
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
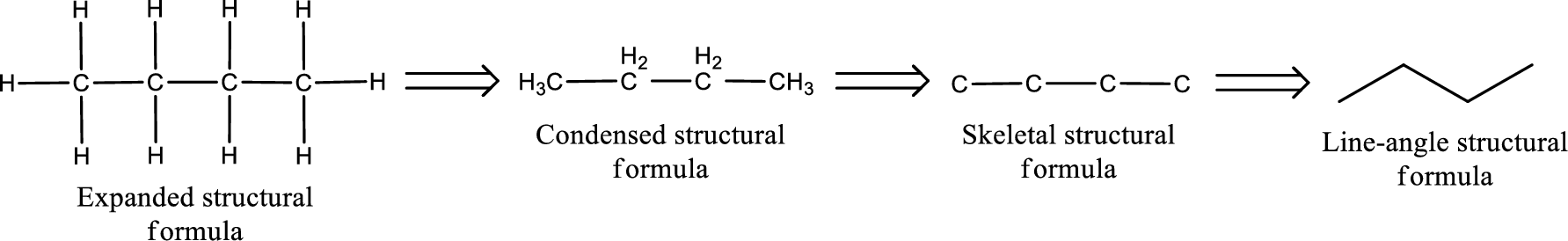
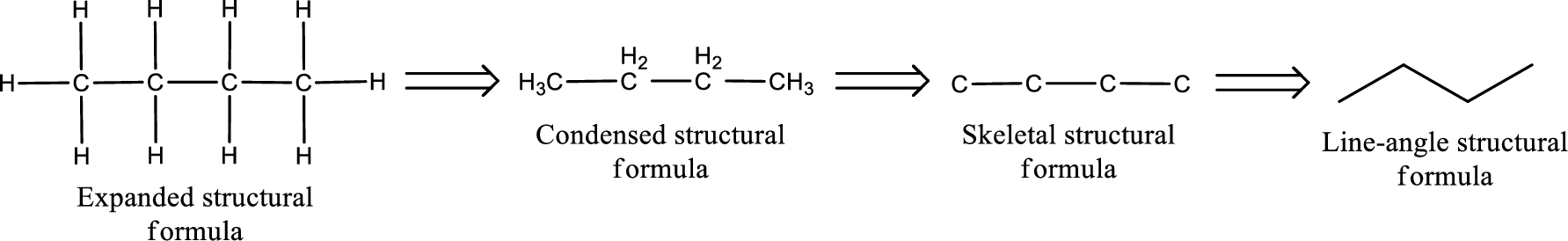
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(a)
Answer to Problem 4.22EP
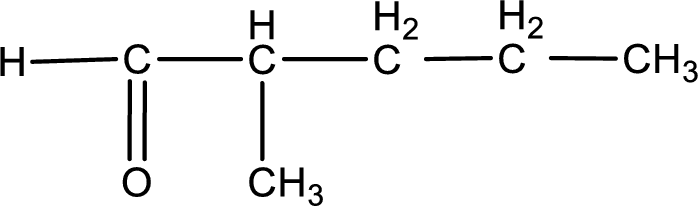
The structural formula for 2-methylpentanal is,
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 2-methylpentanal. From the name it is understood that the parent carbon chain is pentane and it contains five carbon atoms. The parent chain can be drawn as shown below,

From the name of the given aldehyde, the substituents that are present can be identified. In this case, the substituent is a methyl group on second carbon atom. The first carbon atom has to be the carbonyl carbon atom as the given compound is an aldehyde.
