
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas of the product formed from hydrolysis of given acetal in an acid solution has drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Acetals are stable in basic solution. But in acidic solution, they undergo hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is a
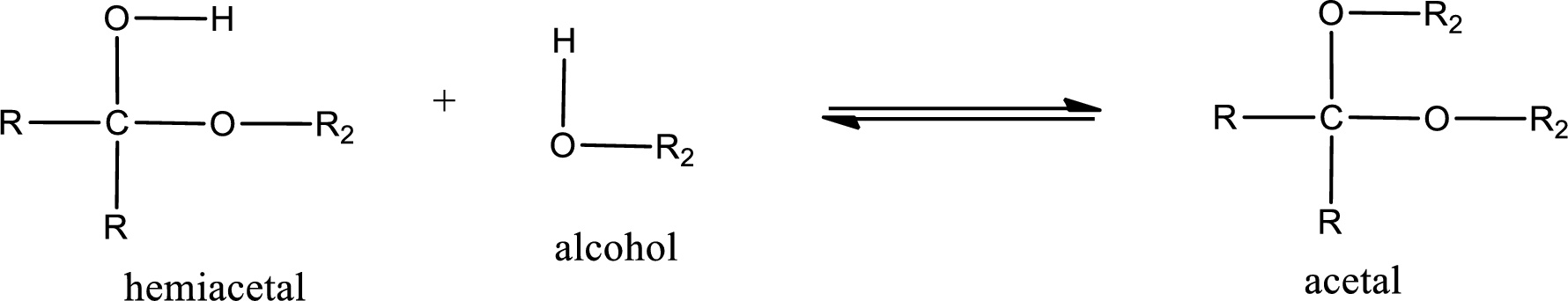
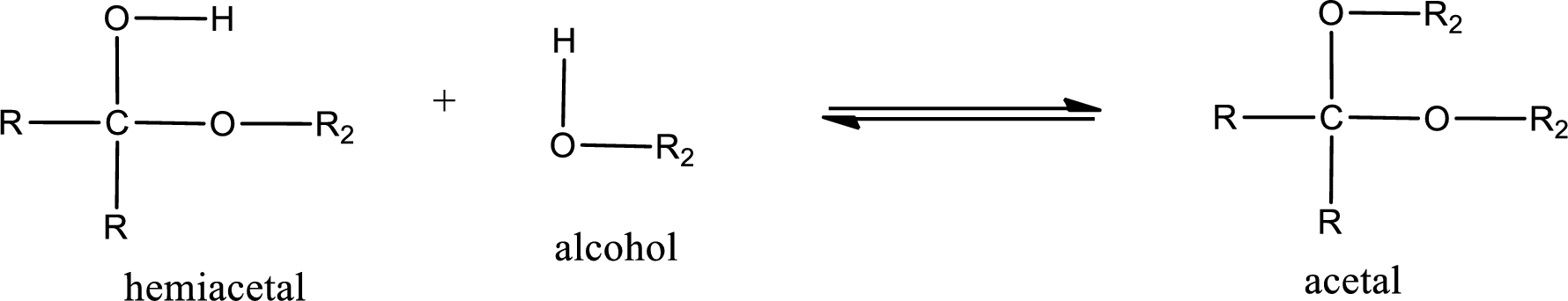
Acetal is formed when the formed hemiacetal reacts with further alcohol molecule so that the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal is converted into alkoxy group. This can be shown as given below,
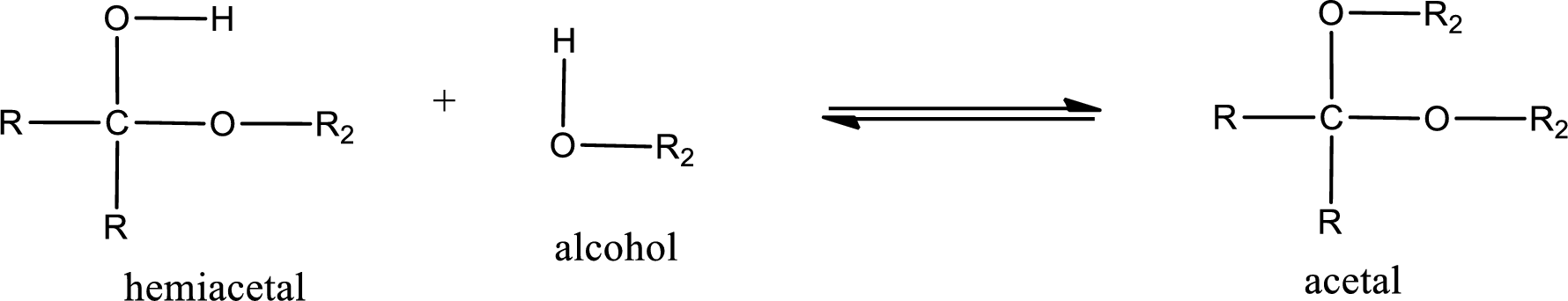
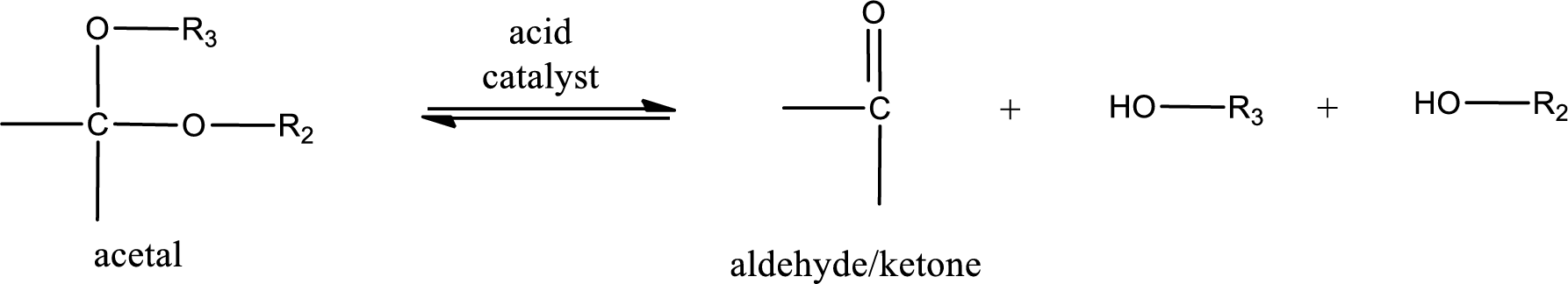
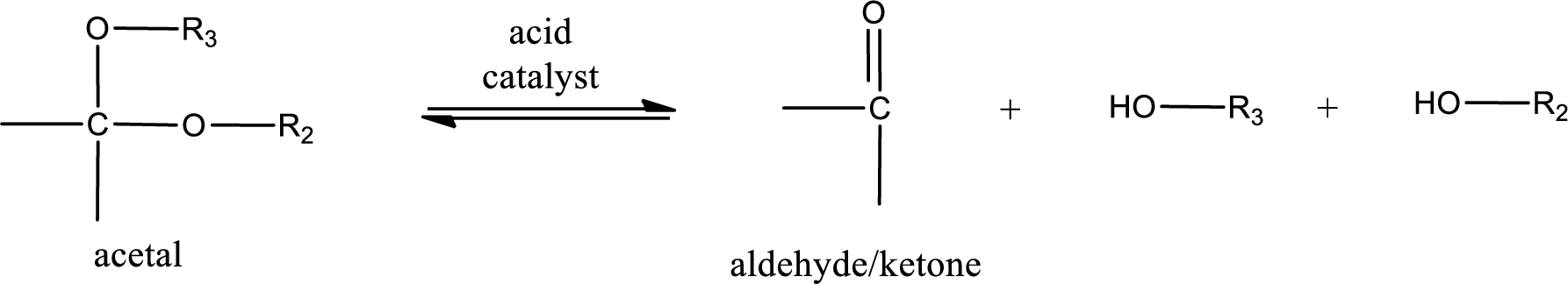
Acetal undergoes hydrolysis in acidic solution to form two alcohol molecules and ketone or aldehyde molecule. The general reaction for hydrolysis of acetal in acid solution,
