
(a)
Interpretation:
The given compound is a hemiacetal or not has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Hemiacetal is a addition product that is obtained by reaction between aldehyde or ketone with alcohol. The general reaction of hemiacetal formation can be given as,
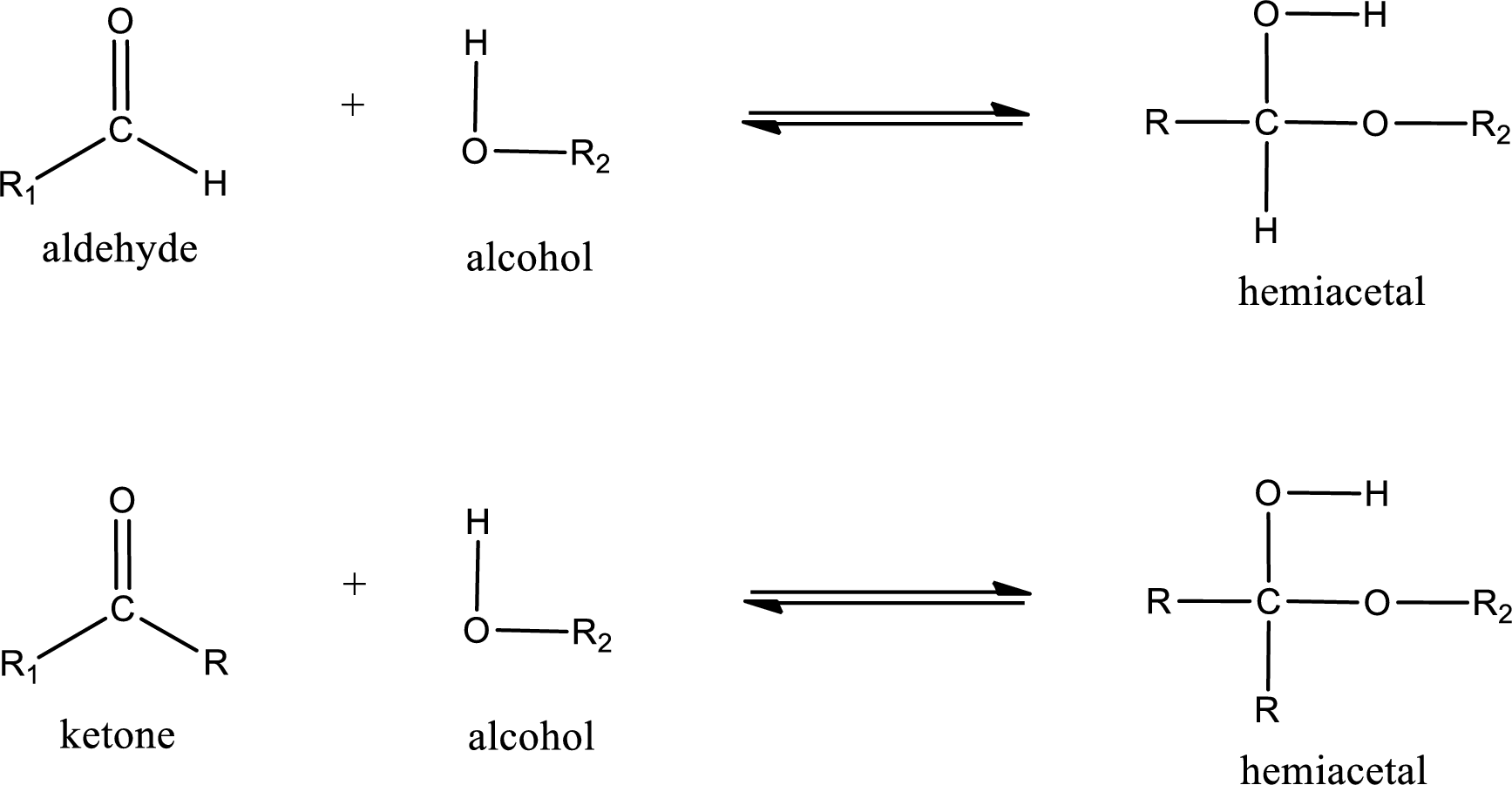
From the above general structure of hemiacetal it is found that it is an organic compound that contains a carbon atom that is bonded to an alkoxy group and a hydroxyl group.