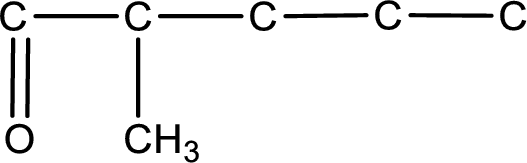
Carbon atom has a valence of four. Hence, carbon atom can form four covalent bonds. The remaining bonds are satisfied by hydrogen atom. The structure is obtained as shown below,
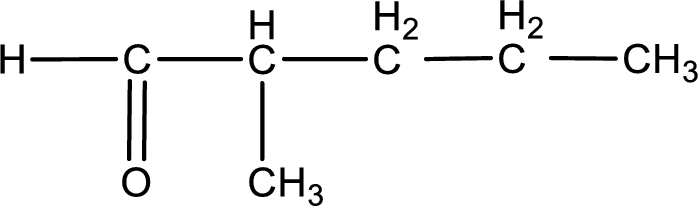
Structural formula for the given aldehyde is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given aldehyde has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
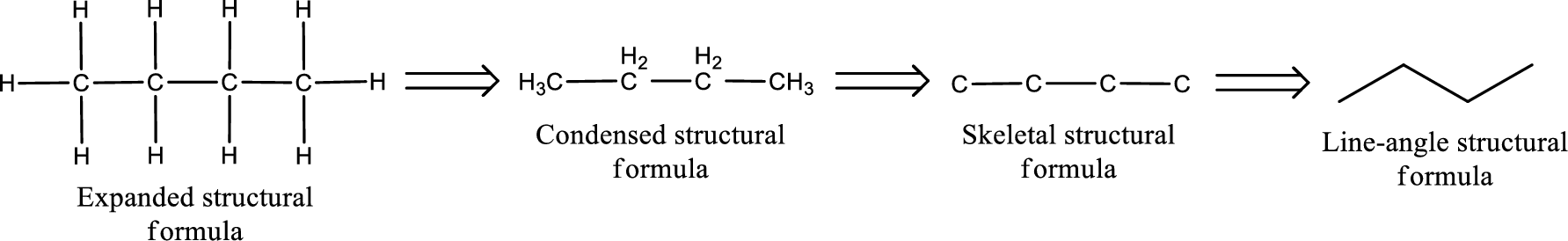
(b)
Answer to Problem 4.22EP
The structural formula for 4-ethylhexanal is,
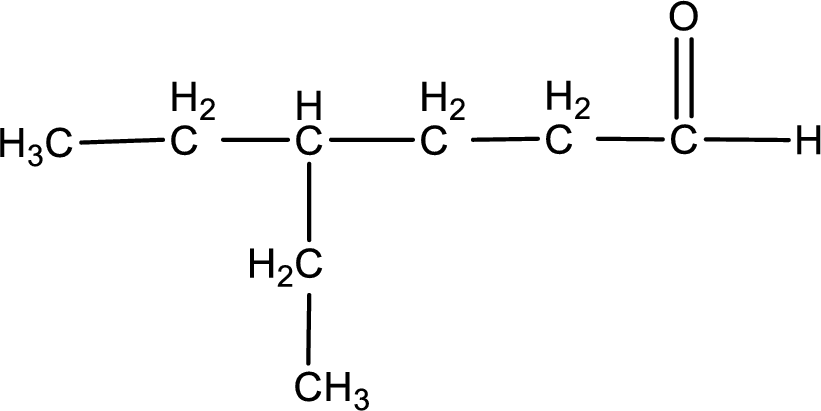
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 4-ethylhexanal. From the name it is understood that the parent carbon chain is hexane and it contains six carbon atoms. The parent chain can be drawn as shown below,
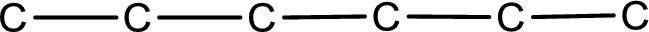
From the name of the given aldehyde, the substituents that are present can be identified. In this case, the substituent is an ethyl group on fourth carbon atom. The first carbon atom has to be the carbonyl carbon atom as the given compound is an aldehyde.