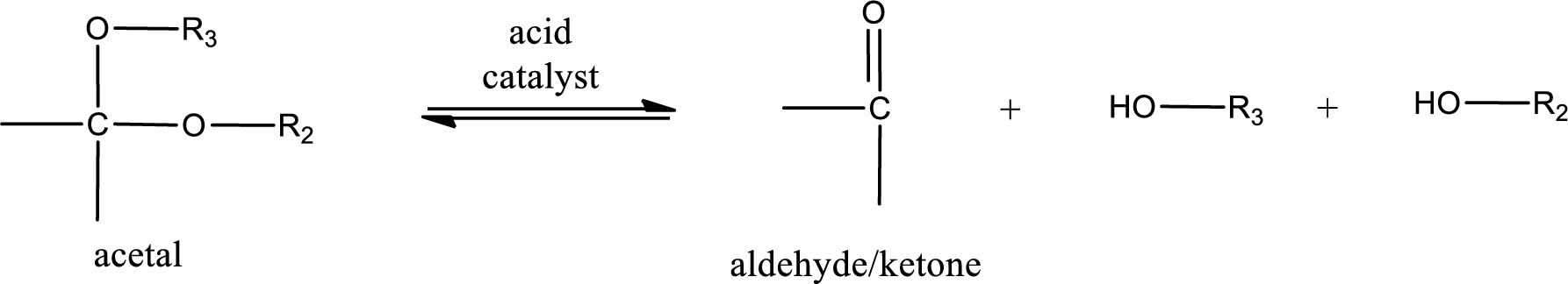
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas of the product formed from hydrolysis of given acetal in an acid solution has drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that is bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom. Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Acetals are stable in basic solution. But in acidic solution, they undergo hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which the compound splits into two or more fragments when water is added to the compound in presence of acid or base as catalyst. Acetals undergo hydrolysis to give the respective starting materials from which it is formed.
Acetal is formed when the formed hemiacetal reacts with further alcohol molecule so that the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal is converted into alkoxy group. This can be shown as given below,
