
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The mass of nitrogen in grams should be determined when total mass of compound is 475 g. 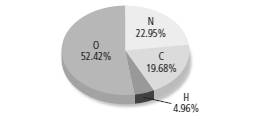
- 33.93 g
- 52.78 g
- 67.86 g
- 109.0 g
- 110.5 g
Concept introduction:
Number of moles is equal to the ratio of given mass to the molar mass.
The mathematical expression is given by:
Number of moles =
Molar mass of the molecule is equal to the sum of the masses of atoms present in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 17STP
Mass of nitrogen in 475 g of compound is
Explanation of Solution
According to the given figure,
Percentage of carbon = 19.68 %
Percentage of oxygen = 52.42 %
Percentage of hydrogen = 4.96 %
Percentage of nitrogen = 22.95 %
Let, total mass of the compound = 100 grams.
Thus, mass of carbon (
Mass of oxygen (
Mass of hydrogen (
Mass of nitrogen (
Now,
Molar mass of carbon = 12.011 g/mole
Number of moles of carbon =
=
Molar mass of oxygen = 15.999 g/mole
Number of moles of oxygen =
=
Molar mass of hydrogen = 1.008 g/mole
Number of moles of hydrogen =
=
Molar mass of nitrogen = 14.007 g/mole
Number of moles of nitrogen =
=
Divide each number of moles by smallest number 1.64.
Number of moles of carbon =
= 1 mole
Number of moles of oxygen =
= 2 moles
Number of moles of hydrogen =
= 3 moles
Number of moles of nitrogen =
= 1 mole
Thus, the formula of compound is
Total mass of compound is 475 g.
Molar mass of
Number of moles of
In
Number of moles of nitrogen = 1 mole
Molar mass of nitrogen = 14.007 g/mole
Thus, mass of nitrogen in 475 g of compound =
=
Mass of nitrogen =
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
- Which of the following are descriptions of possible starting material for this reaction? H ? trace acid an ester a ketone an imine an aldehyde a carboxylic acid an enamine a primary amine a secondary amine a tertiary aminearrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardWhat are the reagents needed for this and the third structure I only got the top right structure rightarrow_forward
- Please label this COZY spectraarrow_forwardPlease label this HNMRarrow_forwardConsider the following gas chromatographs of Compound A, Compound B, and a mixture of Compounds A and B. Inject A B mixture Area= 9 Area = 5 Area = 3 Area Inject . མི། Inject J2 What is the percentage of Compound B in the the mixture?arrow_forward
- Rank these according to stability. CH3 H3C CH3 1 CH3 H3C 1 most stable, 3 least stable O 1 most stable, 2 least stable 2 most stable, 1 least stable O2 most stable, 3 least stable O3 most stable, 2 least stable O3 most stable, 1 least stable CH3 2 CH3 CH3 H₂C CH3 3 CH3 CHarrow_forwardConsider this IR and NMR: INFRARED SPECTRUM TRANSMITTANCE 0.8- 0.6 0.4 0.2 3000 10 9 8 00 HSP-00-541 7 CO 6 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) сл 5 ppm 4 M Which compound gave rise to these spectra? N 1000 1 0arrow_forwardConsider this reaction (molecular weights are under each compound): HC=CH + 2 HCI --> C2H4Cl 2 MW = 26 36.5 99 If 4.4 g of HC=CH are reacted with 110 mL of a 2.3 M HCI solution, and 6.0 g of product are actually produced, what is the percent yield?arrow_forward
- What is the name of the major product of this reaction? OH CH3 H₂SO4, heat 1-methylcyclohexene O2-methyl-1-cyclohexene O 3-mthylcyclohexene 1-methyl-2-cyclohexenearrow_forwardWe added a brown solution of Br2 to one of our products, and the brown color disappeared. This indicated that our product wasarrow_forwardRank the following according to reactivity toward nitration: a) benzene b) bromobenzene c) nitrobenzene d) phenol Od) greatest, c) least Od) greatest, b) least Od) greatest, a) least a) greatest, b) least a) greatest, c) least Oa) greatest, d) least Ob) greatest, a) least O b) greatest, c) least Ob) greatest, d) least O c) greatest, a) least O c) greatest, b) least O c) greatest, d) leastarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