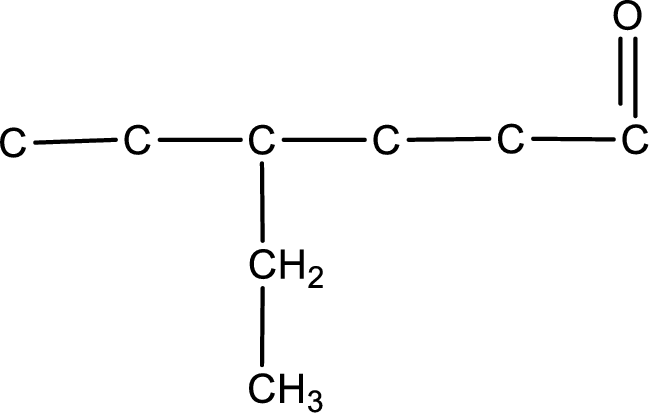
Carbon atom has a valence of four. Hence, carbon atom can form four covalent bonds. The remaining bonds are satisfied by hydrogen atom. The structure is obtained as shown below,
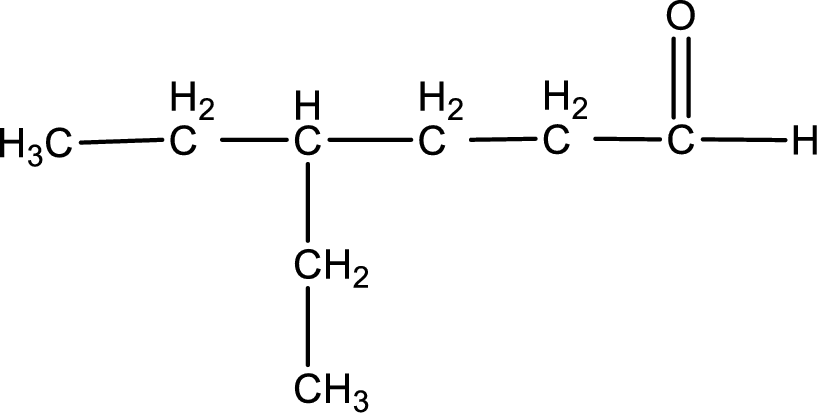
Structural formula for the given aldehyde is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given aldehyde has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(c)
Answer to Problem 4.22EP
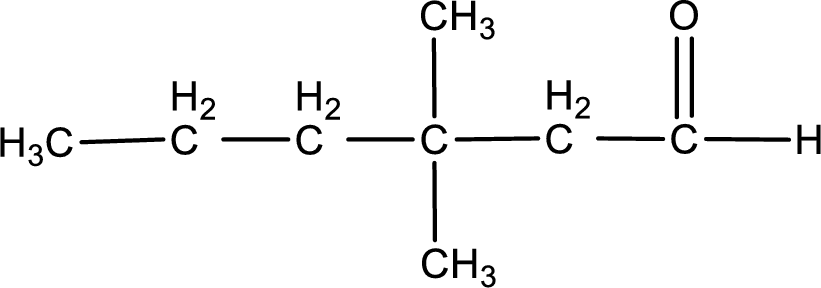
The structural formula for 3,3-dimethylhexanal is,
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 3,3-dimethylhexanal. From the name it is understood that the parent carbon chain is hexane and it contains six carbon atoms. The parent chain can be drawn as shown below,
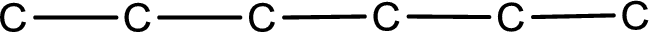
From the name of the given aldehyde, the substituents that are present can be identified. In this case, the substituents are two methyl groups on third carbon atom. The first carbon atom has to be the carbonyl carbon atom as the given compound is an aldehyde.
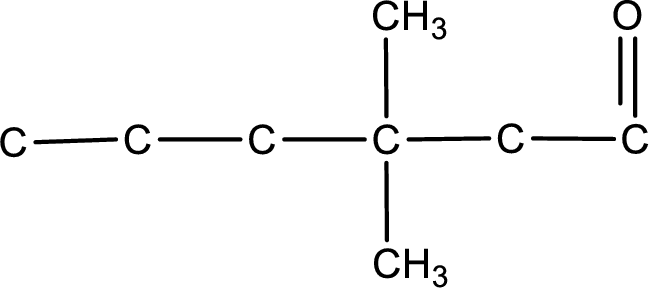
Carbon atom has a valence of four. Hence, carbon atom can form four covalent bonds. The remaining bonds are satisfied by hydrogen atom. The structure is obtained as shown below,
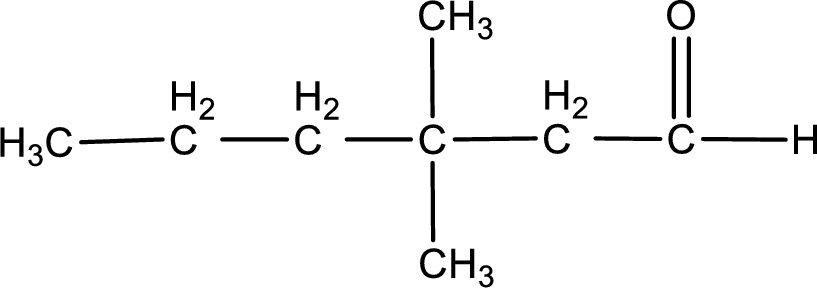
Structural formula for the given aldehyde is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given aldehyde has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(d)
Answer to Problem 4.22EP
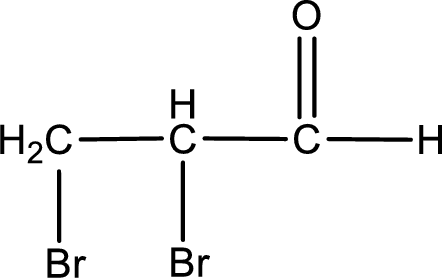
The structural formula for 2,3-dibromopropanal is,
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 2,3-dibromopropanal. From the name it is understood that the parent carbon chain is propane and it contains three carbon atoms. The parent chain can be drawn as shown below,
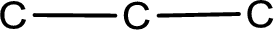
From the name of the given aldehyde, the substituents that are present can be identified. In this case, the substituents are two bromine atoms, each on second carbon atom and third carbon atom. The first carbon atom has to be the carbonyl carbon atom as the given compound is an aldehyde.
