
Concept explainers
a)
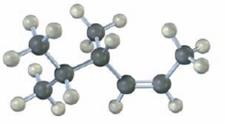
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound – the alkene name ends with the suffix –ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The requirement for cis-trans isomerism is that both the carbons in double bond should be bonded to different substituents. Compounds that have one of their doubly bonded carbons bonded to identical substituents cannot exist as cis-trans isomers.
To name:
The alkene including cis or trans designation.
b)
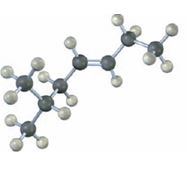
Interpretation:
The alkene shown to be named including cis or trans designation.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound – the alkene name ends with the suffix –ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The requirement for cis-trans isomerism is that both the carbons in double bond should be bonded to different substituents. Compounds that have one of their doubly bonded carbons bonded to identical substituents cannot exist as cis-trans isomers.
To name:
The alkene including cis or trans designation.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw a Newman projection for the molecule below from the perspective indicated. Which of the groups (letters A-H) are methyl groups? CH3 H H H A H B ☑ >> H. ABCDEFG I H -H CH3 G D CH F E Numeric 4 points How many gauche interactions exist in the conformation shown in the previous problem? 1arrow_forward
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward13) When solid barium phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of barium ions to phosphate ions would be: a. 1:1 b. 2:3 c. 3:2 d. 2:1 14) The pH of a 0.05 M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is 15) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of KOH at 25°C isarrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward7) The pH of a 0.05M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is a. 1.3 b. 2.3 c. 3.3 d. 12.7arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning


