
Concept explainers
a)
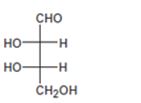
Interpretation:
The configuration as R or S is to be assigned to each chirality center in the monosaccharide given and whether it is a D sugar or L sugar is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In Fischer projection formula, a tetrahedral carbon is represented by two crossed lines. The horizontal line represents bonds coming out of the page and vertical lines represent bonds moving in to the page.
For assigning R or S configuration, the four groups attached to the chiral center are arranged in the order of priority by applying sequence rules. The molecule is then oriented in such a way that the group of lowest priority points away from the viewer. If the arrangement of highest priority to second highest priority to third highest priority is clockwise then R configuration is assigned. If the arrangement of highest priority to second highest priority to third highest priority is counterclockwise then S configuration is assigned.
In Fischer projections, D sugars have the hydroxyl group on right at the farthest chirality center and L sugars have this hydroxyl group on left.
To assign:
The configuration as R or S to each chirality center in the monosaccharide given and to state whether it is a D sugar or L sugar.
b)
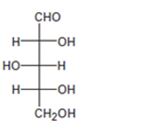
Interpretation:
The configuration as R or S is to be assigned to each chirality center in the monosaccharide given and whether it is a D sugar or L sugar is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
For assigning R or S configuration, the four groups attached to the chiral center are arranged in the order of priority by applying sequence rules. The molecule is then oriented in such a way that the group of lowest priority points away from the viewer. If the arrangement of highest priority to second highest priority to third highest priority is clockwise then R configuration is assigned. If the arrangement of highest priority to second highest priority to third highest priority is counterclockwise then S configuration is assigned.
To assign:
The configuration as R or S to each chirality center in the monosaccharide given and to state whether it is a D sugar or L sugar.
c)
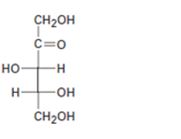
Interpretation:
The configuration as R or S is to be assigned to each chirality center in the monosaccharide given and whether it is a D sugar or L sugar is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In Fischer projection formula, a tetrahedral carbon is represented by two crossed lines. The horizontal line represents bonds coming out of the page and vertical lines represent bonds moving in to the page.
For assigning R or S configuration, the four groups attached to the chiral center are arranged in the order of priority by applying sequence rules. The molecule is then oriented in such a way that the group of lowest priority points away from the viewer. If the arrangement of highest priority to second highest priority to third highest priority is clockwise then R configuration is assigned. If the arrangement of highest priority to second highest priority to third highest priority is counterclockwise then S configuration is assigned.
To assign:
The configuration as R or S to each chirality center in the monosaccharide given and to state whether it is a D sugar or L sugar.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 8. What is the major product of the following reaction? KMnO4 b a TOH OH OH C d OH "OH HO OH OHarrow_forwardChoose the right answerarrow_forward3. Draw ALL THE POSSBILE PRODUCTS AND THE MECHANISMS WITH ALL RESONANCE STRUCTURES. Explain using the resonance structures why the major product(s) are formed over the minor product(s). H₂SO4, HONO CHarrow_forward
- 7. Provide the product(s), starting material(s) and/or condition(s) required for the No mechanisms required. below reaction HO + H-I CI FO Br2, FeBr3 O I-Oarrow_forward6. Design the most efficient synthesis of the following product starting from phenot Provide the reaction conditions for each step (more than one step is required) and explain the selectivity of each reaction. NO MECHANISMS ARE REQUIRED. OH step(s) CIarrow_forwardWhat is the skeletal structure of the product of the following organic reaction?arrow_forward
- If a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardWhat is the major organic product of the following nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction of an acid chloride below?arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
- If a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following questions using the data I included. 1&2arrow_forwardAssign all the Protons in HNMRarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





