 different atoms/groups:
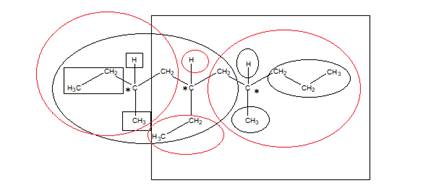
The square represents 4 different atoms and groups for first chiral carbon and oval in red and black color represents 4 different atoms and groups for second and third chiral carbon respectively. Hence, the total number of chiral carbons is 3.
Now, for each chiral carbon in a compound, the total number possible isomer for the compound is
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- In reactions whose kinetic equation is v = k[A]m, the rate coefficient k is always positive. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIf the concentration of A decreases exponentially with time, what is the rate equation? (A). -d[A] (B). dt d[A] = k[A] e-kt dtarrow_forwardGiven the first-order reaction: aA → products. State its kinetic equation.arrow_forward
- The following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?arrow_forwardWhich region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forwardPredict the product of the following reactions: O 0= excess Х Кон ОН H+ H+ Iarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





