
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The difference betweencis - and trans - isomers should be described in terms of geometrical arrangement.
Concept introduction:
The molecule with same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in spatial arrangements of atoms in the molecule are said to be geometric isomers of each other.
Explanation of Solution
Geometric isomerism, or cis-trans, isomerism is most common in
In cis- isomer, the two identical groups or atoms are close to each other whereas in trans- isomer two identical groups or atoms are farther apart.
For example:
The structures for cis -3-hexene and trans -3-hexene (hex represents the parent chain contains six carbon atoms and 3 represents the position of double bond in the chain) is:
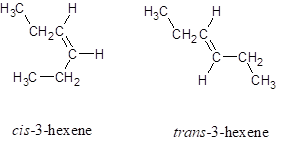
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- 3. Draw ALL THE POSSBILE PRODUCTS AND THE MECHANISMS WITH ALL RESONANCE STRUCTURES. Explain using the resonance structures why the major product(s) are formed over the minor product(s). H₂SO4, HONO CHarrow_forward7. Provide the product(s), starting material(s) and/or condition(s) required for the No mechanisms required. below reaction HO + H-I CI FO Br2, FeBr3 O I-Oarrow_forward6. Design the most efficient synthesis of the following product starting from phenot Provide the reaction conditions for each step (more than one step is required) and explain the selectivity of each reaction. NO MECHANISMS ARE REQUIRED. OH step(s) CIarrow_forward
- What is the skeletal structure of the product of the following organic reaction?arrow_forwardIf a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardWhat is the major organic product of the following nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction of an acid chloride below?arrow_forward
- Would the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forwardIf a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following questions using the data I included. 1&2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