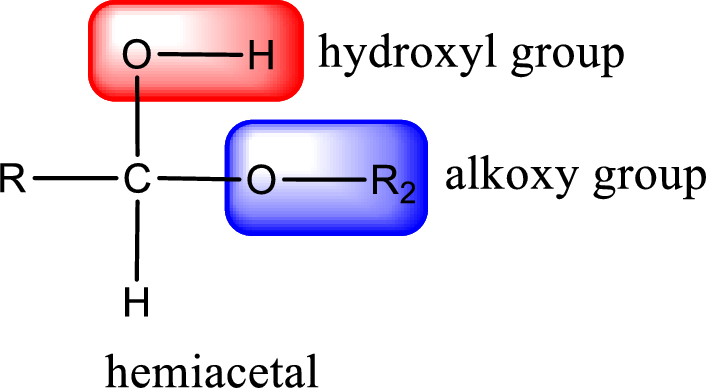
(b)
Interpretation:
The given compound is a hemiacetal or not has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that is bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom. Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Hemiacetal is a addition product that is obtained by reaction between aldehyde or ketone with alcohol. The general reaction of hemiacetal formation can be given as,
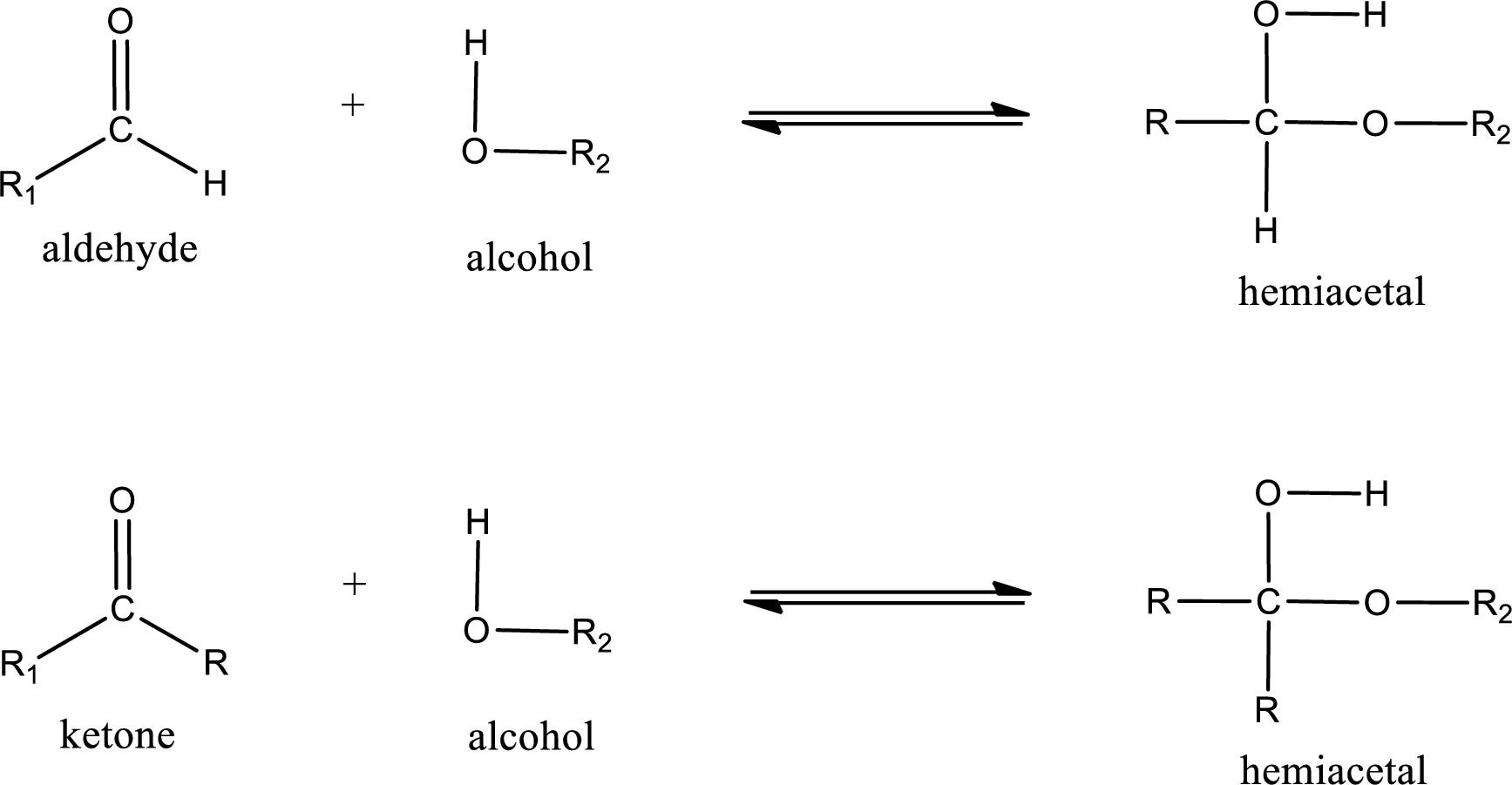
From the above general structure of hemiacetal it is found that it is an organic compound that contains a carbon atom that is bonded to an alkoxy group and a hydroxyl group.
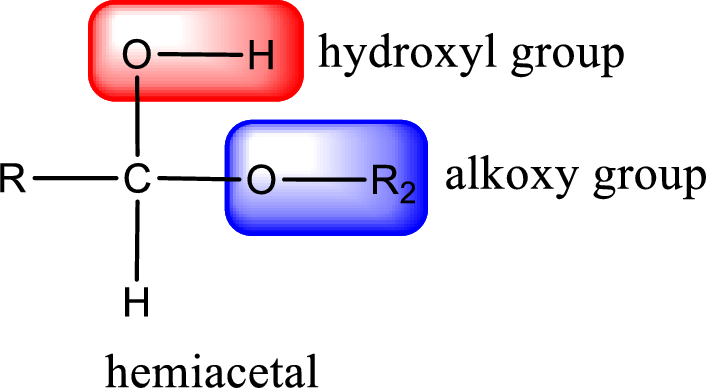
(c)
Interpretation:
The given compound is a hemiacetal or not has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that is bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom. Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Hemiacetal is a addition product that is obtained by reaction between aldehyde or ketone with alcohol. The general reaction of hemiacetal formation can be given as,
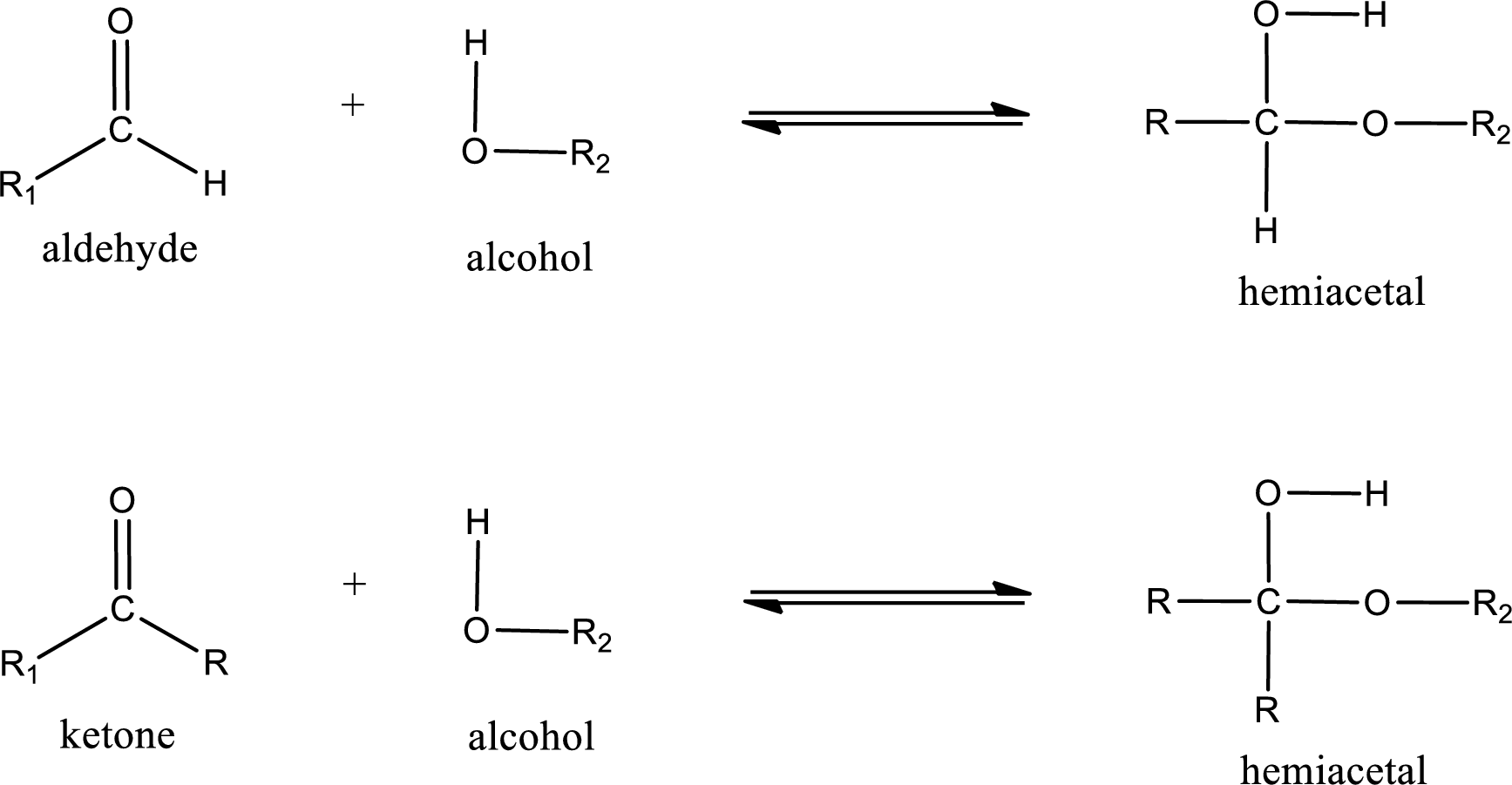
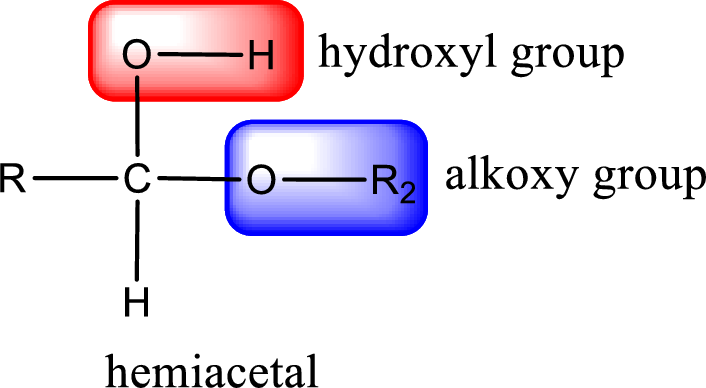
From the above general structure of hemiacetal it is found that it is an organic compound that contains a carbon atom that is bonded to an alkoxy group and a hydroxyl group.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given compound is a hemiacetal or not has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that is bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom. Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Hemiacetal is a addition product that is obtained by reaction between aldehyde or ketone with alcohol. The general reaction of hemiacetal formation can be given as,
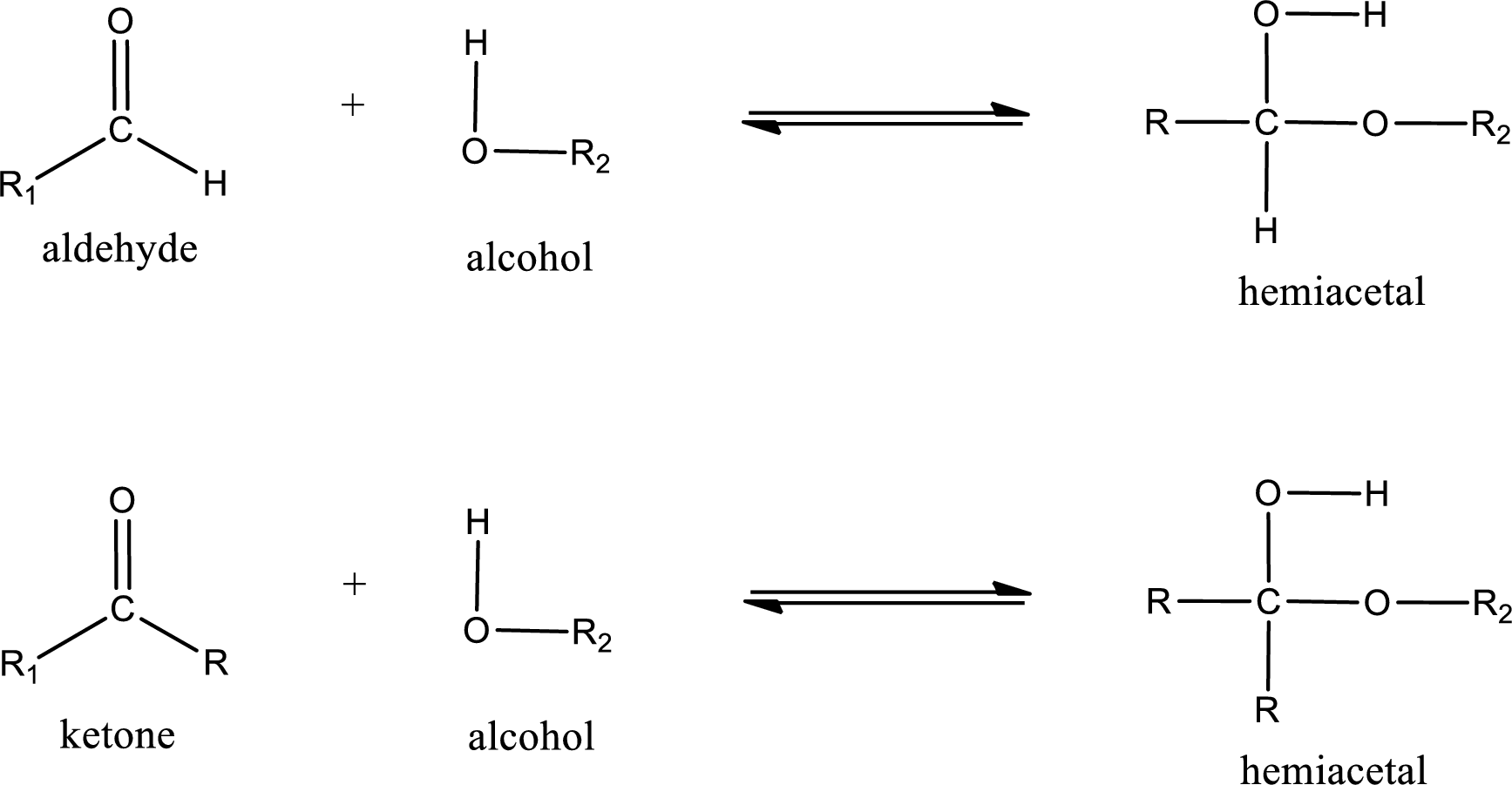
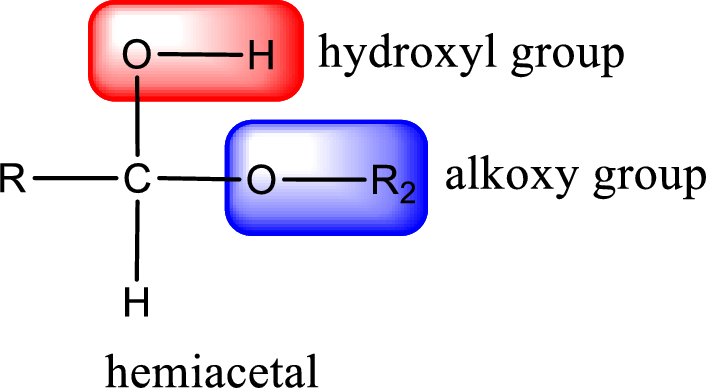