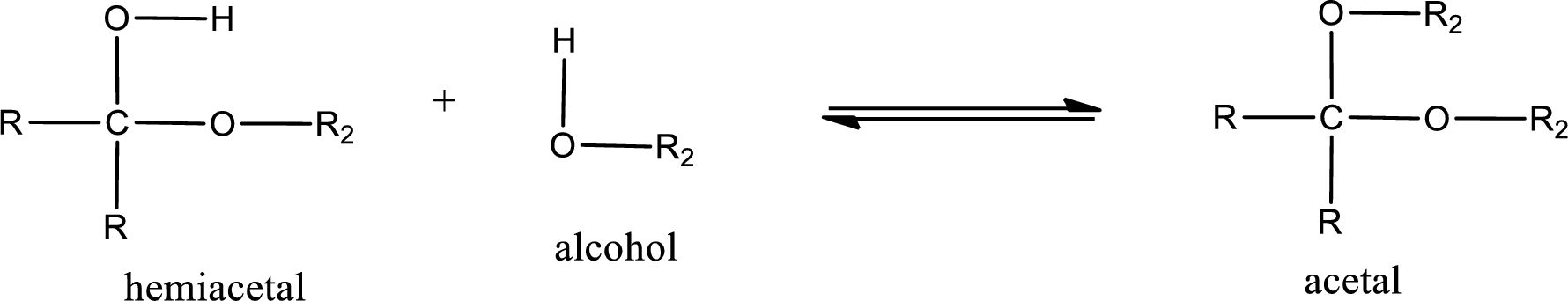
Acetal undergoes hydrolysis in acidic solution to form two alcohol molecules and ketone or aldehyde molecule. The general reaction for hydrolysis of acetal in acid solution,
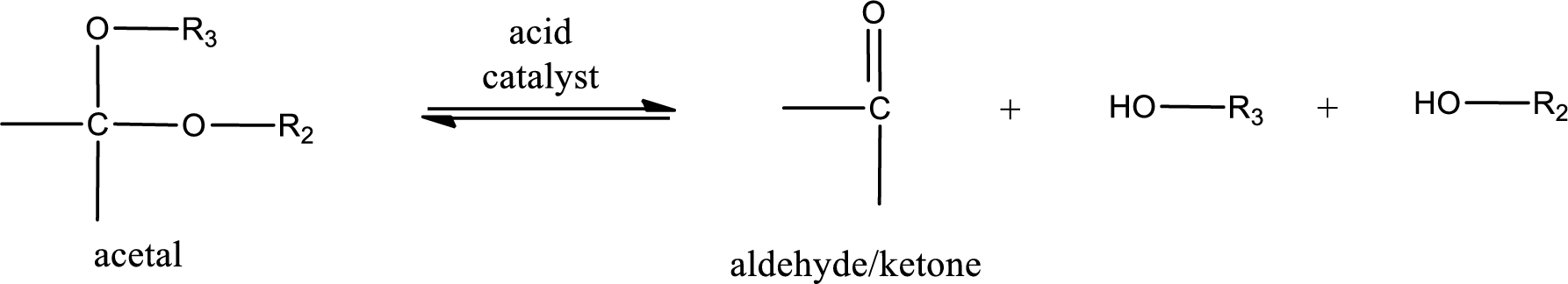
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas of the product formed from hydrolysis of given acetal in an acid solution has drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that is bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom. Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Acetals are stable in basic solution. But in acidic solution, they undergo hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which the compound splits into two or more fragments when water is added to the compound in presence of acid or base as catalyst. Acetals undergo hydrolysis to give the respective starting materials from which it is formed.
