
Concept explainers
If one hydrogen in a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen
a. n-pentane
b. 2-methylbutane
c. 2,4-dimethylpentane
d. methylcyclobutane
(a)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen in n-pentane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Three isomers are obtained when one hydrogen atom of n-pentane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
The given compound n-pentane has five carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain. When hydrogen of first carbon of n-pentane is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
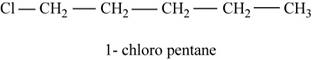
Figure 1
The isomer is
The given compound n-pentane has five carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain. When hydrogen of second carbon of n-pentane is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
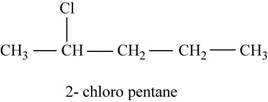
Figure 2
The parent chain contains five carbon atom and chlorine group is attached to second carbon.
The compound
The isomer is
The given compound n-pentane have five carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain. When hydrogen of third carbon of n-pentane is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
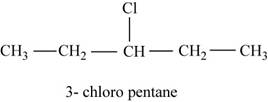
Figure 3
The compound
(b)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Nine isomers are obtained when one hydrogen of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
In the given compound,
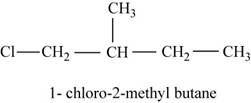
Figure 4
The isomer is
In the given compound,
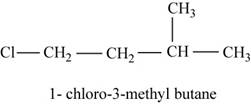
Figure 5
The isomer is
In the given compound,
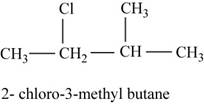
Figure 6
The isomer is
In the given compound,
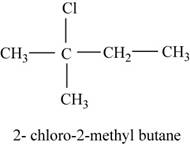
Figure 7
The isomer is
In the given compound,
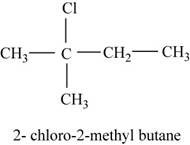
Figure 8
The isomer is
In the given compound,
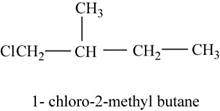
Figure 9
The isomer is
In the given compound,
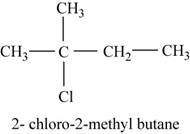
Figure 10
The isomer is
In the given compound,

Figure 11
The isomer is
In the given compound,

Figure 12
(c)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen in
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Two isomers are obtained when one hydrogen of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
The given compound
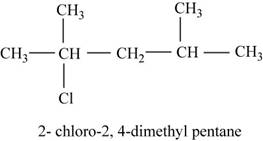
Figure 13
The isomer is
The given compound
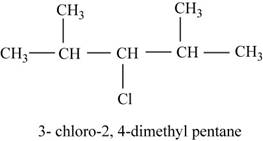
Figure 14
(d)
Interpretation: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen atom in each of the given compound is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Concept introduction: Structural isomerism occurs when two compounds have same number of atoms but the spatial arrangement of the atoms is different from each other. If one hydrogen atom of a hydrocarbon is replaced by a halogen atom, the number of isomers that exists for the substituted compound depends on the number of types of hydrogen in the original hydrocarbon.
To determine: The number of isomers that can be obtained when one hydrogen in methylcyclobutane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Answer to Problem 45E
Answer
Three isomers are obtained when one hydrogen of methylcyclobutane is replaced by a chlorine atom.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The isomer is
In the given compound methylcyclobutane, the ring of four carbon atoms is considered as the parent chain. Methyl group is attached at first carbon. When hydrogen of the methyl group is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
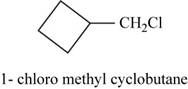
Figure 15
The isomer is
In the given compound methylcyclobutane, the ring of four carbon atoms is considered as the parent chain. Methyl group is attached at first carbon. When hydrogen of the second carbon of the ring is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
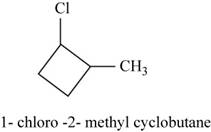
Figure 16
The isomer is
In the given compound methylcyclobutane, the ring of four carbon atoms is considered as the parent chain. Methyl group is attached at first carbon. When hydrogen of the third carbon of the ring is replaced by chlorine atom, then the isomer named
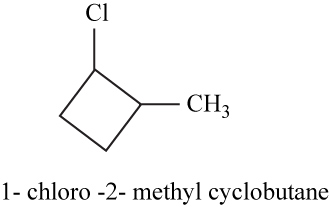
Figure 17
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
- Use the literature Ka value of the acetic acid, and the data below to answer these questions. Note: You will not use the experimental titration graphs to answer the questions that follow. Group #1: Buffer pH = 4.35 Group #2: Buffer pH = 4.70 Group #3: Buffer pH = 5.00 Group #4: Buffer pH = 5.30 Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, the buffer pH provided and the literature pKa value of acetic acid to perform the following: a) calculate the ratios of [acetate]/[acetic acid] for each of the 4 groups buffer solutions above. b) using the calculated ratios, which group solution will provide the best optimal buffer (Hint: what [acetate]/[acetic acid] ratio value is expected for an optimal buffer?) c) explain your choicearrow_forwardHow would you prepare 1 liter of a 50 mM Phosphate buffer at pH 7.5 beginning with K3PO4 and 1 M HCl or 1 M NaOH? Please help and show calculations. Thank youarrow_forwardDraw the four most importantcontributing structures of the cation intermediate thatforms in the electrophilic chlorination of phenol,(C6H5OH) to form p-chlorophenol. Put a circle aroundthe best one. Can you please each step and also how you would approach a similar problem. Thank you!arrow_forward
- A 100mM lactic acid/lactate buffer was found to have a lactate to lactic acid ratio of 2 and a pH of 4.2. What is the pKa of lactic acid? Can you please help show the calculations?arrow_forwardUsing line angle formulas, draw thestructures of and name four alkanes that have total of 7carbons, one of which is tertiary.Please explain this in detail and can you also explain how to approach a similar problem like this as well?arrow_forwardUsing dashed line wedge projections drawthe indicated compounds and indicate whether thecompound you have drawn is R or S.(a) The two enantiomers of 2-chlorobutane. Can you please explain your steps and how you would approach a similar problem. Thank you!arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning  World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