From the above general structure of hemiacetal it is found that it is an organic compound that contains a carbon atom that is bonded to an alkoxy group and a hydroxyl group.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids: Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val A. Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine. B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardGive the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry.[4 only] CH3 A. B. HNO H₂Pt H₂SO4 hano NaN 1. LIAH ether Br 4 2 H₂O C. D. E. CH3CH2-CH2CH3 + HCl Br NH₂ CH3 ON CH-CH3 Br HNOZ CUCI 11,504 HC) 1. HNO H SO NH₂ 2 UMarrow_forwardConsider the Grignard reaction below to answer the following questions. A Mgar 1. ether + MyC CH3 2H3O C B a. The electrophile in this reaction is: b. The nucleophile in this reaction is: c. The alcohol product can be classified as a: a. 1° alcohol b. 2° alcohol C. 3° alcohol d. 4° alcohol HO CH3 CHarrow_forward
- Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry A. CH₂OH PCC CH2Cl2 HOO B. H KCN HCN of b C. 1. CH,MgBr, ether 2 HO* D. Choose the BEST reagent for carrying out each of the following conversions. CO₂CH3 CO₂CH3 OH CO₂H сон ن نے a. LiAlH4, ether at abinayo iss c b. NaBH4, ethanol C. CrO3, pyridine d. H₂/Pd d notsiolarrow_forwardChoose the best reagent for carrying out the following reactions from the list below. Place the letter of the reagent(s) in the box over the reaction arrow. Use only one letter per box. OH OH CH CH CH3 CHS CH3 f OH OCH 3 H A. NaH, then CHI B. C. m-ClC6H4COзH D. E. warm H2SO4/H₂O F. G. H₂/Pd H. I. Cl₂, H₂O J. NaOCH3, CH3OH CH3MgBr in ether, then H3O+ Hg(O2CCF3)2, CH3OH PCC, CH2Cl2 LiAlH4 in ether, then H3O+arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the reaction of 2,4-pentanedione with phenylhydrazine?arrow_forward
- In the reaction of naphthalene with CrO3 in acetic acid. Indicate whether a different product is obtained if carried out at 25°C or with heating (A).arrow_forwardQUESTION: Fill in the answers in the empty green boxes 1. Step 2 2. Step 3 3. Step 4 (SUM) 4. Step 5 (df) (GIVEN) 5. Determine S y/x value *The data values have been provided in the worksheet attached in the first image*arrow_forwardIf the symbol A is placed in a reaction, at what temperature does it take place?arrow_forward
- By malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 3-methyl-4-oxopentanoic acid (indicate the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forwardoalmitic acid is a 16 carbon acid. In a balanced equation, the products of the sponification of tripalmitin (glyceryl tripalmitate are blank.arrow_forwardWrite the esterification reaction mechanism of salicylic acid and acetic acid to produce aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). Note: salicylic acid will act as the alcoholarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