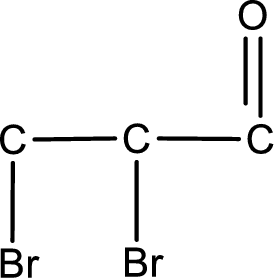
Carbon atom has a valence of four. Hence, carbon atom can form four covalent bonds. The remaining bonds are satisfied by hydrogen atom. The structure is obtained as shown below,
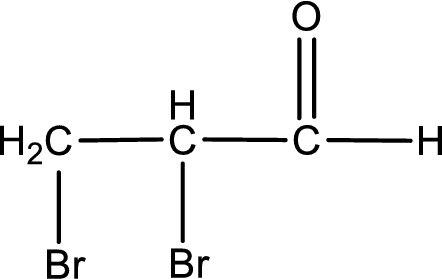
Structural formula for the given aldehyde is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Indicate the product formed in each reaction. If the product exhibits tautomerism, draw the tautomeric structure. a) о + CH3-NH-NH2 CO2C2H5 b) + CoH5-NH-NH2 OC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the compound, that is the result of the N- alquilación (nucleofílic substitution), in which an additional lateral chain was formed (NH-CH2-COOMe). F3C. CF3 NH NH2 Br о OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forwardSynthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole from 1,2-diaminobenceno.arrow_forward
- Synthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole.arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the compound, that is the result of the N- alquilación (nucleofílic substitution), in which an additional lateral chain was formed (NH-CH2-COOMe). F3C. CF3 NH NH2 Br о OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forwardIdentify the mechanism through which the following reaction will proceed and draw the major product. Part 1 of 2 Br KOH EtOH Through which mechanism will the reaction proceed? Select the single best answer. E1 E2 neither Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Draw the major product formed as a result of the reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forward
- What is single-point calibration? Provide an example.arrow_forwardDraw the major product formed via an E1 pathway.arrow_forwardPart 9 of 9 Consider the products for the reaction. Identify the major and minor products. HO Cl The E stereoisomer is the major product and the Z stereoisomer is the minor product ▼ S major product minor productarrow_forward
- Consider the reactants below. Answer the following questions about the reaction mechanism and products. HO Clarrow_forwardjulietteyep@gmail.com X YSCU Grades for Juliette L Turner: Orc X 199 A ALEKS - Juliette Turner - Modul X A ALEKS - Juliette Turner - Modul x G butane newman projection - Gox + www-awa.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/10_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IBxzaplnN4HsoQggFsejpgqKoyrQrB2dKVAN-BcZvcye0LYa6eXZ8d4vVr8Nc1GZqko5mtw-d1MkNcNzzwZsLf2Tu9_V817y?10Bw7QYjlb il Scribbr citation APA SCU email Student Portal | Main Ryker-Learning WCU-PHARM D MySCU YSCU Canvas- SCU Module 4: Homework (Ch 9-10) Question 28 of 30 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited H₂SO heat OH The mechanism of this reaction involves two carbocation intermediates, A and B. Part 1 of 2 KHSO 4 rearrangement A heat B H₂O 2 OH Draw the structure of A. Check Search #t m Save For Later Juliet Submit Assignm 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardThe electrons flow from the electron-rich atoms of the nucleophile to the electrons poor atoms of the alkyl halide. Identify the electron rich in the nucleophile. Enter the element symbol only, do not include any changes.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning


