
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
The configurational stereochemistry of the molecules to be determined.
Answer to Problem 26VC
The Fischer projection follows as
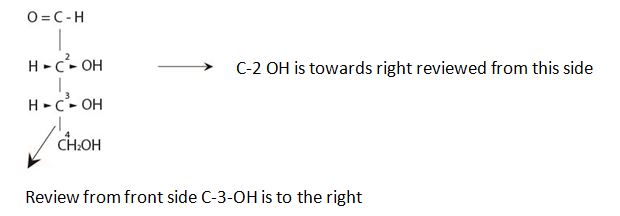
It is D sugar the molecule is a retrose. Elclose or eldotetrose, is 4-carbon elclose.
Explanation of Solution
Concept strategy: The Fischer projection of the given monosaccharide is drawn vertically, by rotating the molecule anticlockwise 90° so that the carbonyl
Review from front side C-3-OH is to the right By convention the molecule has the C-3 hyduxyl at the right. So it is D sugar the molecule is a retrose. Elclose or eldotetrose, is 4-carbon elclose.
Based on the Fischer projection formula for the given sugars it is a B-D-glucopyranose monosaccharide.
b)
Interpretation:
The configurational stereochemistry of the molecules to be determined.
Answer to Problem 26VC
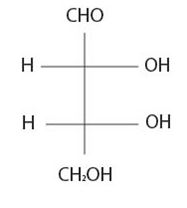
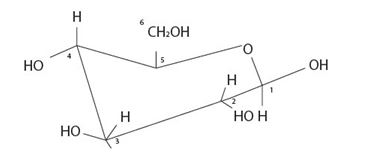
The given model is the cyclic structures of an aldohexose in six membered pyranose form.
Strategy: We redraw the model as
Explanation of Solution
By convention, the terminal -CH2OH group is on the top of the chair Pyranose structure. Thus it is a D sugar. The molecule is an aldohexose is B-D-glucopyranose, all the –OH groups are equatorial (and more stable due to minimum repulsion) conformation.
Based on the Fischer projection formula for the given sugars it is a B-D-glucopyranose monosaccharide.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 1. For each of the reaction "railroads" below, you are either asked to give the structure(s) of the starting material(s) or product(s), or provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the transformation, as indicated by the boxes. a. NaOMe H+ .CO,H HO₂C MeOH (excess) MeOH H3C Br يع CH3 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ 3. PBг3 H3C 1. Et-Li 2. H3O+ -CO₂Me -CO₂Me OH CH3 CH3 ল CH3arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe ག1, ད།་, - + H You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. 2 work up Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Parrow_forwardWhat is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forward
- ΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forwardIdentify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forward
- Identify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forward
