
Interpretation: Comprehend the molecular view of carbon dioxide gas.
Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compound and ionic compound. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The molecular view of any molecule represents the atoms bonded in a molecule with
Answer to Problem 6E
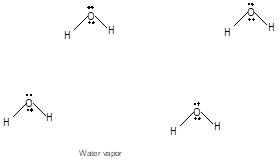
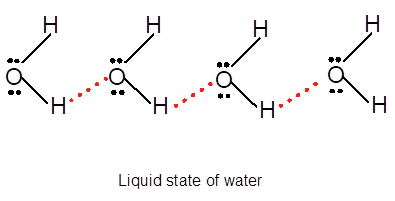
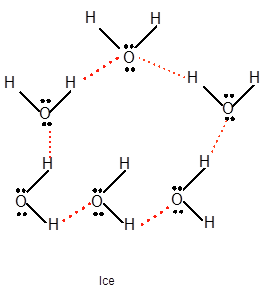
Explanation of Solution
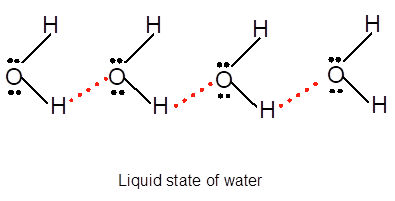
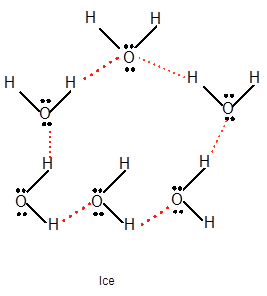
Freezing is the interconversion of liquid state to solid state. When water freezes, the water molecules come close to each other therefore the volume decreases. During freezing of water molecules, water molecules come close to each other but close to freezing point, water molecules arranged in a cage like structure with the help of formation of hydrogen bonds with each other therefore it shows expansion of molecules. Ice is less dense than water due to movement of water molecules slightly apart compared to liquid water. In water vapor molecules are very far from each other as there is no more hydrogen bond between water molecules.
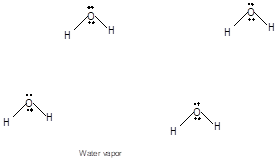
Chapter U3 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- When talking about the acidity of carboxylic acids, is it the same thing to say higher or stronger acidity?arrow_forwardUsing the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$arrow_forwardIndicate characteristics of oxodec acid.arrow_forward
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





