
Interpretation:
The values of k should be calculated for the reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate Law can be expressed as an integrated rate law and a differential rate law.
Differential Rate Law: This describes the change in the concentrations of reactant as a function of time.
Integrated Rate Law: This describes the initial concentrations and the measured concentration of one or more reactants as a function of time.
The proportionality coefficient which relates the
Answer to Problem 14STP
The value of rate constant is equal to 7.93×103 M−2⋅s−1.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Data is given as:
| [A] Initial | [B] Initial | Initial rate ( mol/L⋅s ) |
| 0.10 M | 0.10 M | 7.93 |
| 0.30 M | 0.10 M | 23.79 |
| 0.30 M | 0.20 M | 95.16 |
The general expression of rate law is expressed as:
Rate = k[A]m[B]n
Where, m and n are the experimentally determined values.
Experiment 1:
Rate law expression is written as:
7.93 = k[0.10]m[0.10]n (1)
Experiment 2:
Rate law expression is written as:
23.79 = k[0.30]m[0.10]n (2)
Experiment 3:
Rate law expression is written as:
95.16 = k[0.30]m[0.20]n (3)
Now, divide equation (2) by (1):
23.79 = k[0.30]m[0.10]n7.93 = k[0.10]m[0.10]n
3=(3)m
m =1
Now, divide equation (3) by (2):
95.16 = k[0.30]m[0.20]n23.79 = k[0.30]m[0.10]n
4 =(2)n
22 =(2)n
n =2
Thus, rate law expression is written as:
Rate = k[A]1[B]2
Now,
For experiment 1:
[A]=0.10 M
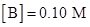
Rate = 7.93 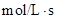
Put the values, in rate law expression:
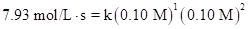
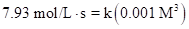
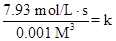
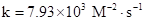
Thus, value of rate constant is equal to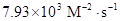
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
- Show the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardDraw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forward
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardPart I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forward
- what are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forwardWhat are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward1) a) Give the dominant Intermolecular Force (IMF) in a sample of each of the following compounds. Please show your work. (8) SF2, CH,OH, C₂H₂ b) Based on your answers given above, list the compounds in order of their Boiling Point from low to high. (8)arrow_forward
- 19.78 Write the products of the following sequences of reactions. Refer to your reaction road- maps to see how the combined reactions allow you to "navigate" between the different functional groups. Note that you will need your old Chapters 6-11 and Chapters 15-18 roadmaps along with your new Chapter 19 roadmap for these. (a) 1. BHS 2. H₂O₂ 3. H₂CrO4 4. SOCI₂ (b) 1. Cl₂/hv 2. KOLBU 3. H₂O, catalytic H₂SO4 4. H₂CrO4 Reaction Roadmap An alkene 5. EtOH 6.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 7. Mild H₂O An alkane 1.0 2. (CH3)₂S 3. H₂CrO (d) (c) 4. Excess EtOH, catalytic H₂SO OH 4. Mild H₂O* 5.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH An alkene 6. Mild H₂O* A carboxylic acid 7. Mild H₂O* 1. SOC₁₂ 2. EtOH 3.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/E:OH 5.1.0 Equiv. NaOEt 6. NH₂ (e) 1. 0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 2. Mild H₂O* Br (f) i H An aldehyde 1. Catalytic NaOE/EtOH 2. H₂O*, heat 3. (CH,CH₂)₂Culi 4. Mild H₂O* 5.1.0 Equiv. LDA Br An ester 4. NaOH, H₂O 5. Mild H₂O* 6. Heat 7. MgBr 8. Mild H₂O* 7. Mild H₂O+arrow_forwardLi+ is a hard acid. With this in mind, which if the following compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices LiBr LiI LiF LiClarrow_forwardQ4: Write organic product(s) of the following reactions and show the curved-arrow mechanism of the reactions. Br MeOH OSO2CH3 MeOHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





