
Concept explainers
a)
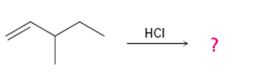
Interpretation:
The product and the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
Concept introduction:
In electrophilic addition reactions, the first step is the attack of the π electrons of the double bond on the hydrogen of the
To predict:
The product and to show the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
b)
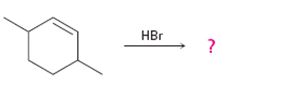
Interpretation:
The product and the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
Concept introduction:
In electrophilic addition reactions, the first step is the attack of the π electrons of the double bond on the hydrogen of the alkyl halide to yield a carbocation. One of the carbon in C=C gets attached to hydrogen while the other acquires a positive charge. In the second step, the carbocation formed can rearrange to give another more stable carbocation either by a hydride shift (shift of hydrogen atom with its electron pair) or by an alkyl shift (shift of an alkyl group with its electron pair) between neighboring carbons. In the last step the carbocation produced reacts with the halide ion to give the alkyl halide.
To predict:
The product and to show the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
c)

Interpretation:
The product and the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
Concept introduction:
In electrophilic addition reactions, the first step is the attack of the π electrons of the double bond on the H+ of the acid to yield a carbocation. One of the carbon in C=C gets attached to hydrogen while the other acquires a positive charge. In the second step, the carbocation formed can rearrange to give a more stable carbocation either by a hydride shift (shift of hydrogen atom with its electron pair) or by an alkyl shift (shift of an alkyl group with its electron pair) between neighboring carbons. In the last step the carbocation produced reacts with the halide ion to give the alkyl halide.
To predict:
The product and to show the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Choose the major product of the reaction with correct regio- and stereochemistry. Br2 H₂O O "Br Br & O 'Br OH Br 吡 O OH OH Br "OH Brarrow_forwardSelect the major product of the following reaction. & Br (CH)CONa (CH₂),COH 0 OC(CH) O &arrow_forwardDraw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forward
- What is the unsaturation number for compounds with the formula C₂H₁₂Cl₂? O õ õ o o 4 3arrow_forwardIndicate the product obtained (formula). F3C. CF3 Br NH2 NH OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forwardWhat are the missing intermediates 1, 2, and 3? Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediates and how they occur.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