Acetal is formed when the formed hemiacetal reacts with further alcohol molecule so that the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal is converted into alkoxy group. This can be shown as given below,
Acetal undergoes hydrolysis in acidic solution to form two alcohol molecules and ketone or aldehyde molecule. The general reaction for hydrolysis of acetal in acid solution,
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas of the product formed from hydrolysis of given acetal in an acid solution has drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group that is bonded to a hydrogen atom and a carbon atom. Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction across the carbonyl group.
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohol to form hemiacetal as the product. This reacts with further molecule of aldehyde or ketone to form acetal.
Acetals are stable in basic solution. But in acidic solution, they undergo hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which the compound splits into two or more fragments when water is added to the compound in presence of acid or base as catalyst. Acetals undergo hydrolysis to give the respective starting materials from which it is formed.
Acetal is formed when the formed hemiacetal reacts with further alcohol molecule so that the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal is converted into alkoxy group. This can be shown as given below,
Acetal undergoes hydrolysis in acidic solution to form two alcohol molecules and ketone or aldehyde molecule. The general reaction for hydrolysis of acetal in acid solution,
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- oalmitic acid is a 16 carbon acid. In a balanced equation, the products of the sponification of tripalmitin (glyceryl tripalmitate are blank.arrow_forwardWrite the esterification reaction mechanism of salicylic acid and acetic acid to produce aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). Note: salicylic acid will act as the alcoholarrow_forwardWhat type of interaction would you expect between the following R groups in the tertiary structure of a protein? O -CH2-CO and -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-NH3+ a. disulfide bonds b. salt bridges c. hydrogen bonds HO abios vist anisinoo tedt bigil s ai loistaslor sale! 10 OUT d. hydrophobic interactions e. peptide bondsarrow_forward
- 4. True or false: This skeletal structure represents a saturated fatty acid. Ini to 0 fale) me OH faistong starrow_forwardBy malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 5-Methyl-2-hexanone (with the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the first photo attached*arrow_forward
- Draw the formula for 3-chlorobenzoic acetic anhydride.arrow_forwardBy malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 2-methylbutanoic acid (indicate the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forwardObtain 2-methylbutanoic acid by malonic or acetylacetic synthesis (indicate the formulas of the compounds involved).arrow_forward
- EFFICIENTS SAMPLE READINGS CONCENTRATIONS Pigiadient) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) 58 6.274 3.898 301.7 151.2 14150 5.277 3.865 348.9 254.8 B 5.136 3.639 193.7 85.9 605 4.655 3.041 308.6 199.6 05 5.135 3.664 339.5 241.4 0139 4.676 3.662 160.6 87.6 90148 5.086 3.677 337.7 242.5 0092 6.348 3.775 464.7 186.4 PART3 5.081 3.908 223.5 155.8 5.558 3.861 370.5 257.1 4.922 3.66 326.6 242.9 4.752 3.641 327.5 253.3 50 5.018 3.815 336.1 256.0 84 4.959 3.605 317.9 216.6 38 4.96 3.652 203.8 108.7 $3 5.052 3.664 329.8 239.0 17 5.043 3.767 221.9 149.7 052 5.058 3.614 331.7 236.4 5.051 4.005 211.7 152.1 62 5.047 3.637 309.6 222.7 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 995 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 04 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 16 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 0.011 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 AVERAGE STDEV COUNT 95% CI Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH₃COCH₃) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH), applying heat to them produces an aldol condensation of the two compounds. If this is correct, draw the formula for the final product.arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH3COCH3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH); if we apply heat (A), what product(s) are obtained?arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





