
Concept explainers
a)
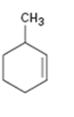
Interpretation:
The name of the cycloalkane shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The maximum number of carbons in the ring is counted. Based on the name of the parent cycloalkane–the cycloalkene is named with the suffix–ene. The cycloalkane is numbered such that the double bond is in between C1 & C2 and the first substituent has the lowest number possible. Usually the position of a double bond is not shown in the name because it is always between C1 & C2. In dienes and trienes, however the position of double bonds is shown.
To name:
The cycloalkane shown.
b)
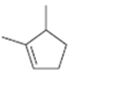
Interpretation:
The name of the cycloalkane shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The maximum number of carbons in the ring is counted. Based on the name of the parent cycloalkane–the cycloalkene is named with the suffix–ene. The cycloalkane is numbered such that the double bond is in between C1 & C2 and the first substituent has the lowest number possible. Usually the position of a double bond is not shown in the name because it is always between C1 & C2. In dienes and trienes, however the position of double bonds is shown.
To name:
The cycloalkane shown.
c)
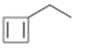
Interpretation:
The name of the cycloalkane shown to be given.
Concept introduction:
The maximum number of carbons in the ring is counted. Based on the name of the parent cycloalkane the cycloalkene is named with the suffix–ene. The cycloalkane is numbered such that the double bond is in between C1 & C2 and the first substituent has the lowest number possible. Usually the position of a double bond is not shown in the name because it is always between C1 & C2. In dienes and trienes, however the position of double bonds is shown.
To name:
The cycloalkane shown.
d)
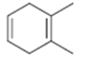
Interpretation:
The name the cycloalkane shown to be given.
Concept introduction:
The maximum number of carbons in the ring is counted. Based on the name of the parent cycloalkane–the cycloalkene is named with the suffix–ene. The cycloalkane is numbered such that the double bond is in between C1 & C2 and the first substituent has the lowest number possible. Usually the position of a double bond is not shown in the name because it is always between C1 & C2. In dienes and trienes, however the position of double bonds is shown.
To name:
The cycloalkane shown.
e)
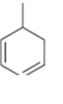
Interpretation:
The name the cycloalkane shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The maximum number of carbons in the ring is counted. Based on the name of the parent cycloalkane–the cycloalkene is named with the suffix–ene. The cycloalkane is numbered such that the double bond is in between C1 & C2 and the first substituent has the lowest number possible. Usually the position of a double bond is not shown in the name because it is always between C1 & C2. In dienes and trienes, however the position of double bonds is shown.
To name:
The cycloalkane shown
f)
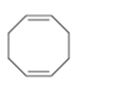
Interpretation:
The name of the cycloalkane shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The maximum number of carbons in the ring is counted. Based on the name of the parent cycloalkane–the cycloalkene is named with the suffix–ene. The cycloalkane is numbered such that the double bond is in between C1 & C2 and the first substituent has the lowest number possible. Usually the position of a double bond is not shown in the name because it is always between C1 & C2. In dienes and trienes, however the position of double bonds is shown.
To name:
The cycloalkane shown.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Steps and explanations pleasearrow_forwardUse diagram to answer the following: 1.Is the overall rxn endo- or exothermic. Explain briefly your answer____________________2. How many steps in this mechanism?_____________3. Which is the rate determining step? Explain briefly your answer____________________4. Identify (circle and label) the reactants,the products and intermediate (Is a Cation, Anion, or a Radical?) Please explain and provide full understanding.arrow_forwardDraw the entire mechanism and add Curved Arrows to show clearly how electrons areredistributed in the process. Please explain and provide steps clearly.arrow_forward
- Match the denticity to the ligand. Water monodentate ✓ C₂O2 bidentate H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate x EDTA hexadentate Question 12 Partially correct Mark 2 out of 2 Flag question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below: Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2✔ Geometry: linear Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x in 12 correct out of 2 question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below. Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2 Geometry: linear 0 Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3Xarrow_forwardCan you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward
- 2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forwardconsider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


